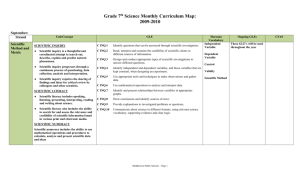
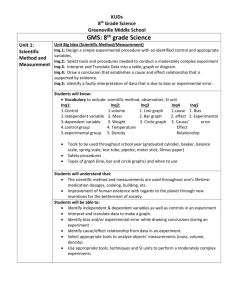
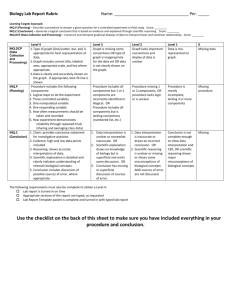
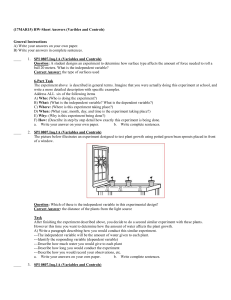
1.14 Embedded Standards
advertisement

Embedded Technology and Engineering Standards: K-12 Learning Progression Conceptual Strand Society benefits when engineers apply scientific discoveries to design materials and processes that develop into enabling technologies. Guiding Question How do science concepts, engineering skills, and applications of technology improve the quality of life? K-2 3-5 6-8 9-12 Embedded Technology and Engineering Standards - Grade/Course Level Expectations GLE 0000.T/E.1 Recognize that GLE 0000.T/E.1 Describe how both natural materials and tools, technology, and human-made tools have inventions help to answer specific characteristics that questions and solve problems. determine their uses. GLE 0000.T/E.2 Recognize that GLE 0000.T/E.2 Apply new tools, technology, and engineering design and creative inventions are always being thinking to solve practical developed. problems. GLE 0000.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. GLE 0000.T/E.4 Recognize the connection between scientific advances, new knowledge, and the availability of new tools and technologies. GLE 0000.T/E.5 Apply a creative design strategy to solve a particular problem generated by societal needs and wants. GLE 0000.T/E.7.1 Explore how technology responds to social, political, and economic needs. GLE 0000.T/E.7.2 Know that the engineering design cycle involves an ongoing series of events that incorporate design constraints, model building, testing, evaluating, modifying, and retesting. GLE 0000.T/E.7.3 Compare the intended benefits with the unintended consequences of a new technology. GLE 0000.T/E.7.4 Differentiate between adaptive and assistive bioengineered products. CLE 0000.T/E.1 Explore the impact of technology on social, political, and economic systems. CLE 0000.T/E.2 Differentiate among elements of the engineering design cycle: design constraints, model building, testing, evaluating, modifying, and retesting. CLE 0000.T/E.3 Explain the relationship between the properties of a material and the use of the material in the application of a technology. CLE 0000.T/E.4 Describe the dynamic interplay among science, technology, and engineering within living, earth-space, and physical systems. 1 K-12 Embedded Technology and Engineering Standards Conceptual Strand Society benefits when engineers apply scientific discoveries to design materials and processes that develop into enabling technologies. Guiding Question How do science concepts, engineering skills, and applications of technology improve the quality of life? Embedded Technology and Engineering K-2 Grade Level Expectations GLE 0207.T/E.1 Recognize that both natural materials and human-made tools have specific characteristics that determine their uses. GLE 0207.T/E.2 Apply engineering design and creative thinking to solve practical problems. Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 0207.T/E.1 Explain how simple tools are used to extend the senses, make life easier, and solve everyday problems. 0207.T/E.2 Invent designs for simple products. 0207.T/E.3 Use tools to measure materials and construct simple products. Embedded Technology and Engineering 3-5 Grade Level Expectations GLE 0507.T/E.1 Describe how tools, technology, and inventions help to answer questions and solve problems. GLE 0507.T/E.2 Recognize that new tools, technology, and inventions are always being developed. GLE 0507.T/E.3 Identify appropriate materials, tools, and machines that can extend or enhance the ability to solve a specified problem. GLE 0507.T/E.4 Recognize the connection between scientific advances, new knowledge, and the availability of new tools and technologies. GLE 0507.T/E.5 Apply a creative design strategy to solve a particular problem generated by societal needs and wants. Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 0507.T/E.1 Explain how different inventions and technologies impact people and other living organisms. 0507.T/E.2 Design a tool or a process to address an identified problem caused by human activity. 0507.T/E.3 Determine criteria to evaluate the effectiveness of a solution a specified problem. 0507.T/E.4 Evaluate an invention that solves a problem and determines ways to improve the design. Embedded Technology and Engineering 6-8 Grade Level Expectations GLE 0807.T/E.7.1 Explore how technology responds to social, political, and economic needs. GLE 0807.T/E.7.2 Know that the engineering design cycle involves an ongoing series of events that incorporate design constraints, model building, testing, evaluating, modifying, and retesting. 2 GLE 0807.T/E.7.3 Compare the intended benefits with the unintended consequences of a new technology. GLE 0807.T/E.7.4 Differentiate between adaptive and assistive bioengineered products. Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 0807.7.1. Use appropriate tools to test for strength, hardness, and flexibility of materials. 0807.7.2 Apply the engineering design process to construct a prototype that meets certain specifications. 0807.7.3 Explore how the unintended consequences of new technologies can impact society. 0807.7.4 Research bioengineering technologies that advance health and contribute to improvements in our daily lives. 0807.7.5 Develop an adaptive design and test its effectiveness. State Performance Indicators SPI 0807.T/E.7.1 Identify the tools and procedures needed to test the design features of a prototype. SPI 0807.T/E.7.2 Evaluate a protocol to determine if the engineering design process was successfully applied. SPI 0807.T/E.7.3 Distinguish between the intended benefits and the unintended consequences of a new technology. SPI 0807.T/E.7.4 Differentiate between adaptive and assistive bioengineered products. Embedded Technology and Engineering 9-12 Course Level Expectations CLE 3210.T/E.1 Explore the impact of technology on social, political, and economic systems. CLE 3210.T/E.2 Differentiate among elements of the engineering design cycle: design constraints, model building, testing, evaluating, modifying, and retesting. CLE 3210-.T/E.3 Explain the relationship between the properties of a material and the use of the material in the application of a technology. CLE 3210.T/E.4 Describe the dynamic interplay among science, technology, and engineering within living, earth-space, and physical systems. Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 3210.1 Select appropriate tools to conduct a scientific inquiry. 3210.2 Apply the engineering design process to construct a prototype that meets developmentally appropriate specifications. 3210.3 Explore how the unintended consequences of new technologies can impact human and non-human communities. 3210.4 Present research on current bioengineering technologies that advance health and contribute to improvements in our daily lives. 3210.5 Design a series of multi-view drawings that can be used by other students to construct an adaptive design and test its effectiveness. State Performance Indicators SPI 3210.T/E.1 Distinguish among tools and procedures best suited to conduct a specified scientific inquiry. SPI 3210.T/E.2 Evaluate a protocol to determine the degree to which an engineering design process was successfully applied. SPI 3210.T/E.3 Evaluate the overall benefit to cost ratio of a new technology. SPI 3210.T/E.4 Assess the principles that determine if a new technology will improve the quality of life for an intended audience. 3 Embedded Inquiry Standards – K-12 Learning Progression Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? K-2 3-5 6-8 9-12 Embedded Inquiry - Grade/Course Level Expectations GLE K-2.Inq.1 Observe the world GLE 3-5.Inq.1 Explore different of familiar objects using the scientific phenomena by asking senses and tools. questions, making logical GLE K-2.Inq.2 Ask questions, predictions, planning make logical predictions, plan investigations, and recording investigations, and represent data. data. GLE 3-5.Inq.2 Select and use GLE K-2.Inq.3 Give an appropriate tools and simple explanation for the data from equipment to conduct an an investigation. investigation. GLE 3-5.Inq.3 Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawing, or diagrams. GLE 3-5.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the findings of multiple investigations. GLE 3-5.Inq.5 Recognize that different people may interpret the same results another way. GLE 3-5.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. GLE 6-8.Inq.1 Design and conduct open-ended scientific investigations. GLE 6-8.Inq.2 Use appropriate tools and techniques to gather, organize, analyze, and interpret data. GLE 6-8.Inq.3 Synthesize information to determine cause and effect relationships between evidence and explanations. GLE 6-8.Inq.4 Recognize possible sources of bias and error, alternative explanations, and questions for further exploration. GLE 6-8.Inq.5 Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. CLE 9-12.Inq.1 Recognize that science is a progressive endeavor that reevaluates and extends what is already accepted. CLE 9-12.Inq.2 Design and conduct scientific investigations to explore new phenomena, verify previous results, test how well a theory predicts, and compare opposing theories. CLE 9-12.Inq.3 Use appropriate tools and technology to collect precise and accurate data. CLE 9-12.Inq.4 Apply qualitative and quantitative measures to analyze data and draw conclusions that are free of bias. CLE 9-12.Inq.5 Compare experimental evidence and conclusions with those drawn by others about the same testable question. CLE 9-12.Inq.6 Communicate and defend scientific findings. 4 K-12 Embedded Inquiry Standards Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? Embedded Inquiry K-2 Grade Level Expectations GLE K-2.Inq.1 Observe the world of familiar objects using the senses and tools. GLE K-2.Inq.2 Ask questions, make logical predictions, plan investigations, and represent data. GLE K-2.Inq.3 Give an explanation for the data from an investigation. Checks for Understanding K-2.Inq.1 Use senses and simple tools to make observations. K-2.Inq.2 Communicate interest in simple phenomenon and plan for simple investigations. K-2.Inq.3 Communicate understanding of simple data using age appropriate vocabulary. K-2.Inq.4 Collect, discuss, and communicate findings from a variety of investigations. Embedded Inquiry 3-5 Grade Level Expectations GLE 3-5.Inq.1 Explore different scientific phenomena by asking questions, making logical predictions, planning investigations, and recording data. GLE 3-5.Inq.2 Select and use appropriate tools and simple equipment to conduct an investigation. GLE 3-5.Inq.3 Organize data into appropriate tables, graphs, drawing, or diagrams. GLE 3-5.Inq.4 Identify and interpret simple patterns of evidence to communicate the findings of multiple investigations. GLE 3-5.Inq.5 Recognize that different people may interpret the same results another way. GLE 3-5.Inq.6 Compare the results of an investigation with what scientists already accept about this question. Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 3-5.Inq.1 Identify specific investigations that could be used answer a particular question and identify reasons for the selection. 3-5.Inq.2 Identify tools needed to investigate specific questions. 3-5.Inq.3 Maintain a science journal that includes observations, data, diagrams, and interpretations. 3-5.Inq.4 Analyze and communicate findings from multiple investigations of similar phenomena to reach a conclusive explanation. 5 State Performance Indicator SPI 3-5.Inq.1 Select an investigation that could be used to answer a specific question. Embedded Inquiry 6-8 Grade Level Expectations GLE 6-8.Inq.1 Design and conduct open-ended scientific investigations. GLE 6-8.Inq.2 Use appropriate tools and techniques to gather, organize, analyze, and interpret data. GLE 6-8.Inq.3 Synthesize information to determine cause and effect relationships between evidence and explanations. GLE 6-8.Inq.4 Recognize possible sources of bias and error, alternative explanations, and questions for further exploration. GLE 6-8.Inq.7.5 Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 6-8.Inq.1 Design and conduct an open-ended scientific investigation to answer a question that includes a control and appropriate variables. 6-8.Inq.2 Identify tools and techniques needed to gather, organize, analyze, and interpret data collect from a moderately complex scientific investigation. 6-8.Inq.3 Use evidence from a set of data to for determine cause and effect relationships that explain a phenomenon. 6-8.Inq.4 Review an experimental design to determine possible sources of bias or error, state alternative explanations, and identify questions for further investigation. 6-8.Inq.5 Design a method to explain the results of an investigation using descriptions, explanations, or models. State Performance Indicators SPI 6-8.Inq.1 Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. SPI 6-8.Inq.2 Select tools and procedures needed to conduct a moderately complex experiment. SPI 6-8.Inq.3 Interpret and translate data into a table, graph, or diagram. SPI 6-8.Inq.4 Draw a conclusion that establishes a cause and effect relationship that is supported by evidence. Embedded Inquiry 9-12 (Biology) Course Level Expectations CLE 3210.Inq.1 Recognize that science is a progressive endeavor that reevaluates and extends what is already accepted. CLE 3210.Inq.2 Design and conduct scientific investigations to explore new phenomena, verify previous results, test how well a theory predicts, and compare opposing theories. CLE 3210.Inq.3 Use appropriate tools and technology to collect precise and accurate data. CLE 3210.Inq.4 Apply qualitative and quantitative measures to analyze data and draw conclusions that are free of bias. CLE 3210.Inq.5 Compare experimental evidence and conclusions with those drawn by others about the same testable question. CLE 3210.Inq.6 Communicate and defend scientific findings. 6 Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 3210.Inq.1 Trace the historical development of a scientific principle or theory, such as cell theory, evolution, or DNA structure. 3210.Inq.2 Conduct scientific investigations that include testable questions, verifiable hypotheses, and appropriate variables to explore new phenomena or verify the experimental results of others. 3210.Inq.3 Select appropriate tools and technology to collect precise and accurate quantitative and qualitative data. 3210.Inq.4 Determine if data supports or contradicts a hypothesis or conclusion. 3210.Inq.5 Compare or combine experimental evidence from two or more investigations 3210.Inq.6 Recognize, analyze, and evaluate alternative explanations for the same set of observations. 3210.Inq.7 Analyze experimental results and identify possible sources of experimental error. 3210.Inq.8 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models using logic and evidence. State Performance Indicators SPI 3210 Inq.1 Select a description or scenario that reevaluates and/or extends a scientific finding. SPI 3210 Inq.2 Analyze the components of a properly designed scientific investigation. SPI 3210 Inq.3 Determine appropriate tools to gather precise and accurate data. SPI 3210 Inq.4 Evaluate the accuracy and precision of data. SPI 3210 Inq.5 Defend a conclusion based on scientific evidence. SPI 3210 Inq.6 Determine why a conclusion is free of bias. SPI 3210 Inq.7 Compare conclusions that offer different, but acceptable explanations for the same set of experimental data. 7 8