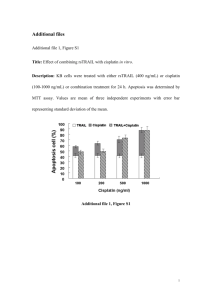
2014 Research Scholarship Recipients
advertisement
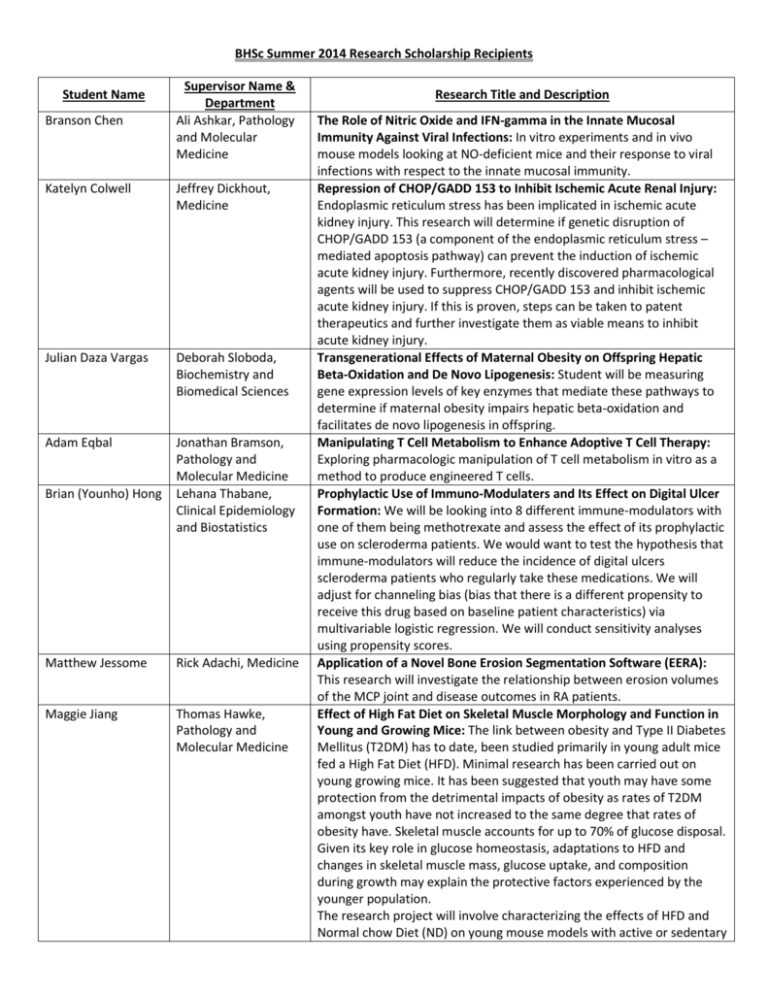
BHSc Summer 2014 Research Scholarship Recipients Student Name Branson Chen Supervisor Name & Department Ali Ashkar, Pathology and Molecular Medicine Katelyn Colwell Jeffrey Dickhout, Medicine Julian Daza Vargas Deborah Sloboda, Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences Adam Eqbal Jonathan Bramson, Pathology and Molecular Medicine Lehana Thabane, Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Brian (Younho) Hong Matthew Jessome Rick Adachi, Medicine Maggie Jiang Thomas Hawke, Pathology and Molecular Medicine Research Title and Description The Role of Nitric Oxide and IFN-gamma in the Innate Mucosal Immunity Against Viral Infections: In vitro experiments and in vivo mouse models looking at NO-deficient mice and their response to viral infections with respect to the innate mucosal immunity. Repression of CHOP/GADD 153 to Inhibit Ischemic Acute Renal Injury: Endoplasmic reticulum stress has been implicated in ischemic acute kidney injury. This research will determine if genetic disruption of CHOP/GADD 153 (a component of the endoplasmic reticulum stress – mediated apoptosis pathway) can prevent the induction of ischemic acute kidney injury. Furthermore, recently discovered pharmacological agents will be used to suppress CHOP/GADD 153 and inhibit ischemic acute kidney injury. If this is proven, steps can be taken to patent therapeutics and further investigate them as viable means to inhibit acute kidney injury. Transgenerational Effects of Maternal Obesity on Offspring Hepatic Beta-Oxidation and De Novo Lipogenesis: Student will be measuring gene expression levels of key enzymes that mediate these pathways to determine if maternal obesity impairs hepatic beta-oxidation and facilitates de novo lipogenesis in offspring. Manipulating T Cell Metabolism to Enhance Adoptive T Cell Therapy: Exploring pharmacologic manipulation of T cell metabolism in vitro as a method to produce engineered T cells. Prophylactic Use of Immuno-Modulaters and Its Effect on Digital Ulcer Formation: We will be looking into 8 different immune-modulators with one of them being methotrexate and assess the effect of its prophylactic use on scleroderma patients. We would want to test the hypothesis that immune-modulators will reduce the incidence of digital ulcers scleroderma patients who regularly take these medications. We will adjust for channeling bias (bias that there is a different propensity to receive this drug based on baseline patient characteristics) via multivariable logistic regression. We will conduct sensitivity analyses using propensity scores. Application of a Novel Bone Erosion Segmentation Software (EERA): This research will investigate the relationship between erosion volumes of the MCP joint and disease outcomes in RA patients. Effect of High Fat Diet on Skeletal Muscle Morphology and Function in Young and Growing Mice: The link between obesity and Type II Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) has to date, been studied primarily in young adult mice fed a High Fat Diet (HFD). Minimal research has been carried out on young growing mice. It has been suggested that youth may have some protection from the detrimental impacts of obesity as rates of T2DM amongst youth have not increased to the same degree that rates of obesity have. Skeletal muscle accounts for up to 70% of glucose disposal. Given its key role in glucose homeostasis, adaptations to HFD and changes in skeletal muscle mass, glucose uptake, and composition during growth may explain the protective factors experienced by the younger population. The research project will involve characterizing the effects of HFD and Normal chow Diet (ND) on young mouse models with active or sedentary Tony Jin Shucui Jiang, Yalda Karimi Ali Ashkar, Pathology and Molecular Medicine Guillaume Pare, Pathology and Molecular Medicine Joanne (Jeehyun) Kim Joshua Koenig Manel Jordana, Pathology and Molecular Medicine Philipp Kolb Kjetil Ask, Medicine Ben Li Jonathan Bramson, Adam Suleman Eric Brown, Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences Christine (Pei-Wen) Wang Geoff Werstuck, Medicine Tina Wang Shucui Jiang, Surgery lifestyles. Mice between 3 and 6 weeks of age will undergo selective training and exercise tests. Mice will then undergo glucose tolerance, and body composition tests. Extraction of various muscle fibre samples will occur at 6 weeks of age to measure palmidate oxidation, and measures of muscle morphology including fibre size, fibre type, lipid content and mitochondrial content. Determining Whether Inhibition of Intracellular Calcium Levels Affects Guanosine-Induced Anti-Apoptosis in Schneider 2 Cells: To link changes in intracellular calcium levels with cellular apoptosis to elucidate the signal transduction mechanisms involved with G1 receptor, intracellular calcium release will be inhibited or untouched in experimental groups involving Schneider 2 cells with transfected G1 receptors. Apoptosis will be induced using anti-myosin C in these cells and caspase 3 will be quantified and used as the hallmark biochemical indicator of the extent of apoptosis or anti-apoptosis. The Regulatory Effect of type 1 IFN Signaling on TLR-4 Signaling: This project will investigate the modulatory effect of type 1 IFN on the immune cell’s response to TLR-4 ligands. Associations Between Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Gene Polymorphisms on Intracerebral Hemorrhage: The study objective is to determine how ethnic background affects the effect size of APOE polymorphisms on risk for intracerebral hemorrhage. Elucidating Mechanisms Underlying Peanut Sensitization and Anaphylaxis in Murine Models: Experiments will be conducted on mouse models to further understand and identify factors that are key to the induction of peanut sensitization and anaphylaxis. TGF-ß1 Induced Fibroblast Differentiation In Vitro and Pharmaceutical Intervention of this Process: The overall goal of my summer research project is to decrease fibroblast differentiation through pharmaceutical intervention in vitro. I developed an assay my 3H03 project which can reliably cause differentiation through TGFβ which can be measured using flow cytometry. This step though simple in theory is key to moving this project forward. Now that we have a system in place we can start administering drugs and seeing if we can inhibit differentiation or more ideally even cause established myofibroblasts to de-differentiate. Manipulating T Cell Metabolism to Enhance Adaptive T Cell Therapy: Exploring the structure-function relationship of the tri-functional T cellantigen coupler (Tri-TAC) components and the anti-tumour activity of the T cells. Mapping the Genetic Interactions of E Coli Genes Under Minimal Conditions: Goal is to create deletions in a subset of genes that are essential under nutrient-limited conditions, combine them with the Keio collection and analyze the interactions. Characterization of a Novel Mouse Model of Hyperglycemia-Induced Atherosclerosis: This project will involve the measurement and analysis of lipid and protein levels from various tissues isolated from a novel mouse model of hyperglycemic (as well as normoglycemic controls). Determination of the Regionalization and Localization of the G1 Receptor: Guanosine, a non-adenosine based purine, is a neurotrophic, neuroprotective and neurorestorative agent that has been shown to exhibit its therapeutic effects in vitro as well as in vivo. The G1 receptor is a potential guanosine specific receptor discovered in Dr. Jiang’s lab. Kai Yi Wu Peter Gross, Medicine Sean Xia John Turnbull, Neurology Anne Xia Bhagwati Gupta, Biology Grace Zhang Radhey Gupta, Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences Currently, its distribution in the brain is unknown. The purpose of this project is to determine the presence and density of the G1 receptor in various areas of the brain (i.e. amygdala, frontal cortex etc.) using the fluorescent and confocal microscopy. The localization of G1 on various cell types (i.e. astrocytes, microglia etc.) will also be investigated using the same technique. Do Statins Inhibit PAR4-PLCß3 in Platelets?: Platelets from wild-type and eNos-deficient mice are to be isolated and activated with PAR4 agonist. A western blot will be used (blotting with anti-PLCß3 and antiphospho-PLCß3 (pSer537)). The ratio of anti-phospho intensity to antiPLCß3 intensity will serve as a measure of PLCß3 activation. The expected result will be impaired PAR4-agonist-induced PLCß3 activation in atorvastatin-treated platelets. Effect of PERK and PKR Inhibitor Treatment in ALS-like G93A Mice: Each year, thousands of patients are diagnosed with ALS in the US alone, and survival rates are low. Targeting the UPR pathway represents a novel and promising therapeutic approach. Identifying Genes and Pathways Involved in C. Elegans Neuronal Degeneration: Using a novel microfluidics system to probe the neuronal activity of different strains of c. elegans to identify neuronal control of movement. Mutant strains with alterations in dopamine expression will be studied to identify role of dopamine in movement. Comparative Analyses of Eukaryotic Genomes: Protein sequences of eukaryotic genomes will be analyzed and compared in order to elucidate evolutionary relationships between species.