Progressive Era Reforms - Killingly Public Schools
advertisement

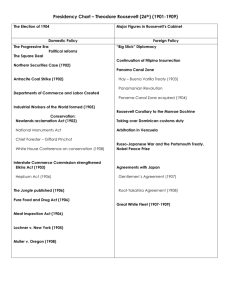
Progressive Movement Socialist/Communist philosophies in Europe start trend. U.S. lags far behind in protection of workers, even to this day In politics/society/economy: - Australian Ballot – secret voting and listing every candidate - Federal Reserve Act – 1913 3rd National Bank? - 16th amendment – income tax - 17th Amendment – 1913, Senators elected directly by the people. - 18th Amendment – prohibition 1919 (repealed by XXI) - 19th Amendment – 1920, gave women the right to vote - recall, referendum & initiative - use of initiative (legislation proposed by the people) referendum (legislation approved by the people) and recall (getting rid of bad politicians – Gray Davis) on state and local level (eg killingly budget) - Municipalities – opposition to corrupt political machines Muckrakers – Investigative reporters focused on exposing corruption (very influencial until 1910) - International Worker of the World (IWW or Wobblies) Radical - AFL 4 million members by 1920 - Socialist/Communist Appeal and fears - Modern school system begins to emerge in late 1800’s (supported by social philosophers like John Dewey) - mandatory attendance, age/grade system, professional teachers, PTA, Kindergarten (effort to Americanize immigrants) - Labor - Child labor - by 1900, almost 20% of children 10-15 are employed (very poor conditions and many injuries in factories) - 1900 most states have no minimum wage by 1914 every state but one did - 1906 The Bitter Cry of Children 1906 by John Spargo (socialist) - most local laws are weak and unenforced (today as well???) - 1912 Congress passes the Children’s Bureau to investigate abuses against kids - 1916 Congress passes the Keating-Owen Act forbidding interstate trade of goods made by kids – Supreme Court overturns - still by 1930 only 4% of kids age 10-15 work. - Women – considered weaker, paid lower wages - a few states pass max hours/day laws just for women - 1908 Supreme Court upholds these laws, and 39 states follow suit by 1917 - minimum wage laws for women are next by some states (just for women), but these wages are still below poverty line. Teddy Roosevelt - “to work out methods of controlling the big corporations without paralyzing the energies of the business community” – TR - rugged outdoorsman and “show off” - Reform background – Civil Service Commissioner - First modern president – uses every power at his disposal, bully pulpit. - modern lobbying of congressmen – no longer the aloof, hands off president that sits back and watches Congress wrangle and debate, then signs whatever they pass. - increases efficiency of executive branch, merit system hiring - establishes press secretary and office - labor- coal strike on 1902 - Americans fear not fuel for winter heat. - unions want 8 hour work day, raises, and union recognition (union house) - TR sets up a commission to mediate between owners and labor. Owners refuse. TR uses army to take control of mines, alarmed, the owners now agree to arbitration. Union gets 9 hour day, 10% raise but not recognition. “To hell with the Constitution, the people want coal” – TR - 1907 & 1908 pushes unsuccessfully for 8 hour workday. - Corporate Regulation - reputation as a trust buster not really earned. Political cartoon – “good” trusts on a leash, bad trust shot dead. - brings 44 antitrust suits, but avoids corporate giants. - most suits have inconclusive outcomes, but establish ACTIVE regulatory role of natl. govt. - Food and Drug Act (establish FDA), Meat Inspection Act (The Jungle – Sinclair 1906), Hepburn Act 1906 (gives ICC power to set max rail rates) - pushes unsuccessfully for stock market regulation