38. Station Models
advertisement

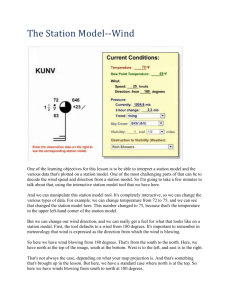
Name ___________________________________ Date _______________ Class Period _____ Instructor _____________ Lab Period ______ 5 points Station Models Data Sheet Fill in the following table, decoding and encoding in the appropriate spaces. Decode Encode 1 275 1 998.9 mb 2 795 2 1027.6 mb 3 000 3 1002.1 mb 4 748 4 884.2 mb Wind Flags 1. 3. 2. 4. SHOW UNITS Fill out the chart based on the station models. Information Dry Bulb (Air Temp.) Example A Example B Example C Dew Point Present weather Visibility Wind Speed Wind Direction Precipitation (last 6 hours) Barometric Pressure Barometric Trend Cloud Cover SHOW UNITS ON THE TABLE ABOVE. Bonus: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5 Example D Example E Lab #38 Station Models Introduction: A lot of information needs to be represented on a weather map without cluttering up the map. Meteorologists devised a way of showing a lot of information in an abbreviated fashion and called it a station model. A typical station model can be found on page 13 of your Earth Science Reference Tables. Some of the information is explained and this lab will help you understand how the station models work. Procedure: Using page 13 of your Earth Science Reference Tables, fill in the table on the back of this sheet. In order to complete the problems, you will need to know how to decode and encode barometric pressure readings. BAROMETRIC PRESSURE Weather maps generally use millibars (mb.) for air pressure. Inches and centimeters of mercury are also used. DECODING: If the station model reading is: less than 500 put a "10" in front and add a decimal place 251 becomes 1025.1 mb 005 becomes 1000.5 mb greater than 500 put a "9" in front and add a decimal place 887 becomes 988.7 mb 962 becomes 996.2 ENCODING: Work in reverse. remove the "9" or "10" and remove the decimal 1032.6 becomes 326 977.9 becomes 779 Fill in the table on the answer sheet, decoding and encoding in the appropriate spaces. WIND FEATHERS The wind direction and speed is shown by “wind arrows”. The stick points to the direction that the wind comes from. A short feather stands for 5 knots, a whole feather equals 10 knots and a flag represents 50 knots. A knot equals 1.15 miles per hour. In general, the wind speed can be considered the same for miles per hour and knots because they are so close. Use the samples below to help you with the wind arrow problems. Wind Arrow Examples From the east at 5 knots From the west at 25 knots From the north at 10 knots From the east at 65 Draw wind arrows and feathers for the following conditions. 1. Wind from the north at 15 knots 2. Wind from the southeast at 30 knots 3. Wind from the southwest at 75 knots 4. Wind from the east at 55 knots CLOUD COVER The amount of cloud cover is shown by the amount of the circle that is colored in on the station models. A completely filled circle means overcast; half filled means partly cloudy and an open circle equals clear skies. OTHER WEATHER DATA The other data such as temperature, dewpoint, present conditions, visibility and precipitation are explained on the Earth Science Reference Tables. Complete the data table using the following station models. A. 43 3/4 38 973 +05 .17 53 071 -15 B. 1/4 * 48 .1 C. 21 3/4 20 889 +25 D. 73 1/4 72 893 -05 .22 E. 1/4 BONUS: ,,65 253 64 .12 -13 For each station model, list the weather conditions that could not exist or probably shouldn’t exist (i.e. rain at 23oF).