NCLEX Study Guide - Mrs. Neto's Classroom
advertisement

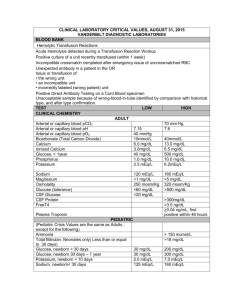
N-CLEX Study guide Decision Tree: 1. What is the topic? a. Simplify topic b. Look at answers for clues 2. Assessment or Implementation (If all implementation or assessment go to step 3) do u need validation for a diagnosis before implementation? If yes, pick assessment 3. Physical before Psychosocial-Maslow? (All physical-go to step 4) (All psychosocial-step 5) (If both, eliminate psychosocial, and implement ABCs) 4. ABCs (For all physical only) 5. What does each answer mean? a. Expected vs. Unexpected Abnormal b. Worse Case Scenario-ABCs c. Chronic vs. Acute TRANSMISSION-BASED PRECAUTIONS: Remember ADC - airborne, droplet, contact AIRBORNE My – Measles (rubeola) Chicken - Chicken Pox Hez - Herpez Zoster TB Private Room - negative pressure with 6-12 air exchanges/hr or cohort (same organism) Mask, N95 for TB, door closed, place mask on patient if being transported DROPLET think of SPIDERMAN! S - sepsis S - scarlet fever S - streptococcal pharyngitis P - parvovirus B19 P - pneumonia P - pertussis I - influenza D - diptheria (pharyngeal) E - epiglottitis R – rubella (german measles) M - mumps M - meningitis M - mycoplasma or meningeal pneumonia An - Adenovirus Private Room or cohort Mask, door may remain open, mask on patient being transported, visitors wear mask if less than three feet away, maintain separation of 3-feet between infected patient and visitors or other patients CONTACT PRECAUTION MRS.WEE M - multidrug resistant organism (MRSA, VRE) R - respiratory infection (RSV) S - skin infections W - wound infxn E - enteric infxn - clostridium difficile E - eye infxn - conjunctivitis SKIN INFECTIONS VCHIPS V - varicella zoster (chicken pox) C - cutaneous diphtheria H - herpez simplex I - impetigo P - pediculosis S – scabies *also includes mononucleosis Private room or cohort Gloves (remove and dispose in patient’s room) Gown (remove before leaving room) LABS Electrolytes Sodium: 135-148 mEq/L Potassium: 3.5-5 mEq/L Chloride: 95-105 mEq/L Magnesium: 1.5-3.0 U/L Total Serum Calcium: 8.5-10.5 mg/dL Renal: BUN: 7-20 mg/dL Creatinine: 0.6-1.5 mg/dL Creatinine Clearance: 1.6-2.5 ml/s Liver: AST: 8-40 ALT: 8-40 Amylase: 6-160 Lipase: <200 Aspire pH: <4 GI: Random: CO2: 24-30 mEq/L, different for ABGs Glucose: 60-100 mg/dL fasting, Infants: 40-50 mg/dL, >125 hyperglycemia, >150 in preterm Albumin: 3.5-5 g/dL Ionized Calcium: 4.5-5.2 mg/dL Urine Specific Gravity: 1.010-1.030 CVP: 3-11 cm H2O, or 2-5 mmHg Glucose Tolerance Test: Fasting: 60-110, 1 hour: 190, 2 hour: 140, 3 hour: 125 Cholesterol: <150 if no CAD, <100 if CAD LDL: optimal <70 or 100 HDL: >40 Triglycerides: 100-200 CBC: RBC: 4-5.5, men: 4.5-6.2, women: 4.2-5.4, children: 3.2-5.2 WBC: Adults: 5,000-10,000, children: 5,000-13,000 Hemoglobin: 12-17 Hematocrit: 36-51% Platelets: 150,000-400,000 Bleeding: Prothrombin Time (PT): 9.5-12 sec, check with coumadin Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT): 20-45 sec, Heparin: 1.5-2X normal for therapeutic levels. INR: Normal: 1.0, anticoag: 2-3, heart valves: 2.5-3.5 ABGS: PH: 7.35-7.45 PaCO2: 35-45 PaO2: 80-100 HCO3: 22-26 BE: +/-1 O2 Sat/SaO2: 95-99% Growth and Development: Toddler: (Separation): Teach parents to expect regression Preschooler: (Mutilation): Allow children to play with models or equipment, encourage expression of feelings School-ager: (loss of control): Explain procedures in simple terms, allow choices when possible Adolescent: (Loss of Independence/being different from peers/body image): Involve in procedures and therapies, expect resistance, express understanding of concerns, point out strengths. EKG: Rate: o o o o o Regular: count the number of little boxes between 2 r-waves, multiple 1500 by the number or little boxes between r-waves. Irregular: count the number of QRS complexes in 6 second strip and multiply by 10 PR-Interval: .12-.2 QRS: .04-.1 QT: .36-.44 Heart Sounds: Aortic: 2 ICS, Right Sternal border Pulmonic: 2 ICS, Left SB Erb’s Point: 3 ICS, Left SB Tricuspid: 5 ICS, Left SB Mitrial: 5 ICS, Left MCL (apex) S1, S3, S4 heard at mitral area, S2 heard at aortic area Eriksons Stages: Drug Levels: Aminophylline: 10 to 20 mcg/mL, Toxicity: Nausea, Vomiting, Abdominal pain, Mild metabolic acidosis, Hypokalemia, Hypophosphatemia, Hypomagnesemia, Hypocalcemia/hypercalcemia, Hyperglycemia, Tachycardia Digoxin: 0.8 to 2.0 ng/mL, Toxicity: N/V visual disturbances, green halo, decreased HR Lithium: 0.8 to 1.2 mEq/L, Toxicity: N/V, temors, confusion, seizures, lethargy, weakness, diarrhea Dilantin/Phenytoin: 10 to 20 mcg/mL (Toxicity: uncontrollable eye movements, loss of coordination, slow or slurred speech, uncontrollable shaking of a part of the body, nausea, vomiting, difficulty understanding reality, coma (loss of consciousness for a period of time) Theophylline: 10 to 20 mcg/mL, Toxicity: Nausea, Vomiting, Abdominal pain, Mild metabolic acidosis, Hypokalemia, Hypophosphatemia, Hypomagnesemia, Hypocalcemia/hypercalcemia, Hyperglycemia, Tachycardia Valproic acid: 50 to 100 mcg/mL, Toxicity: tremor, stupor, respiratory depression, coma, metabolic acidosis and death. Quinidine: 2 to 5 mcg/mL Salicylate: 100 to 250 mcg/mL Methotrexate: greater than 0.01 mcmol Phenobarbital: 10 to 30 mcg/mL Gentamicin: 5 to 10 mcg/mL, OTO toxic Lidocaine: 1.5 to 5.0 mcg/mL Carbamazepine: 5 to 12 mcg/mL Pediatric Dosing: 1 kilo=2.2 pounds BSA (M2)= √(weight (pounds) X Height (inches))/3131 BSA (M2)= √(weight (kilos) X Height (cm))/3600 Pediatric Fluid Requirements: 1-10 kg= 100 ml/kg/day 11-20 kg= 1000 ml + 50 ml/kg for each kg over 10 >20 kg= 1500ml + 20 ml/kg for each kg over 20 >30 kg= 1750 ml + 10 ml/kg for each kg over 30 Medical Math: Volume= cc or ml Flow rate= gtt/min Infusion Time= Minutes or hours Dosage= units or mg IV tubing calibration= gtt/mL Pediatric/Microdrip Set= 60 gtt/mL Heparin Normal Range= 20,000-40,000 Units/24 hours Pregnancy: Multipara: Quickening at 18 weeks Primapara: Quickening at 20 weeks Weight Gain: First trimester: 2-4 lbs Second trimester: 12-14 lbs Third trimester: 8-12 lbs Rescue position for pregnant woman is LEFT side Fetal Heart Rate: 120-160, If there is a deceleration, it should always return to baseline Massage fundus until it is firm- no time limit, just until firm Saturated Peripad=each one is 100 mL At 24 weeks gestation, expression of colostrum is normal Fundal height raises 1 cm a week until week 30. At 20 weeks its at the umbilicus. 6-12 hours after delivery, the fundus is at the level of the umbilicus and it drops 1 fingerbreadth a day for each day after that. GTPAL: gravida (# or pregnancies), term (after 38 weeks), Preterm (before 38 weeks), Abortion (less than 20 weeks or <500 g), Living children. Gravida is number of times being pregnant, Para is the number of births Weight gain during pregnancy: total 24-28 lbs. 1st: 2-4 lbs 2nd: 12-14 lbs 3rd: 8-12 lbs Fetal Heart tones: positive sign of pregnancy, heard at 12 weeks with Doppler, and at 18-20 weeks with auscultation Rupture of membranes: Infection risk Babies/Children: Infant BP 60-80/40-45 High Pitched Cry= hypoglycemia or drug addiction Infants: Birth weight doubles by 5 or 6 months Sit w/o support at 7-8 months Moro reflex, strongest for first 2 months, disappears by months 3 or 4. Newborn: Head Circumference: 33-35 cm Chest Circumference: 30.5-33 cm Heart Rate: 120 (asleep)-180 (crying) Respiratory Rate: 30-60 Risk factors for lead poisoning: Poverty and renters or old house with chipping paint Infant with Heroin withdraw: excessive mucus and high pitched cry about 12 hours after birth 12 month old should not drink more than 24 ounces of milk per day Lead Poisoning: houses before 1975, old toys, peeling paint School-aged screening: hearing, vision, dental, height/weight, scoliosis Adolescent: PPD/TB test, sexuality, puberty, self exams, paps smear Pathologic Jaundice: within 24 hours, r/t Rh or ABO incompatability Physiologic Jaundice: occurs after 24 hours, peaks at 72 hours, lasts 5-7 days. Occurs due to immature hepatic function. Infant Output: 10-12 wet diapers, 2-3 stools a day Feed Infant every 2 hours, only get formula nothing else Lead Poisoning: want 0 level- S/S: loss of coordination and weight loss Teach through play with children Psychology/Drugs: Akathisia: doll eyes, side to side movement Oculogyric crisis: eyes roll up Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: Treat with cooling blankets, Ice, fluids, reduce fever, and give bromocriptine and dantrolene Drug addicts use manipulation Heroin is an opioid, respiratory depression, pinpoint pupils Speed/Meth/Cocaine: potent vasoconstrictors (worried about chest pain), dilated pupils SSRI’s: suicide watch the 1st few weeks, takes 4-6 weeks to take effect Disease: Breast Cancer….aka cancer of the lymph nodes Obesitypressure on the tissueschronic inflammationcancer Only 1st degree relatives with cancer history puts you at risk for cancer (genetic/familial) Infants and old people don’t have fever or leukocytosis with infection, first sign is usually tachypnea. IUD is only for monogamous relationships cause it sits in the cervix and creates and open cervix so there is increased risk for STDs affecting more than just reproductive tract, but also kidneys Crohn’s disease: low fat/residual/fiber, high protein STOP metformin 2 days prior to CT scan with contrast because it causes lactic acidosis Never check the monitor, always check the patient Rheumatoid Arthritis (juvenile): to stretch joints, hang on the monkey bars-NCLEX question Slim Fast/Adkins diet: cause lactic acidosis and gout from excessive protein Aspirin is an acid Anterior wall MI leads to left sided heart failure so check lungs RICE for first 48 hours after musculoskeletal injury BKA: lay prone occasionally (3 days post-op) to prevent hip flexion contracture Tick bites cause lyme disease which cause bulls eye rash, intermittent fever, fatique, muscle pain, stiff neck. Mammograms after age 40, colonoscopy after 50(every 10 years), sigmoidoscopy (every 5 years) Latex allergies have cross allergies with avocado, peaches, banana, kiwi. Common pts with latex allergies: neural tube defect, urogenital problems, spinal cord injury pts Kussmaul Respirations: air hunger, increasing rate and depth, like with respiratory acidosis. Should see fluctuations in water seal chamber CPR: CAB, adult: 30:2, child: 1 rescuer: 30:2, 2 rescuer: 15:2 Cane/Crutches: Bad foot first going down stairs, good foot first going up stairs The BIGGER incision wins. Immunocompromised: cook meat to 165 Degrees F Spleenomegaly: avoid trauma/sports for 6 months at least NG Tube placement: Initially-chest x-ray, after check residual and gastric acid pH Never suction without assessment first Salmonella: infectious for a year TB: we can put u in jail if you refuse meds Blood Transfusion: 1. Get transfusion hx, 2. Start IV, 3. Get blood from bank, 4. Double check with 2 RNs, 5. Run at 5 ml/min (Must start within 30 minutes of receiving from bank, must complete within 4 hours) Older patients: smaller doses: renal insufficiency CNAs: comfort care, accuchecks, tube feeding (PEG), no NG tube, can check residuals Fats, Proteins, Fibers: slow digestion Sugar: speeds digestion Laproscopic SX: Inject CO2 to spread arteries/tissues, so CO2 floats to shoulder and causes pain, treat by ambulating patient and have them fart Vaccines: TB, Measles, Varivcella-airborn- gloves, gown, mask Menigococcal/Meningitis: Droplet, gloves, gown, mask, googles Meningicoccal vaccine is given to college/dorm students to prevent meningitis (bacterial) Flu vaccine contraindicated for fowl allergy Contraindications for vaccines: Altered immune system Vaccine contraindicated for fever is greater than 101.0 Previous allergic response Recent acquired passive immunity Rubella: Incubation 14-21 days, communicable days 5-7 before rash onset. If infected during 1st trimester, abortion is recommended. Rubella Vaccine (live), SQ, DO NOT get pregnant for 3 months after vaccination DTP is tetanus shot for kids, DT is for adults or for cuts if 7-10 years has passed since vaccine