DBMS Midterm Study Guide: Chapters 1-3, 5, 8-12
advertisement

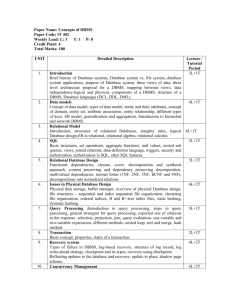
CSCE 4523 DBMS – Midterm Study Guide – covers Chapters 1-3, 5, 8-12
Open book, open notes, emphasis is on understanding the material, grading is on a curve
DBMS Architecture - Chapters 1-3
Three layer architecture (physical, logical = conceptual, application) – mappings between the layers –
logical and physical independence properties (encapsulation boundaries)
How DBMS relates to logic, information retrieval (e.g., google)
Closed world assumption
Data Models – Chapter 3
What is a data model?
Relational model
Primary key, candidate key, foreign key
Entity Integrity – Referential Integrity
Give example of integrity constraint and integrity constraint violation
Relational Algebra – Chapter 5
Why is it called an algebra? Relational closure
Project, select, join (theta, outer, natural), union, intersection
Aggregation operators like Sum, Average
Views
Triggers 1
Relational Calculus – SQL – Chapter 3, 5
Why is it called a calculus?
Data definition language - Create/Alter/Drop {catalog, schema, table, view, domain}
Data manipulation language - Insert/Update/Delete
Query language - Select .. from .. where .. group by .. having .. order by ..
Joining a table with itself e.g. courses and their prerequisites
Nested queries: selects, joins, … inside of selects
Null values – meaning of nulls and truth table
Views – what they are – materialized views – can you update views (what problem do you run into)
Interfacing a programming language to a DBMS – ODBC – Chapter 8, esp. 8.5
Physical Data Organization – Chapter 9
Records
Disk organization, sectors, seek-rotational latency-block transfer
Virtual memory
Access paths – Primary index, secondary index
Heap, Hash, Tree index – relative access cost
Clustered//Unclustered and Sparse/Dense indexes 1
Multiple attributes, Multi-level index 1
Static/Dynamic indexes
B-tree, B+-tree
Extendable hashing, linear hashing 1
Join indexes 1
Logical and physical pointers
Grid-based storage (in class, not in the book)
Query Processing, Optimization and Tuning – Chapter 9.8, 10, 11, 12
Query tree, query execution plan
Identities, Join-order
Main steps in optimization, Heuristic vs. cost-based optimization
Join alternatives – nested loop join, sort-merge join, hash join
External sorting
Tuning – design decisions, monitoring, 80-20 rule
SURLY – SURLY Spec
Representation of tuples, tables, indexes
Methods an index must handle
Tradeoffs re Heap, Hash, and Tree index
1
Not covered in class or on test, but read about this – worth knowing.