Study Guide for Nervous System Test
advertisement
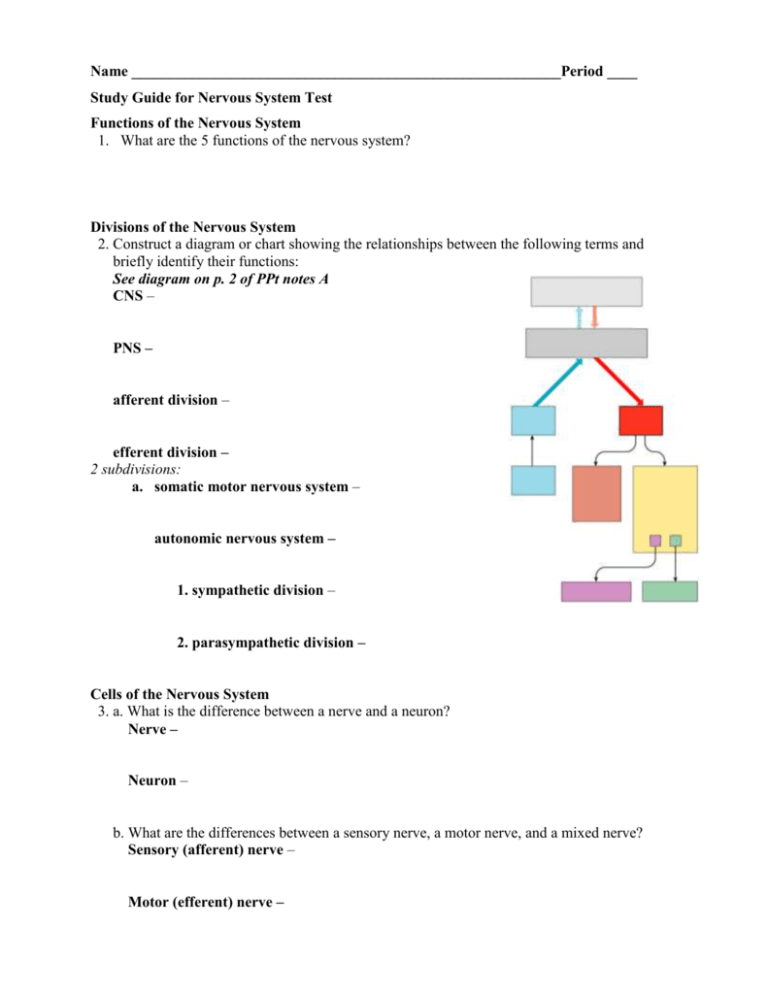
Name _________________________________________________________Period ____ Study Guide for Nervous System Test Functions of the Nervous System 1. What are the 5 functions of the nervous system? Divisions of the Nervous System 2. Construct a diagram or chart showing the relationships between the following terms and briefly identify their functions: See diagram on p. 2 of PPt notes A CNS – PNS – afferent division – efferent division – 2 subdivisions: a. somatic motor nervous system – autonomic nervous system – 1. sympathetic division – 2. parasympathetic division – Cells of the Nervous System 3. a. What is the difference between a nerve and a neuron? Nerve – Neuron – b. What are the differences between a sensory nerve, a motor nerve, and a mixed nerve? Sensory (afferent) nerve – Motor (efferent) nerve – Mixed nerves Interneurons or association neurons – c. Give several examples of each type of nerve. Sensory (afferent) nerve – Motor (efferent) nerve – Mixed nerves – 4. Name and describe the 3 different types of neurons and their functions. (p. 195) Multipolar – Bipolar – Unipolar – 5. List the 5 different neuroglia and their functions. (p. 195) Astrocytes – Microglia – Ependymal cells – Oligodendrocytes – Schwann cells – 6. The autonomic nervous system includes structures called ganglia. a. What are ganglia? b. What is meant by the preganglionic neuron? Postganglionic neuron? 7. Distinguish between gray matter – and white matter- Propagation of Action Potentials 8. Distinguish between resting membrane potential – and an action potential – Distinguish between depolarization – and repolarization – Describe the ion concentration inside and outside the membrane. See previous question. Describe the role that mitochondria play – 9. Describe the parts of a synapse and the role each part plays. (Refer to CP 72 – READ also) 10. What are proprioceptors? 11. What are the 5 basic components of a reflex arc? **See color plate 72 and be able to identify the parts of the synapse at the bottom of the page! Central Nervous System: See brain chart handout. 12. What are the 2 main parts of the CNS? 13. What are the 4 major regions of the brain? (See brain chart handout for this question and questions 14, 15 & 16a) 14. The brain stem consists of 3 parts; what are they and what are their functions? 15. The diencephalon consists of 3 parts; what are they and what are their functions? 16. The cerebrum has lobes named for the portion of the skull that covers it. a. What are the 4 lobes of the cerebrum and what are their primary functions? b. What are the 2 main fissures and what purpose do they serve? Longitudinal fissure – Parieto-occipital sulcus – c. What are gyri and what is their purpose? c. What are sulci? 17. For the functional areas of the cerebral cortex, give the location and the primary function. a. Olfactory area – b. Language comprehension area – c. Motor speech area (Broca’s Area) – d. Frontal association area – e. Premotor area – f. Primary motor area – g. Somatic sensory area – h. Gustatory area – i. Speech/Language area (Wernicke’s area) – j. General interpretation area – k. Visual area – l. Auditory area – **See the second PowerPoint note packet “The Nervous System: Reflexes and the Brain” Be able to identify the above functional areas on the picture “Specialized Areas of the cerebrum” 18. Describe the location of the corpus callosum. Is it white or gray matter? What is the function of the corpus callosum? 19. Describe two pieces of evidence that demonstrate the difference between right and left hemispheres of the cerebrum. 20. Distinguish between meninges – and ventricles – 21. What is the function of the cerebellum? See brain chart handout 22. Name and describe the three membranes which surround the central nervous system. Dura mater – Arachnoid mater – Pia mater – What is the major function of the cerebrospinal fluid? Peripheral Nervous System 23. Distinguish between cranial nerves and. spinal nerves. Cranial nerves – Spinal nerves – Brain dysfunctions: Remember the Clinical Focus worksheets on the CNS & PNS. Be able to describe characteristics of the following: *muscular dystrophy – gradual breakdown of myelin sheath of Schwann cells *multiple sclerosis – autoimmune condition – inflammation in areas of brain & spinal cord ; myelin sheaths around axons become sclerotic resulting in poor conduction of action potentials *polio – viral infection of CNS; damages the somatic motor neurons which extend into the PNS; muscles become paralyzed& they atrophy *menengitis – inflammation of the meninges; stiff neck, headache, fever; can cause paralysis, coma or death *cerebral edema- swelling – may compress & kill brain tissue *contusion – bruise – destroys nerve tissue . *Alzheimer’s disease – degenerative disease w/ abnormal protein deposits –characterized by memory loss, irritability *concussion- slight brain injury – “brusie that goes away” *cerebral vascular accident – CVA or stroke – ruptured blood vessel *Parkinson’s disease – caused by low amount of dopamine *Cerebral palsy – loss of motor function *epilepsy –brain disorders w/ seizure episodes Differentiate b/n both petit mal and grand mal seizures









