Generic Drug Name:
advertisement
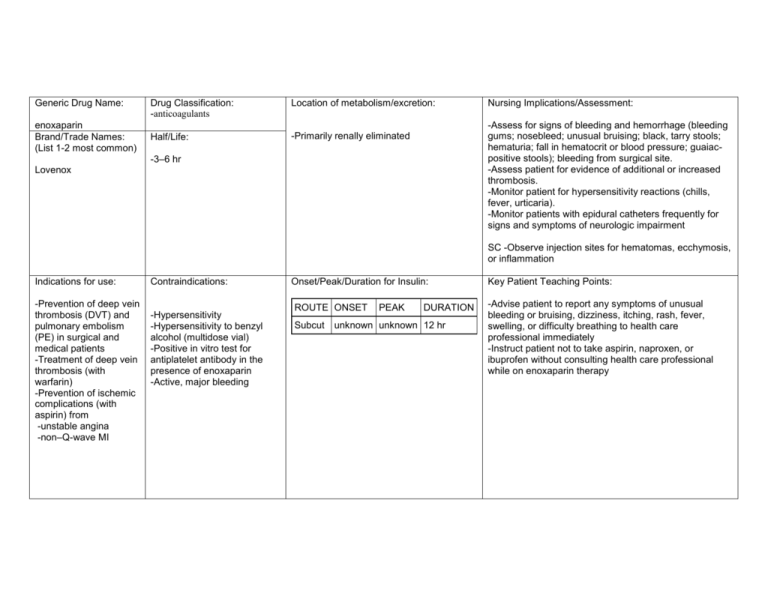
Generic Drug Name: enoxaparin Brand/Trade Names: (List 1-2 most common) Drug Classification: -anticoagulants Location of metabolism/excretion: Half/Life: -Primarily renally eliminated Nursing Implications/Assessment: -Assess for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage (bleeding gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising; black, tarry stools; hematuria; fall in hematocrit or blood pressure; guaiacpositive stools); bleeding from surgical site. -Assess patient for evidence of additional or increased thrombosis. -Monitor patient for hypersensitivity reactions (chills, fever, urticaria). -Monitor patients with epidural catheters frequently for signs and symptoms of neurologic impairment -3–6 hr Lovenox SC -Observe injection sites for hematomas, ecchymosis, or inflammation Indications for use: -Prevention of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in surgical and medical patients -Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (with warfarin) -Prevention of ischemic complications (with aspirin) from -unstable angina -non–Q-wave MI Contraindications: -Hypersensitivity -Hypersensitivity to benzyl alcohol (multidose vial) -Positive in vitro test for antiplatelet antibody in the presence of enoxaparin -Active, major bleeding Onset/Peak/Duration for Insulin: ROUTE ONSET Subcut PEAK DURATION unknown unknown 12 hr Key Patient Teaching Points: -Advise patient to report any symptoms of unusual bleeding or bruising, dizziness, itching, rash, fever, swelling, or difficulty breathing to health care professional immediately -Instruct patient not to take aspirin, naproxen, or ibuprofen without consulting health care professional while on enoxaparin therapy Action: -Potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa and thrombin Adverse Reactions/Side Effects: Routes and Dosage range for each route: dizziness, headache, insomnia,bleeding, anemia, thrombocytopenia. Therapeutic Effects: (expected outcome) Interactions: -Risk of bleeding may be ↑ by concurrent use of drugs that affect platelet function and coagulation , including warfarin, aspirin, thrombolytic agents, NSAIDs, dipyridamole, some penicillins, clopidogrel, abciximab, eptifibatide, tirofiban, ticlopidine, and dextran DVT Prophylaxis • SC (Adults): Knee replacement surgery —30 mg q 12 hr starting 12–24 hr after surgery; Hip replacement—40 mg 12 hr before surgery then once daily; may be continued for up to 3 wk after hospital discharge; Abdominal surgery—40 mg 2 hr prior to surgery, then every 24 hr postop for 7–12 days or until ambulatory (up to 14 days); Medical patients with acute illness—40 mg once daily. Treatment of DVT/PE • SC (Adults): Outpatient —1 mg/kg every 12 hr; Inpatient —1 mg/kg every 12 hr or 1.5 mg/kg every 24 hr. Warfarin should be started within 72 hr; enoxaparin may be continued for 5–17 days or until therapeutic anticoagulation with warfarin is achieved (INR >2 for two consecutive days). Angina/Non–Q-wave MI • SC (Adults): 1 mg/kg q 12 hr for 2–8 days (up to 12.5 days). Renal Impairment • SC (Adults CCr < 30 ml/min): DVT prophylaxis for abdominal, knee or hip surgery —30 mg once daily; Angina/Non–Q-wave MI, treatment of DVT—1 mg/kg once daily; -Prevention of thrombus formation Evaluation criteria: -Monitor CBC, platelet count, and stools for occult blood periodically during therapy. If thrombocytopenia occurs, monitor closely. If hematocrit decreases unexpectedly, assess patient for potential bleeding sites -Special monitoring of clotting times (aPTT) is not necessary in most patients. Monitoring of the aPTT may be considered in certain patient populations (such as obese patients or patients with renal insufficiency) -May cause ↑ in AST and ALT levels -May cause hyperkalemia Labs to monitor (if applicable): -Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism -Resolution of acute deep vein thrombosis -Prevention of ischemic complications (with aspirin) in patients with unstable angina or non-Q-wave MI









