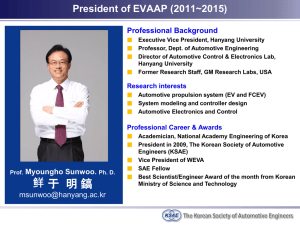
Automotive_Engineering_scope_and_sequence_for_2013
advertisement

Automotive Engineering and Technology Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 2008/16333[v5] Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 1 Copyright © School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2009 This document—apart from any third party copyright material contained in it—may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes by educational institutions, provided that it is not changed in any way and that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner. Teachers in schools offering the Western Australian Certificate of Education (WACE) may change the document, provided that the Authority’s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act or by permission of the Authority. Copying or communication of any third party copyright material contained in this document can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act or by permission of the copyright owners. Currency statement This document may be subject to minor updates. Users who download and print copies of this document are responsible for checking for updates. Advice about any changes made to the document is provided through the Authority communication processes. 2 Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 Automotive Engineering and Technology—Scope and sequence of content UNIT 1A Automotive systems UNIT 1B Automotive servicing UNIT 1C Automotive tuning UNIT 1D Automotive components Automotive mechanics Principles Maintenance and repair basic scientific principles underpinning: Otto cycle; reciprocating and rotary motion; hydraulics; forces; mechanical advantage; alignment; transmission of electrical and mechanical power and the conversion of heat energy into mechanical energy in their relation to automotive functioning. testing techniques involved with daily/weekly checks and monitoring of performance and operation tune-ups, oil changes and service schedules to maintain optimal performance tools and equipment used in repair and correction of minor mechanical faults. Systems roles of the various systems that make up an automotive power plant or vehicle: driveline; wheels and tyres; steering and suspension; body and frame construction; electrical systems; cooling systems and hydraulic braking systems. operation of automotive vehicles and the underpinning basic scientific, geometric and mathematical principles different uses of automotive vehicles. simple testing techniques involved with daily/weekly checks and monitoring of operation of single- or multi-cylinder engines tune-ups, oil changes and service schedules to maintain optimal performance tools, equipment, parts and materials used in repair and correction of minor mechanical faults OSH practices and techniques for the safe storage, use and care of tools and machinery. basic knowledge of systems, subsystems and components, and naming the different parts and functions of each. operation of automotive vehicles and the underpinning basic scientific, geometric and mathematical principles different uses of automotive vehicles. simple testing techniques involved with daily/weekly checks and monitoring of operation of single- or multi-cylinder engines tune-ups, oil changes and service schedules to maintain optimal performance tools, equipment, parts and materials used in repair and correction of minor mechanical faults OSH practices and techniques for the safe storage, use and care of tools and machinery. basic knowledge of systems, subsystems and components, and naming the different parts and functions of each. Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 operation of automotive vehicles and the underpinning basic scientific, geometric and mathematical principles different uses of automotive vehicles. simple testing techniques involved with daily/weekly checks and monitoring of operation of single- or multi-cylinder engines tune-ups, oil changes and service schedules to maintain optimal performance tools, equipment, parts and materials used in repair and correction of minor mechanical and automotive body faults Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) practices and techniques for the safe storage, use and care of tools and machinery. basic knowledge of systems, subsystems and components, and naming the different parts and functions of each. 3 UNIT 1A Automotive systems UNIT 1B Automotive servicing UNIT 1C Automotive tuning UNIT 1D Automotive components Impact of the automotive industry Rules and regulations Social and economic implications Environmental consequences 4 storage, use and care of tools and machinery basic Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) procedures, working safely in the workshop and safe use of prescribed machinery and technologies basic rules associated with the use of vehicles. different forms of transportation used in society broad categories of occupations and careers associated with the automotive industry. changes in environmental features necessary for the safe use of vehicles impact of materials processing and use on the environment and society sustainability of materials. basic traffic rules associated with the safe and sustainable personal use of vehicles road and vehicle design. different forms of transportation currently used in society broad categories of occupations and careers associated with the automotive and affiliated industries consumer awareness rights and responsibilities of both the vendor and buyer. change to our environment to accommodate the use of different types of automotive vehicles and varying traffic demands environmental considerations of materials used and automotive emissions. basic traffic rules associated with the safe and sustainable personal use of vehicles road and vehicle design. different forms of transportation currently used in society broad categories of occupations and careers associated with the automotive and affiliated industries consumer awareness rights and responsibilities of both the vendor and buyer. change to our environment to accommodate the use of different types of automotive vehicles and varying traffic demands environmental considerations of materials used and automotive emissions. Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 basic traffic rules associated with the safe and sustainable personal use of vehicles road and vehicle design. different forms of transportation currently used in society broad categories of occupations and careers associated with the automotive and affiliated industries consumer awareness rights and responsibilities of both the vendor and buyer. change to our environment to accommodate the use of different types of automotive vehicles and varying traffic demands environmental considerations of materials used and automotive emissions. UNIT 1A Automotive systems UNIT 1B Automotive servicing UNIT 1C Automotive tuning UNIT 1D Automotive components Developments in the automotive industry Materials Design Managing production different types of component materials and their application to various design concepts basic understanding of some physical and mechanical properties in prescribed contexts matching properties with human needs and understanding how they reflect aesthetic and environmental values. designing skills including brainstorming, investigating and generating ideas, fundamentals of communicating design by graphics and graphical representation designing for others, design values, market understanding and responsiveness, and consumers. sequential production plans, time planning, identification of resource needs, and evaluation of manufacturing processes. different types of materials in various design concepts and how they address environmental and cultural constraints physical and mechanical properties of basic materials used in automotive technologies workshop-based, computer-assisted fabrication techniques. elements of design and techniques for generating and communicating design ideas market research and responsiveness to consumer’s demands. planning for, and management of manufacturing processes and strategies for standard automotive designs economic implications and quality assurance issues of mass production lines. different types of materials in various design concepts and how they address environmental and cultural constraints physical and mechanical properties of basic materials used in automotive technologies workshop-based, computer-assisted fabrication techniques. elements of design and techniques for generating and communicating design ideas market research and responsiveness to consumer’s demands. planning for, and management of manufacturing processes and strategies for standard automotive designs economic implications and quality assurance issues of mass production lines. Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 different types of materials in various design concepts and how they address environmental and cultural constraints physical and mechanical properties of basic materials used in automotive technologies workshop-based, computer-assisted fabrication techniques. elements of design and techniques for generating and communicating design ideas market research and responsiveness to consumer’s demands. planning for, and management of manufacturing processes and strategies for standard automotive designs economic implications and quality assurance issues of mass production lines. 5 UNIT 2A The world of automotive vehicles UNIT 2B The world of engines UNIT 3A Automotive innovations and the future UNIT 3B Automotive construction Automotive mechanics Principles refinement of scientific principles and the influence of these in modifying and selecting automotive technologies for improved performance. modification of automotive technologies and the impact upon continual refinement of scientific principles underpinning automotive operations simple mathematical and geometrical explanation of principles and the effect of heat underpinning automotive operations. current and futuristic developments in the automotive operations and the impact upon the scientific, geometric and mathematical principles diagrammatic representations of geometric principles with annotated mathematical explanations and the effects of heat that underpin current automotive components and operations. scientific principles underpinning: the Otto cycle; reciprocating and rotary motion; quantitative consideration of hydraulic forces operating and the production of heat in an automotive system; mechanical advantage; alignment; transmission of electrical and mechanical power, in their relation to automotive functioning alternative principles underpinning the operation of current and futuristic developments in automotive technologies detailed diagrammatic representations of geometric principles with mathematical explanations that underpin current automotive components and operations including power train, steering systems and braking systems application of the following mathematical relationships to explain current automotive components, operations and assist in diagnosis of system operation: F r Torque [τ], Rotational Power [Pr], Pr 2 n 60 Pressure [P] or Stress[σ], ( P) 6 Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 F A UNIT 2A The world of automotive vehicles UNIT 2B The world of engines UNIT 3A Automotive innovations and the future UNIT 3B Automotive construction Automotive mechanics Maintenance and repair Systems maintenance and repair of major electrical components in a motor vehicle electrical system, cooling system, fuel and lubrication system adjustment of bearings and removal and repair of motor vehicle components including wheels, body and mechanical parts diagnostic testing using electronic equipment and specialised tools problem-solving principles servicing, repair and maintenance requirements of various types of engines materials and parts required optimising performance of various types of engines safety data information and workshop Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) regulations for both individuals and small groups. operating within systems, subsystems and components during specific automotive operations. maintenance and repair of major electrical components in a motor vehicle electrical system, cooling system, fuel and lubrication system adjustment of bearings and removal and repair of motor vehicle components including wheels, body and mechanical parts development of flow charts and problem-solving skills to diagnose faults in conjunction with the use of specialised tools and equipment servicing, repair and maintenance requirements of more advanced engines, and the skills, knowledge, materials, parts and equipment needed to optimise performance Occupational Safety and Health requirements for different processes and collaborative practices involved in workshop activities. technological improvements in systems, subsystems and components in response to performance testing feedback loops and their role in monitoring and controlling systems. maintenance and repair of major electrical components in a motor vehicle electrical system, cooling system, fuel and lubrication system adjustment of bearings and removal and repair of motor vehicle components including wheels, body and mechanical parts individualised servicing, repair and maintenance schedules for engines modified for particular reasons specialised problem-solving techniques, skills, knowledge, materials, equipment and parts needed to optimise performance of modified automotive vehicles codes of practice and personal responsibility and duty of care for others when carrying out workshop activities. advanced systems, subsystems and components that influence development and performance of automotive vehicles integration of feedback loops in monitoring and control functions. Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 maintenance and repair of major electrical components in a motor vehicle electrical system, cooling system, fuel and lubrication system adjustment of bearings and removal and repair of motor vehicle components including wheels, body and mechanical parts computerised modelling processes and problem-solving techniques to develop diagnostic flow charts and data specifications for servicing, repair and maintenance schedules development of tools equipment and materials to optimise performance of emerging automotive technologies legal implications associated with OSH issues and managing risks associated when working with new and emerging technologies. adaptation of current systems, subsystems and components to predicted future technologies and challenges monitoring and control mechanisms necessary for these automotive advancements. 7 UNIT 2A The world of automotive vehicles UNIT 2B The world of engines UNIT 3A Automotive innovations and the future UNIT 3B Automotive construction Impact of the automotive industry Rules and regulations Social and economic implications Environmental consequences 8 relationship between regulations and rules, and different societies and their expectations authorities responsible for rules and regulations, and legal implications of vehicle design and road use Australian design rules. relationships between changes in automotive technologies and impacts on communities and society changing nature of careers and vocations in the automotive industry in relation to market forces, consumer needs and demands of society. state and federal authorities and laws relating to servicing, repair and modification of automotive systems evolution of laws for automotive vehicles and their use. advanced automotive technologies and implications for consumers, training and the profile of the workforce. current legislation and environmental regulations associated with engine designs and manufacture of automotive technologies community environmental responsibilities for public transport and road design. historical perspective of the relationships between changing global concerns for environmental sustainability, advancements in automotive technologies, and increased demands for transport of materials and people. current rules and regulations and automotive design rules that meet needs of new and emerging automotive technologies rules and regulations from state, federal and international perspectives. current and future environmental considerations to effectively implement emerging automotive technologies and the consequences for patterns of consumer use, town planning processes and location of manufacturing industries. interrelationships between potential social, economic and environmental implications of new and emerging automotive technologies, consumer use and the workforce. future global environmental challenges posed by the increasing use of automotive technologies by third world countries and interrelationships to current safeguards and sustainable practices exercised by communities and countries. new and emerging fuel sources, innovative designs, manufacturing processes, methods of public transport and road design that are sustainable on a global scale, and relate these innovations to changes needed in current consumer demands, practices, attitudes and values. Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 rules and regulations governing the export and import of different types of automotive vehicles futuristic trends in design, purpose and use of automotive vehicles and the impact on society and the environment. UNIT 2A The world of automotive vehicles UNIT 2B The world of engines UNIT 3A Automotive innovations and the future UNIT 3B Automotive construction Developments in the automotive industry Materials Design Managing production historical perspectives of materials used in the automotive industry, and how they have evolved with changing values and needs of society service repair and maintenance of automotive vehicles using computerassisted techniques and fabrication skills. historical perspective of changes in design elements of automotive technologies, and their interaction with changing cultural values computer-assisted techniques to develop promotional materials for market research. advent of computerised mass production lines and changes in the workforce, planning, production and management processes, and testing regimes for quality assurance. advancement in materials and performance testing for their use in automotive technologies considering environmental and cultural constraints modification of automotive vehicles using computer-assisted techniques and fabrication skills. relationship of current and advanced materials technology to the development of futuristic automotive technologies that are environmentally and culturally compatible construction of a futuristic automotive model using computer-assisted techniques and fabrication skills. influence of national and international compliance codes on proposed advancements in the design elements of automotive technologies underpinning role of market research in developing proposed advancements. planning for, and management of small-scale production of prototypes, incorporating innovative design elements underpinned by research, evaluation of performance testing for quality assurance and economic viability. market research findings, current design elements and principles and their relationship to proposed design concepts for future automotive technologies. environmental and cultural constraints on design of automotive technology. interpretation of innovative, futuristic automotive designs and changes required in planning for, and management of, processes and strategies, quality control and economic viability for small scale manufacture. social, economic and environmental implications of scenarios where there is increased computerisation of mass production alternative materials and power sources used in automotive technology. Automotive Engineering and Technology: Scope and sequence For teaching and examination in 2013 scenarios for the predicted uses of new and emerging materials selected for their properties and behaviours in the construction and use of automotive technologies, and that are globally sustainable construction of an automotive technology using computer-assisted fabrication skills. 9