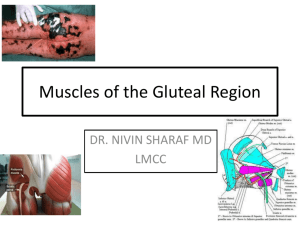
Gluteal Region and Posterior Thigh
advertisement

Gluteal Region and Posterior Thigh 1/23/2009 10:02:00 AM Plate 486 Three parts of the hip bone. Sacrum articulates with the ilium Plate 353 Sacrotuberous and sacrospinous make the lesser and greater sciatic foramina Plate 489 Lower extremity is broken into to thigh, leg and foot. Femur articulates with hip proximally and the tibia distally At the juntion of the neck and shaft, there are a greater and lesser trocanter. They are the location of many musclular attachemtns The intertrochanteric crest connects the greater and lesser trochanter. The glutal tuberosity is inferolateral to the lesser trochanter on the posterior side of the femur The linea aspera is a posterior ridge that splits at the the distal 1/3 of the femur to form the medial and lateral supracondylar ridges. The angle between the shaft and the neck of the femur is said to be around 125-135 degree range. Angle is called the angle of inclination. Changes of the angle of inclination manifest most noticeably in the knee. o Angle is too high—Coxavalgus. Causes bowleggedness o Angle is too low—Coxavarus. Causes Knock-kneed o Coxa means hip joint Plate 513 Tibia is more medial. Anterior shaft of the tibia is the shin bone. There is a very prominent tuberosity on the anterior aspect of the tibia that is an important attachment for many muscles called the tibial tuberosity Fibula is more lateral. Mostly buried in muscle. Does not participate in the knee joint. It articulates with the lateral aspect of the tibia. The head of the fibula is prominent and is an important attachement of many muscles. Plate 164 S1 and S2 are important dermatomes. S1 lateral S2 medial Plate 545 Both Dorsal and ventral rami contribute to the gluteal innervation. Called the cluneal nerves. The deep fascia of the thigh is called the fascia lata. The fascia lata does extend up to the iliac crest where it attaches. It dos cross the knee but it has a name change. The lateral fascia lata is very thick and tough. It is called the iliotibial band/tract. There are not many subcutaneous veins in the leg and thigh. Most are tributaries of the saphenous system of veins Plate 495 The most superficial in the gluteal region is the gluteus maximus. It has a rather extensive origin across the ala of the ilium. It comes of at a 45 degree angle to attach to the gluteal tuberosity. Only the inferior ¼ inserts on a bone. The superior ¾ insert on the iliotibial band. The gluteus maximus is a powerful extensor of the hip. Not involved with walking on a flat surface (most of that is hamstring). Extension when going from a sit to a stand, climbing stairs, running. Plate 494 Majority of the superior fibers of the gluteus maximus attaches to the iliotibial band There is a muscle that originates on the anterior iliac crest and part of the ASIS. The tensor fascia lata is invested in the fascia lata and completely inserts into the fascia lata. It’s a flexor of the hip joint. Plate 495-Gluteus maximus is reflected laterally Next visible group is the gluteus medius. Takes its origin from the ala of the ilium. Gluteus medius inserts on the greater trochanter. Gluteus minimus is deep to the gluteus medius. Originates on the ala of the ilum inserting on the greater trochanter. Both the medius and minimus are abductors of a non weightbearing limb. They are NECESSARY for normal gait. Contraction of the minimus and medius of a weight bearing limb causes a reversal in origin and insertion and tips the hip so the foot may clear the ground for the foot swing in normal gait. To test for paralysis for the medius or minimus (trendelenburg test) have pt stand on affected side. If the test is positive they will have to put their foot right back down. Plate 502—Nerve supply Piriformis m attaches to the greater trochanter. That is the reference point for navigating the nerves of the gluteal and posterior thigh. The gluteal nerves and vessels are named in their relation to the piriformis. o Superior gluteal nerve and vessels supply the gluteus minimus, medius and the tensor fascia lata o Inferior gluteal nerve supplies the gluteus maximus The greater sciatic foramen also gives passage to the sciatic nerve and the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh. o Sciatic tends to stay deep. o Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh becomes subcutaneous Plate 503 There are three small muscles inferior to the piriformis all taking insertion on the greater trochanter. They are involved with external rotation of the hip o Superior Gemellus muscle from the ischial spine o Obturator Internus from within the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen o Inferior Gemellus from the ischial tuberosity Quadratus femoris The piriformis, superior gemellus, obturator internus, inferior gemellus, and the quadratus femoris are external rotators of the hip o All receive innervation by named nerves from the sacral plexus (nerve to X) Obturator externus is inferior to the inferior gemellus, deep to the quadratus femoris. It is also an external rotator of the hip and inserts on the greater trochanter. The sciatic nerve is a combination of the tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve within a common fascial sheath. Typically they are wrapped together. They can sometimes be in non-common sheaths. The common fibular nerve is almost always inferior to the tibial nerve. The tibial nerve can pierce through the piriformis or superior to piriformis. Piriformis hypertrophy can cause sciatica by compressing the structures that exit the greater sciatic foramen with the piriformis (sciatic nerve) Safe place to give an injection is superior to e gluteus maximus. Safe area is superior lateral into gluteus medius. Plate 489 Adductor tubercle is on the medial aspect of the distal femur Plate 545 Posterior Thigh runs from the glutal crease to the knee joint. Short saphenous vein runs from the ankle and passes deep to the fascia lata just superior to the knee joint. Plate 505-Cross section of the Thigh Plate 495-Hamstring compartment Collectivly the long strap like muscles are the hamstrings. o The lateral one attaches to the head of the fibula. It is the long head of the biceps femoris. o The semitendonosus and semi membranousus are medial. o All three have an origin from the ischial tuberosity Semimembranosus has a significant portion that is long and sheath like. Insert on the proximal tibia Semitendonosus has a significant portion that is very compact CT that is tendonous. Insert on the proximal tibia The short head of the biceps femoris originates from the shaft of the femur (linea aspera). The long and short head have a common tendon. o The short head is not considered a hamstring muscle. The nerve supply for the three long muscle are all innervated by the tibial nerve. The short head is innervated by the common fibular nerve. The hamstrings extend the hip joint and flex the knee. They cross two joints. Active insufficiency is when you ask a muscle to give maximal performance no two joints at the same time. Passive insufficiency is when you stretch the muscle at two joints. High kicks are an example of passive insufficiency. Passive insufficiency is probably more related to connective tissue surrounded the muscle where as active insufficiency is more related to the muscle fibers themselves. Plate 540 As the sciatic nerve approaches the distal third of the femur, the two components separate. The tibial nerve generally stays midline, the common fibular nerve passes lateral. Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is generally deep the fascia lata. It supplies a greater area of skin than any other cutaneous nerve in the body. 1/23/2009 10:02:00 AM 1/23/2009 10:02:00 AM