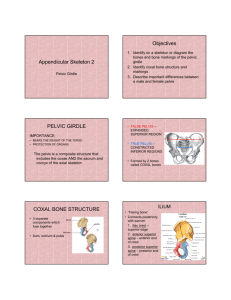
The Pelvis
advertisement

PELVIS AND PERINEUM Conceptual Overview General Description -- false (major or great) pelvis: between iliac crests and the pelvic brim (linea terminalis) -- true (lesser, deep, minor) pelvis: inferior to the pelvic inlet -- sexual differences in the pelvis: Functions -- Contain and support bladder, rectum, anal canal, and reproductive tracts -- Anchors the roots of the external genitalia Component parts -- pelvic inlet -- pelvic wall -- pelvic outlet tip of coccyx ischial tuberosities inferior pubic ramus sarcotuberous ligament pubic symphysis -- pelvic floor pelvic diaphragm -- pelvic cavity birth canal gastrointestinal tract 1 urinary tract reproductive organs Key features The pelvic cavity projects posteriorly: angle 50-60o Important structures cross the ureters in the pelvic cavity The prostate is anterior to rectum The perineum is innervated by sacral spinal cord segments Nerves are related to bone Ischial spine Pudendal nerve block 6. Parasympathetic innervation from spinal cord levels S2 to S4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. control erection: inferior hypogastric plexus 7. Muscle and fascia of the pelvic floor and perineum intersect at the perineal body Levator ani muscle Sphincters 8. Gender determines the course of the urethra 2 Perineum Definition: The area between the ischial tuberosities, extending from the pubis to the coccyx; separate from the main pelvic cavity by pelvic diaphragm Perineal membrane Superficial perineal pouch Deep perineal pouch Ischioanal (ischiorectal) fossa -- subcutaneous region about the anal canal -- boundaries: 1. Superiorly: levator ani muscle 2. Anterolaterally: obturator internus muscle 3. Posterolaterally: sacrotuberosu lig. 4. Anteriorly: external urethra sphincter and deep transverse perineal body -- content: 1. fat tissue: resistant to resorption with starvation; gluteus 2. 3. maximus muscle compresses the fat internal pudendal vessel inferior rectal vessel pudendal n. inferior rectal n. innerve external anal sphincter and perineal skin Somatic nerves (Fig 5.76) Pudendal(S2~4;從greater sciatic foramen穿出,再從lesser sciatic foramen穿入) ├ inferior rectal (external anal sphincter) ├ perineal │ ├ motor branches │ └ posterior scrotal/labial (sensory) 3 └ dorsal n. of penis/clitoris (sensory) Arteries (Fig 5.77) Internal iliac (anterior trunk) └ internal pudendal ├ inferior rectal─ middle (internal iliac) & superior rectal (IMA) ├ perineal │ └ posterior scrotal/labial ├ a. of bulb of penis/vestibule ├ urethral ├ deep a. of penis/clitoris └ dorsal a. of penis/clitoris External iliac ├ femoral─ external pudendal─ superficial & deep br.─ anterior scrotal/labia │ └ inferior epigastric─ cremasteric Abdominal aorta─ testicular Vein (Fig 5.78) Two major drainage ┌ internal pudendal─ internal iliac └ external pudendal─ femoral 4 Exceptions ┌ Deep dorsal v. of penis ─ v. plexus of prostate └ Deep dorsal v. of clitoris─ v. plexus of bladder Lymphatics (Fig 5.79) internal iliac nodes: deep parts of perineum superficial inguinal nodes: superficial tissues of penis/clitoris deep inguinal & external iliac nodes: glans penis/clitoris, labia minora lateral aortic & preaortic nodes: testes Divisions The transverse diameter (a line connecting the ischial tuberosities) divides the perineum into Anal triangle -- External anal sphincter: voluntary muscle deep superficial subcutaneous -- innervation inferior rectal br. of pudendal n. br. directly from anterior rami of S4 Urogenital triangle -- Superficial fascia fatty layer membranous layer (Colles’ fascia) -- Superfical perineal pouch -- Deep perineal pouch -- Erectile structures corpus cavernosum corpus spongiosum(♂ )/bulbs of vestibule(♀ ) -- Skeletal muscles ischiocavernous bulbospongiosus superficial transverse perinaeal 5 Male urogenital triangle Penis Ligament Suspensory ligament Fundiforms ligament of penis Bulb of the penis corpus spongiosum gland penis external urethral meatus right & left crura of the peins corpora cavernosa propuce (foreskin) frenulum -- innervation pudendal n. and pelvic plexuses -- vasculation 1. Erectile tissue: femoral a. internal pudenal a. deep a. of penis, a. of the bulb, dorsal a. of the penis 2. Superficial skin: femoral a. internal and external pudenal a. perineal br. 3. Deep dorsal v. of the penis prostatic v. plexus internal pudendal v. Scrotum midline raphe dartos layer (smooth muscle) -- innervation 1. anterior: ilioinguinal, genitofemoral 2. posterior: pudendal n., and perineal br. of posterior femoral cutaneous n. -- vasculation 1. anterior scrotal a.: external pudendal br. of femoral a. 2. posterior scrotal a: scrotal br. of the internal pudendal a. -- lymph drainage 1. scrotum: superficial inguinal lymph nodes 2. testis and epididymis: lumbar (para-aortic) lymph node Spermatic cord -- forms during the descent of the testes 6 -- External spermatic fascia: deep fascia of the external oblique muscle -- Cremaster muscle: internal oblique muscle -- Internal spermatic fascia: transversalis fascia -- Tunica vaginalis:pariental peritoneum,visceral peritoneum Superficial perineal pouch (space) -- Boundaries: between deep layer of superficial perineal fascia and inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm (perineal membrane) -- Contents Corpora cavernosa Bulb of the penis Ischiocavernosus muscle Bulbocavernosus muscle Superficial transverse perineal muscle Deep perineal pouch -- Boundaries: between superior and inferior fascial planes of the deep transverse perineal muscle -- Content Deep transverse perineal muscle External urethral sphincter Paired bulbourethral gland (cowper’s gland) Dorsal nerve and artery of penis Female urogenital triangle Vagina Clitoris: homology to penis Body of the clitoris Vestibular bulbs Glans clitoris Labia minor (prepuce) -- Vasculation 1. Internal iliac a. internal pudendal a. 2. Deep dorsal v. vesical v. plexus -- Innveration br. of pudendal n. 7 Vulva Labia major Anterior commissure mons pubis Posterior commissure Labia minor Prepuce: superior to the clitoris Frenulum: inferior to the clitoris Fourchette (frenulum of the labia) Vestibule (urogenital sinus) External urethral ostium Vaginal introitus Fossa navicularis (between vaginal introitus and fourchette) -- Vasculation 1. Internal and external pudendal a. 2. Internal pudendal v. -- Innervation br. of pudendal n. Superifical perineal pouch Crura of the clitoris, ischiocavernosus Bulbs of the vestibule, bulbospongiosus Superficial transverse perineal muscles Branches of internal pudendal vessels, perineal nerves Greater vestibular glands (Bartholin’s glands) Deep perineal pouch Proximal part of the urethra External urethral sphincter muscle Deep transverse perineal muscles Dorsal nerve and artery of clitoris 8 Pelvis Bones Coxal (hip or pelvic) bone: ilium, ischium and pubic bone join and fuse at the acetabulum; Two hip bones form the pelvic girdle. ilium (1) alar plate: attachment for the thigh musculature (2) iliac fossa: attachment for the iliacus muscle (3) iliac crest: attachment for back and abdominal musculature (4) Iliac spines (5) greater sciatic notch 1. piriformis muscle 2. suprapiriform recess: superior gluteal neurovascular bundle 3. infrapiriform recess: inferior gluteal neurovascular bundle, sciatic nerve, pudendal neurovascular bundle (5) arcuate line (iliopectineal line; linea terminalis) ischium (1) ischial ramus: (2) ischial tuberosity: attachment of posterior thigh muscles and sacrotuberous ligament. (3) ischial spine: attachment for the sacrospinous ligament (4) lesser sciatic notch 1. obturator internus, n. to the obturator internus 2. pudendal neurovascular bundle pubis (1) superior pubic ramus, pubic crest, body of pubic (2) pectineal line (3) inferior pubic ramus (4) pubic symphysis, superior and inferior pubic lig. Sacrum A. median sacral crest: spinous processes B. ala: transverse processes 9 C. sacral foramina: (1) posterior sacral foramina: transmit dorsal primary rami (2) anterior sacral foramina: transmit ventral primary rami D. sacral hiatus E. sacral cornua Coccyx Joint and ligaments Lumbosacral joint Zygapophyisal joint Intervertebral disc (Anterior longitudinal ligament) Sacroiliac joint: alar plates of sacrum and ilium A. sacrotuberous ligament: sacrum to the ischial tuberosity B. sacrospinous ligament: sacrum to the ischial spine C. iliolumbar ligament: iliac crest and transverse processes of L5 D. lumbosacral ligament E. dorsal sacroiliac ligament: posterior-superior iliac spine and dorsum of the sacrum F. ventral sacroiliac ligament: G. interosseous ligaments: between sacroiliac articular surfaces Pubic symphysis joint Gender differences Pelvic inlet ♂: heart-shaped ♀: circular-shaped Pubic arch ♂: 50-60o ♀: 80-85o 10 True pelvis Pelvic inlet pubic symphysis pubic tubercle Linea terminalis pubic crest, pecten pubis, arcuate line sacral alae sacral promontory Pelvic wall anterior – pubic bone lateral – hip bond, obturator foramen, obturator internus muscle posterior – sacrum, coccyx, piriformis ligaments - sacrospinous ligament, sacrotuberous ligament Muscle -- lateral rotate extended hip joint; abduct flexed hip Obturator internus origin : pelvic surfaces of ilium and ischium; obturator membrane insertion : Greater trochanter of femur innervation : n. to obturator internus pass through lesser sciatic foramen Piriformis origin : superior margin of greater sciatic notch; sacrotuberous ligament insertion : upper border of Greater trochanter of femur innervation : n. to piriformis pass through great sciatic foramen Apertures Obturator canal obturator n. v. Greater sciatic foramen superior gluteal n. v. 11 Sciatic n. inferior gluteal n. v. posterior femoral cutaneous n quadratus femoris n. v Less sciatic foramen pudendal n. internal pudendal v. nerve to obturator internus obturator internus muscle Pelvic floor pelvic diaphragm A. coccygeus muscle: ischial spine --> inferior end of sacrum *sacrospinous ligament is a degenerated portion of the coccygeus muscle B. levator ani muscle 1. pubococcygeus -- anterior fibers -- levator prostate or sphincter vaginae 2. puborectalis -- intermediate fibers -- most massive portion of the levator ani muscle -- medialmost part of pubococcygeus 3. iliococcygeus -- posterior fibers Perineal membrane and deep perineal pouch External urethral sphincter Sphincter urethovaginalis Compressor urethra Deep transverse perineal muscle Perineal body Levaor ani muscles Deep transverse perineal muscle Superficial transverse perineal muscle Sphincter urethrovaginalis 12 External anal sphincter Bubosponngiosus muscle of perineum 13 Pelvic cavity and Viscera Gastrointestinal system Rectum -- upper 2/3 is covered by peritoneum A. rectal ampulla: above the plevic diaphragm B. rectal sling: form by puborectalis muscle of levator ani muscle C. internal structure: 3 transverse rectal folds a. inferior rectal fold: 1 inch above the anal canal b. middle rectal fold c. superior rectal fold D. muscular coat: outer longitudinal and inner circular Anal canal -- upper 2/3: simple columnar epithelium pectinate line anal column anal valves anal sinus -- lower 1/3 anal pecten: nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium anocutaneous(white) line: true skin Arteries 1. superior rectal a. inferior mesenteric a. 2. middle rectal a. internal iliac a. 3. inferior rectal a. internal pudendal a. Veins 1. superior rectal v. inferior mesenteric v. 2. middle rectal v. internal iliac v. 3. inferior rectal v internal pudendal v. internal iliac v. Innervation 1. parasympathetic innervation: pelvic splanchnic n., nervi erigentes (S2-4) inferior mesenteric plexus 14 2. sympathetic innervation: lumbar splanchnic n. (L1-L2) inferior 3. 4. hypogastric plexuses pelvic plexus afferent innervation: pelvic splanchnic n. S2-4 referd pain: posterior thigh and posterior leg Lymphatic drainage 1. superficial and deep inguinal node (below the pectinate line) 2. internal iliac nodes (above the pectinate line) *internal hemorrhoids: occur above the pectinate line *external hemorrhoids: occur below the pectinate line 15 Urinary system Ureter Correlation -- anterior to common iliac a.; internal iliac a. -- crossed by ductus deferens(♂)/uterine a.(♀) Urinary bladder -- lies behind the pubic symphysis and the superior pubic rami A. external structure a. apex, body, fundus, neck uvula b. base i. trigone: where ureters enter and the urethra leaves ii. next to the prostate gland c. anterior surface: retropubic space d. posterior surface: cover by peritoneum i. Relate to the rectovesical pouch, rectovesical septum and seminal vesicles ii. Relate to vesicouterine pouch and vesicovaginal septum e. median umbilical ligament (urachus) -- remnant of allantoic duct -- support the bladder superiorly f. medial umbilical ligaments -- remnant of the umbilical a. -- support the bladder anterolaterally g. at base support by urogenital diaphragm and endopelvic fascia B. internal structure: a. detrusor muscle b. mucosal lining consists of transitional epithelium c. trigone d. uvula: longitudinal mucosal folding at the trigone apex C. vasculature: a. superior vesical a.; umbilical a. b. middle vesical a. 16 c. inferior vesical a.: internal iliac a. or deferential a. d. venous return: prostatic venous plexus internal iliac v. e. lymph node internal and external iliac nodes D. innervation: a. sacral parasympathetic n. pelvic splanchnic n. b. afferent n. hypogastric n. T12-L2 c. refered pain upper lumbar dermatomes, lowest thoracic dermatome Urethra A. in male (20 cm) a. Preprostatic urethra = internal urethral sphincter b. prostatic urethra: the thickest wall of the urethra i. urethral crest ii. seminal colliculus iii. prostatic utricle iv. openings of ejaculatory ducts c. membranous urethra -- the narrowest and least distensible portion of the urethra -- correlate to the external urethral sphincter d. spongy urethra -- begin at the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm and terminate at the external urethral meatue of the glans penis (navicular fossa) B. in female a. corresponds to prostatic urethra and membranous urethra of the male b. urethral orifice lies in the vestibule between the labia minor c. the external urethral sphincter in the female is incomplete d. paraurethral mucous glands (Skene’s glands) 17 Reproductive system Male internal genital organs Testes *Seminiferous tubule rete testis efferent ductules Epididymis Efferent ductules Head True epididymis body, tail Ductus deferens (Vas deferens) a. duct of epididymis vas deferens b. external portion: spermatic cord internal spermatic fasciainguinal canal abdominal cavity c. internal course: lies within the transversalis fascia deep inguinal ring testicular neurovascular bundle external iliac vessels obturator neurovascular bundle deep pelvis passes anterosuperior to the ureters ampulla (at the base of prostate gland) Seminal vesicles a. join the vas deferens where the ampulla become the ejaculatory duct b. location: posterior base of the urinary bladder c. these glands do not store sperm d. lateral pelvic plexus parasympathetic n; hypogastric plexus sympathetic n. (for contraction) e. ejaculatory duct: thin-walled terminal intraprostatic portion of the vas deferens Prostate gland -- lies between the base of the urinary bladder and the deep transverse perineal muscle a. Anterior surface: retropubic space; puboprostatic ligament 18 b. Posterior surface: seminal vesicles and the rectovesical septum; c. d. e. f. g. rectal ampulla lobes: anterior, median, posterior, lateral right, and lateral left prostatic duct supply by inferior vesical and middle rectal a. (high variation) prostatic venous plexus internal iliac v. or vertebral v. plexus lateral pelvic plexus parasympathetic n; hypogastric plexus sympathetic n. (for contraction) Bulbourethral gland 19 Female internal genital organs Ovary -- 3x 1.5x1 cm3 -- lies on the posterior side of the broad ligament a. ovarian fossae: triangular depression bounded by external and internal iliac vessel b. ligamentous support: i. mesovarium broad ligament ii. suspensory ligament (infundibulopelvic ligament ) contains the ovarian neurovascular bundle lateral pelvic wall iii. ovarian ligament: uterus round ligament of uterus c. cortex: functional portion of the ovary d. medulla: connective tissue and vasculature e. abdominal aortaovarian a. tubal vr. f. right ovarian v inferior vena cava; left ovarian v. left renal v.; ovary tubal v. uterine v. g. lymph node para-aortic nodes at L1 aortic plexus automonic innervation of the ovary; T10-12 sympathetic pathway of ovary Uterine tube a. infundibulum: fimbriae b. ampulla c. isthmus d. intramural part Uterus -- 8x2.5x5 cm3 fundus body i. ii. iii. cervix i. cornu uterine cavity isthmus: corresponds with the internal os. internal os. 20 ii. cervical canal iii. external os 1. relations a. anteriorly: uterovesical pouch b. superiorly: bladder c. posteriorly: rectouterine pouch, sigmoid colon d. laterally: broad ligament, uterine a. and v. 2. support a. levator ani muscle and urogenital diaphragm bladder uterus b. mesometrium (broad lig.) c. round ligament of uterus d. transverse cervical ligament (cardinal lig.) e. uterosacral (sacrocervical) and pubocervical ligament 3. blood supply a. internal iliac a. uterine a. (run in the transverse cervical lig. At the base of the broad lig.) b. uterine a. ascending br. tubal br. anastomoses with ovary a. c. uterine a. descending br. (vaginal br. ) anastomoses with ovary a. and internal pudendal a. d. venous return generally parallel the arterial supply e. lymph drainge i. uterine fundus para-aortic nodes (L1) ii. uterine body internal iliac nodes iii. cervix internal iliac nodes and sacral nodes 4. nerve supply: inferior hypogastric plexue Vagina anterior fornix posterior fornix: relates to the rectouterine pouch right lateral fornix left lateral fornix 21 1. relations a. anteriorly: base of the bladder, lower half of the urethra b. posteriorly: rectrovaginal septum, perineal body c. laterally: levator ani muscle, endopelvic fascia, ureters and uterine a. d. upper 2/3 within the pelvic cavity; lower 1/3 within the perineum 2. support a. Upper: levatores ani muscle, transverse cervical lig., pubocervical lig., sacrocervical lig. b. Middle: urogenital diaphragm c. Lower: perineal body 3. blood supply: a. vaginal br. of the uterine a.; vaginal br. of internal iliac a.; vaginal br. of middle rectal a.; vaginal br. of internal pudendal a.: run along the lateral vaginal wall b. vaginal venous plexus internal iliac v. c. lymphatic drainage i. upper 1/3 external and internal nodes ii. middle 1/3 internal iliac nodes iii. lower 1/3 internal iliac nodes and superficial inguinal nodes 4. nerve supply i. uterobaginal plexus upper 2/3 ii. pudendal n. lower 1/3 22 Pelvic fascia parietal fascia A. location: covers the piriformis muscle and obturator internus muscle B. subdivisions: at the arcus tendineus i. superior fascia: visceral fascia ii. inferior fascia: superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm iii. pudendal canal: inferior arcus tendineus visceral fascia -- lies between the peritoneum and the pelvic viscera pelvic ligaments -- thicken fascial continuities between the parietal and visceral fascia In female: Pubocervical ligament Transverse cervical (cardinal ligament) Uterosacral ligament In male: Prostatic fascia Rectovesical septum Pelvic peritoneum parietal peritoneum -- cover portions of the pelvic wall and visceral fasciae visceral peritoneum -- lines the uterus, ovaries, and uterine tubes In female: Vesico-uterine pouch Recto-uterine pouch In male: Rectovesical pouch (pouch of Douglas) Somatic nerves lumbar plexus (T12-L4) -- lies in the posterior abdominal wall and iliac fossa 1. subcostal n. (T12) 23 2. iliohypogastric n (T12-L1) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ilioinguinal n. (L1) genitofemoral n. (L1-l2) lateral femoral cutaneous n. (L2-L3) femoral n. (L2-L4) obturator n. (L2-L4) lumbosacral trunk (L4-L5) 1. anterior division; tibial portion of the sciatic n. 2. posterior division: superior and inferior gluteal n., common peroneal portion of the sciatic n. sacral plexus (L4-S3) -- in the deep pelvis; in front of the piriformis muscle 1 parietal pelvic fascia separate the plexus from internal iliac vessels 2 sciatic n. A. common peroneal n. a. infrapiriformis region of the greater sciatic foramen b. posterior component of the sciatic n. 3 4 5 6 7 c. innervate the posterior aspect of the leg and the dorsum of the foot B. tibial n. a. anterior component of the sciatic n. b. infrapiriformis region of the greater sciatic foramen c. innervate the posterior region of the thigh and leg and the plantear surface of the foot superior gluteal n.: a. suprapiriformis portion of the greater sciatic formation b. gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscle inferior gluteal n. a. infrapiriform region of the greater sciatic foramen b. gluteus maximus muscle nerve to the quadratus femoris muscle, inferior gemellus nerve to the obturator internus muscle, superior gemellus posterior cutaneous n. of the thigh (posterior femoral 24 cutaneous n.) 8 Perforating cutaneous n.: sacrotuberous lig. skin of inferior part of buttocks 9 pudendal n.: a. Infrapiriform region of the greater sciatic foramen b. Pudendal canal: lesser sciatic foramen c. Inferior rectal n. d. Deep and superficial perineal n. e. Dorsal nerve of penis 10 nerves to the piriformis muscle 11 anococcygeal n.: S5 & Co + S4 sacrospinous and sacrotuberous lig. skin of anal triangle Visceral plexuses 1. paravertebral sympathetic chain superior hypogastic plexus hypogastric n. inferior hypogastric plexus 2. postganglionic sympathetic fibers + anterior rami of sacral n. 3. sacral splanchnic n. + prevertebral plexus (sympathetic fiber) 4. pelvic splanchnic n. + parasympathetic fiber pelvic plexus (inferior hypogastric plexus) 5. Pelvic splanchnic nerve: arise form spinal nerve S2-S4; anterior ramus S4 only has a ventral division. 6. parasympathetic fiber inferior hypogastric plexus rectal, uterovaginal , prostatic, and vesical plexus vasodilation, bladder contraction, erection 7. inferior hypogastric plexus cavernous n. erectile tissues 8. sympathetic fiber sacral splanchnic n. vasocontraction internal urethral sphincter, internal anal sphincters, smooth muscle contraction, ejaculation. 9. refered pain Arteries 1. common iliac a.: at L4 left and right common iliac a. 2. external iliac a.: supplies somatic structures; inguinal ligamentfemoral a. A. inferior epigastric: cremasteric a. B. deep iliac circumflex a. 3. internal iliac a.: 25 A. anterior trunks: a. Umbilical a.: supply urinary bladder; medial umbilical ligament Umbilical a. > abdominal aorta Umbilical a. superior vesical a. b. Obturator a.: 30% arise from inferior epigastric a. c. Uterine a.: tubal br. oviducts, ovary; vaginal br. d. Deferential a.(a. of ductus deferens): supply the vas deferens and epididymis e. middle rectal a.: Inferior mesenteric a. superior rectal a. middle rectal a. inferior rectal a. internal pudendal a. f. internal pudendal a.: infrapiriform portion of the greater sciatic foramen lesser sciatic foramen g. inferior gluteal a.: infrapiriform portion of the greater sciatic foramen; supply coccygeus, piriformis, levator ani muscles, gluteus maximus, lateral roator muscles, and hip joint h. inferior vesical a (in male): supply the neck of the urinary bladder, prostate, seminal vesicle B. 4. 5. 6. i. Vaginal a. (in female): vaginal a. uterine a. posterior trunks: a. Iliolumbar a. lumbar br. -- supply the psoas and quadratus lumborum muscle, lower lumbar vertebral and dural sac iliac br. -- supply the iliacus muscle b. Lateral sacral a. c. superior gluteal a.: the largest br.; pass through suprapiriformis portion of the greater sciatic foramen; supply gluteus maximus, medius, minimus., and hip joint Superior rectal a. Ovarian a. Median sacral a. Veins 1. follow the course of all br. of the internal iliac a. (except umbilical 26 a. & iliolumbar a.) 2. rectal venous plexus: connect the portal system 3. Vesical venous: lie about the base of the bladder and prostate; drain into internal iliac v. vertebral venous plexus, obturator v. and rectal plexus 4. deep dorsal vein: prostatic plexus of veins (in male) or vescial plexus of vein (in female) 5. superficial vein of penis external pudendal v great saphenous v 6. median sacral veins left common iliac vein or junction of the two common iliac veins 7. ovarian veins left renal vein (left), inferior vena cava (right) Lymphatic drainage 1. 2. 3. 4. preaortic nodes lumbar trunk lateral aortic nodes: along lateral surfaces of the abdominal aorta External iliac nodes: along external and common iliac vessels internal iliac nodes (pelvic nodes): along the internal iliac vessels 27