Present and Participle Adjectives
advertisement

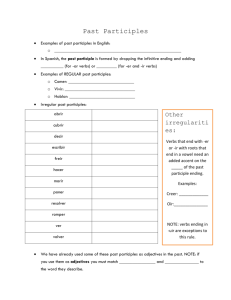
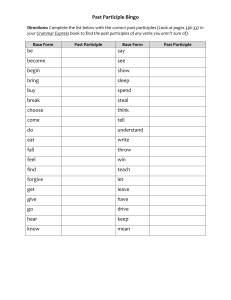
Participles Used as Adjectives Both present and past participles are used with the verbs to be and to have to create common verb tenses, but they can also be used as adjectives. Since there is a slight difference in meaning between the present and the past participles when they are used as adjectives, it is very important to choose the appropriate form. Present participles are formed by adding –ing to the verb stem. As an adjective, a present participle modifies a noun that affects someone or something else. The new song is interesting. The new song was interesting. Past participles are formed by adding –ed, to the verb stem, but some of the irregular forms may end in –d, –en, –n, or –t. As an adjective, a past participle modifies a noun that is affected by someone or something else. The fans are interested in the new song. The fans were interested in the new song. Participles generally come before the noun they modify. They may also be linked to the subject of the sentence by a linking verb such as to be or to feel. The park is a frightening place at night. Steve felt frightened as he walked alone in the park at night. A list of -ed, -ing Participial Adjectives The confused class. (all the students) The chicken has eaten. (perfect aspect:) The chicken was eaten. (passive voice) The following words are past participle adjectives verb - present participle - past participle aggravate - aggravating - aggravated alarm - alarming - alarmed amaze - amazing - amazed amuse - amusing - amused annoy - annoying - annoyed appall - appalling - appalled astonish - astonishing - astonished 2|Page astound - astounding - astounded bewilder - bewildering - bewildered bore - boring - bored calm - calming - calmed captivate - captivating - captivated challenge - challenging - challenged charm - charming - charmed comfort - comforting - comforted compel - compelling - compelled confuse - confusing - confused convince - convincing - convinced depress - depressing - depressed devastate - devastating - devastating disappoint - disappointing - disappointed disgust - disgusting - disgusted distract - distracting - distracted distress - distressing - distressed disturb - disturbing - disturbed embarrass - embarrassing - embarrassed enchant - enchanting - enchanted encourage - encouraging - encouraged entertain - entertaining - entertained excite - exciting - excited overwhelm - overwhelming - overwhelmed please - pleasing - pleased puzzle - puzzling - puzzled refresh - refreshing - refreshed relax - relaxing - relaxed reward - rewarding - rewarded satisfy - satisfying - satisfied shock - shocking - shocked sicken - sickening - sickened startle - startling - startled surprise - surprising - surprised tempt - tempting - tempted terrify - terrifying - terrified threaten - threatening - threatened tire - tiring - tired welcome - welcoming - welcomed worry - worrying - worried frighten - frightening - frightened The -ing form of the verb expresses the cause of the feeling. The -ed form of the verb expresses the result. In the case of the verb "to bore" Akira said she is BORING which means Akira is actually BORING and not the class. Akira should say because this class is BORING, I am BORED, or simply I am BORED. The class is the cause of her feeling, so it is described with an -ing form, in this case BORING. Her feeling, or the result, is described with an -ed form, in this case BORED. Basically you should remember that things can only be described with the -ing form because things cannot produce feelings. People can be described with either the -ing or -ed forms because they can produce feelings in other people or experience feelings themselves. Adjectives and Adverbs: Using Participles as Adjectives 1. A participle is a verb form which can be used as an adjective to describe a noun. an interesting book an interested student 2. When the present participle (-ing from) is used, the noun it describes is (or was) the performer of the activity named by the participle. For example, in the sentence The dog barks The dog is the performer of the action (bark). It is a barking dog. 3. When the past participle (-ed, -en form) is used, the noun it describes is (or was) acted upon. For example, in The child is frightened by the dog, the child is the receiver of the action and is described as a frightened child. 3|Page 4. The use of the present or past participle does not depend on the verb tense of the sentence, but rather on the performer/receiver situation. The dog barks The dog barked The dog frightens the cat. The dog frightened the cat. The problem confuses the students. The students are confused by the problem. The story amused the children. The children were amused by the story. The class bores the students. The students are bored by the class. 5. It is a barking dog It was a barking dog It is a frightening dog. It was a frightening dog. It is a confusing problem. They are confused students. It was an amusing story. They were amused children. It is a boring class. They are bored students. The use of participles is not restricted to the subject of a sentence. In other words, the same statement can produce both a present (active) and a past (passive) participle. Examples: The dog frightens the cat. The problem confuses the students. The story amused the children. The class bores the students. 4|Page The frightening dog runs after the cat. The frightened cat runs away. The confusing problem frightens the students. They are confused students. It was an amusing story. The amused children laughed alot. What a boring class it is! The bored students have stopped listening to the teacher. 6. Participles used as adjectives often come after the noun they modify, following a linking verb like Be, Become, or Seem Examples Mathematics is interesting. My friends are interested in sports You seem confused Problems often become frustrating. I am fascinated by my children. My children quickly became tired at school. School can be tiring for young children The clown was entertaining the family. (active verb) The family was entertained by the clown. (passive verb) The clown was entertaining. (present participial adjective ) The family was entertained. (past participial adjective ) Cause of the feeling or emotion The present participle serves as an adjective formed from an active verb. Receiver of the feeling or emotion The past participle serves as an adjective formed from the passive form of the verb. Examples: an amusing ride (The ride causes the amusement.) 5|Page an amused child (The child receives the feeling of amusement.) Interesting people will speak during the 2-day class. (People cause others to feel interest.) Interested people can sign up for the 2-day class. (The people feel interest in the subject.) Boring speakers put their attendees to sleep. (The speaker causes others to be bored.) Bored speakers should find something exciting to say. (The speaker feels boredom while speaking!) Amusing short films are shown at the animated film festival. (The films cause the amusement.) Amused viewers enjoy the short films. (The viewers feel the amusement.) Overwhelming amounts of work are given to University students. (The amount of work causes the overwhelming.) Overwhelmed students end up dropping a course or two . (The students feel overwhelmed.) 6|Page Practice Exercise In the sentences below, fill in the correct participles of the verbs in parentheses. 1. People who constantly complain are very __________ (annoy) to me. 2. Whenever Adrian gets __________ (bore), he goes fishing. 3. The students were __________ (confuse) by the Professor’s lecture. 4. Most of the news on television is __________ (depress). 5. The Ruttles were very ________ (excite) to learn that their concert was sold out. 6. Babysitting young children can be __________ (exhaust) for many people. 7. Steve was so __________ (fascinate) by the book that he finished it in one evening. 8. Would you be __________ (frighten) if you saw a vampire? 9. After eating a __________ (satisfy) meal, the cat washed her face. 10. When Dagmar looked in the mirror, she was __________ (surprise) to see that she had a leaf in her hair. Answer Key Exercise 1. People who constantly complain are very annoying to me. 2. Whenever Adrian gets bored, he goes fishing. 3. The students were confused by the Professor’s lecture. 4. Most of the news on television is depressing. 5. The Ruttles were very excited to learn that their concert was sold out. 6. Babysitting young children can be exhausting for many people. 7. Steve was so fascinated by the book that he finished it in one evening. 8. Would you be frightened if you saw a vampire? 9. After eating a satisfying meal, the cat washed her face. 10. When Dagmar looked in the mirror, she was surprised to see that she had a leaf in her hair. 7|Page