The Bits vs
advertisement

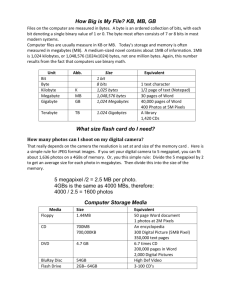
The Bits vs. Bytes Confusion Let's start with some background information on prefixes, by mentioning the Metric system: kilo (k)* = 10 ^ 3 = 1,000 thousand mega (M) = 10 ^ 6 = 1,000,000 million giga (G) = 10 ^ 9 = 1,000,000,000 billion tera (T) = 10 ^ 12 = 1,000,000,000,000 trillion * Note that according to the Metric system, the "k" or "kilo" prefix is always lowercase. The binary forms of kilobytes and megabytes have become standard throughout the computer industry, although they are incorrect uses of the SI prefixes (in the IT field lowercase "k" is used to describe decimal kilobits, and capital "K" is used for binary kilobytes). When used to describe Data Transfer Rate, bits/bytes are calculated as in the metric system In data communications, a kilobit is a thousand bits, or 1,000 bits. It's commonly used for measuring the amount of data that is transferred in a second between two telecommunication points. Kilobits per second is usually shortened to kbps or Kbps**. Some sources define a kilobit to mean 1,024 bits. Although the bit is a unit of the binary number system, bits in data communications are discrete signal pulses and have historically been counted using the decimal number system. For example, 28.8 kilobits per second (kbps) is 28,800 bits per second. 1 bit (b) = 0 or 1 = one binary digit 1 kilobit ( kb) = 10^3 bits = 1,000 bits 1 Megabit (Mb) = 10^6 bits = 1,000,000 bits 1 Gigabit (Gb) = 10^9 bits = 1,000,000,000 bits ** Note: Although technically speaking, the term kilobit should have a lowercase initial letter, most published reports capitalize it in abbreviation, resulting in "56 Kbps," or even the really confusing "56K." That leaves you with the sometimes omitted lowercase "b" to distinguish between bits (b) and bytes (B). When used as a measurement of network data transfers, or throughput, always assume the word is bits first. When used to describe Memory Size, or Data Storage bits/bytes are generally calculated as some exponent of 2 In Data storage, and when describing Memory size, a Kilobyte is 2^10, or 1024 bytes. Because of binary computer architecture and memory address boundaries, bytes are always some multiple or exponent of two. 1 byte (B) = 8 bits (b) 1 Kilobyte (K / KB) = 2^10 bytes = 1,024 bytes 1 Megabyte (M / MB) = 2^20 bytes = 1,048,576 bytes 1 Gigabyte (G / GB) = 2^30 bytes = 1,073,741,824 bytes 1 Terabyte (T / TB) = 2^40 bytes = 1,099,511,627,776 bytes Although data storage capacity, such as on hard drives is generally expressed in binary Megabytes (2^20), most Hard disk manufacturers, and some newer BIOSes use decimal megabytes (10^6), which is slightly different and it gets confusing... 1 byte (B) = 8 bits (b) 1 Kilobyte (K / KB) = 10^3 bytes = 1,000 bytes 1 Megabyte (M / MB) = 10^6 bytes = 1,000,000 bytes 1 Gigabyte (G / GB) = 10^9 bytes = 1,000,000,000 bytes 1 Terabyte (T / TB) = 10^12 bytes = 1,000,000,000,000 bytes Abbreviations Table bit b 0 or 1 byte B 8 bits kilobit kb 1000 bits kilobyte (binary) KB 1024 bytes kilobyte (decimal) KB 1000 bytes Megabit Mb 1000 kilobits Megabyte (binary) MB 1024 Kilobytes Megabyte (decimal) MB 1000 Kilobytes Gigabit Gb 1000 Megabits Gigabyte (binary) GB 1024 Megabytes Gigabyte (decimal) GB 1000 Megabytes Bandwidth Quick Reference Table Bandwidth Quick Reference Table Circuit Name: Capacity Comment DS0 64 kbps Building Block for Fractional T1 ISDN 64 kbps / 128 kbps 1 or 2 DS0's Frame Relay (Fractional T1) 64 kbps / 1.54 Mbps North America T1, DS-1 1.544 Mbps North America E1, DS-1 2.048 Mbps Europe, Asia T2, DS-2 6.312 Mbps North America E2 8.448 Mbps Europe E3 34.368 Mbps Europe and Japan T3 or DS3 44.736 Mbps 672 DS0's, 28 T1's OC-1, STS1 51.840 Mbps Optical Fiber, ATM* switches, SONET Fast Ethernet 100.00 Mbps Wireless Broadband OC-3, STS3 155.520 Mbps Optical Fiber; 3 x 51.840Mbps OC-3c 155.520 Mbps Optical Fiber; "c"= concatenated T4 274 Mbps equivalent of 6 T3's OC-12, STS12 622.080 Mbps Optical Fiber, ATM* switches, SONET OC-48 2.488 Gbps Optical Fiber, ATM* switches, SONET OC-96 4.976 Gbps Optical Fiber, ATM* switches, SONET OC-192 10 Gbps Optical Fiber, ATM* switches, SONET OC-255 13.21 Gbps Optical Fiber, ATM* switches, SONET * ATM - Asynchronous Transfer Mode. ATM (asynchronous transfer mode) is a dedicated connection switching technology that organizes digital data into 53byte cells (packets) and transmits them using digital signal technology. Individually, a cell is processed asynchronously relative to other related cells and is queued before being multiplexed over the line. Because ATM is designed to be easily implemented by hardware (rather than software), faster processing speeds are possible. The pre-specified bit rates are either 155.520 Mbps or 622.080 Mpbs.