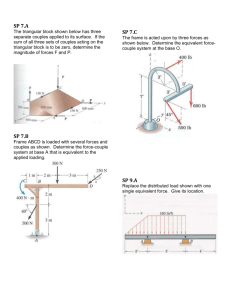
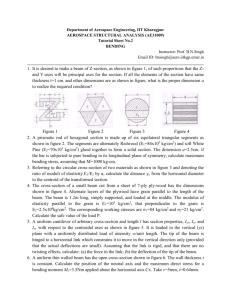
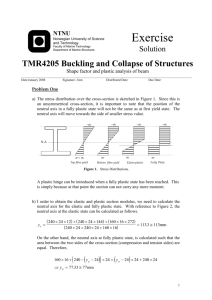
Problem One
advertisement

Norges Teknisk Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Fakultet for Ingeniørvitenskap og Teknologi Institutt for Marin Teknikk Contact person: Name: Jørgen Amdahl Phone: 95544 MID TERM TEST TMR 4205 BUCKLING AND COLLAPSE OF STRUCTURES Date: Monday 14 March 2005 Time: 0915-1100 Credits: 7.5 Sp This mid term test counts 25% of the final grade Allowed during exam: C – Type-approved, simple calculator is allowed. No printed of hand-written material THIS SET CONSISTS OF 3 PAGES TRM 4205 BUCKLING AND COLLAPSE OF STRUCTURES Mid-term test 14 March 2005 Page 2 of 3 PROBLEM 1 15 q 10 250 4000 15 200 Figure 1 I-beam subjected to uniform load (dim. in mm) a) Figure 1 shows the cross-section of a beam with I-profile. The moment of inertia is I = 9.2·107 mm4. Calculate the plastic section modulus and the shape factor for the profile. What is the plastic bending moment, MP? What is the plastic bending moment, MPred, if the contribution from the web is neglected? Yield stress Y = 300 MPa. b) What is the plastic shear capacity, QP, of the cross-section? Assume that the cross-section is subjected to combined bending moment and shear force and is in a fully plastic utilized state. Sketch the axial stress distribution and shear stress distribution over the cross-section when the shear force has reached its fully plastic capacity Q = QP. Sketch qualitatively the bending moment – shear force capacity interaction function for the cross-section (no calculations!) Use relative magnitudes M/MP and Q/QP. c) The beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load, q, as shown in Figure 1. The ends of the beam can be assumed to be rotationally clamped. Introduce a reasonable collapse mechanism and calculate the plastic collapse load for the beam. Comment your choice of bending moment values in the plastic hinges, and check afterwards if your choice was reasonable. d) Compared to the load causing first yield in the beam there are two sources of additional resistance, which is accounted for in the plastic collapse load. What are they? Sketch qualitatively and explain (key words only!) the load versus mid span deformation curve for the beam up to the plastic collapse load level. For the calculation of the collapse load to be correct, the cross-section of the beam must satisfy certain compactness requirements. What do we mean by this? TRM 4205 BUCKLING AND COLLAPSE OF STRUCTURES Mid-term test 14 March 2005 Page 3 of 3 PROBLEM 2 EI N w Figure 2 a) Figure 2 shows a column subjected to an axial compressive force. Sketch qualitatively (no calculations) and in the same diagram the relationship between the axial force, N, and the lateral displacement, w, for the column for the following cases: i. Column is perfectly straight ii. For an initially imperfect column, for two different magnitudes of maximum out-of-straightness. iii. Perfect column – large deflection solution What do we mean by a bifurcation point? Show the position of a bifurcation point in the diagram. b) When the axial force is zero and the beam-column is subjected to a uniformly distributed lateral load of 2.5 kN/m, the mid span displacement is 20 mm and the mid span moment is 5 kNm. Estimate mid span displacement and the mid span moment when the axial force is N = 5 EI/2 and the lateral load is 5.0 kN/m. c) Describe how we can develop a column buckling curve using the concept of an equivalent initial imperfection. What are the major effects the equivalent imperfection accounts for? Set up the expression for the failure criterion, on which the column curve is based (Solution for the critical stress is not required)