Lesson 4
advertisement

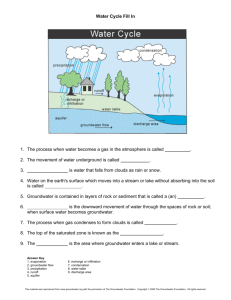
SEED Lesson Plan Session # 4 Objective: Students will be able to__ explain the groundwater part of the water cycle and how groundwater can be contaminated Assessment Ideal “What did you learn” Sentence Groundwater is water that is found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand and rock. 2-3 End of Semester Quiz Questions 1. Where does water go after it rains on the ground? 2. How can groundwater come to the surface? Lesson Cycle As You Enter Question (Include time to discuss responses if teachers should do that) What happens when water falls onto the ground? (many students have probably never thought about it, so take ideas, then tell them that we’ll learn that today) Introduction to Lesson (Teacher presentation-limit to 5-10 min. Indicate what is large and smallgroup instruction) When rain falls to the ground, the water does not stop moving. Some of it flows along the surface to streams or lakes, some of it is used by plants, some evaporates and returns to the atmosphere, and some sinks into the ground. Groundwater is water that is found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand and rock. Groundwater is stored in--and moves slowly through-layers of soil, sand and rocks called aquifers. Aquifers typically consist of gravel, sand, sandstone, or fractured rock, like limestone. These materials are permeable because they have large connected spaces that allow water to flow through. The speed at which groundwater flows depends on the size of the spaces in the soil or rock and how well the spaces are connected. The area where water fills the aquifer is called the saturated zone (or saturation zone). The top of this zone is called the water table. The water table may be located only a foot below the ground’s surface or it can sit hundreds of feet down. Water in aquifers is brought to the surface naturally through a spring or can be discharged into lakes and streams. Groundwater can also be extracted through a well drilled into the aquifer. A well is a pipe in the ground that fills with groundwater. This water can be brought to the surface by a pump. Shallow wells may go dry if the water table falls below the bottom of the well. Some wells, called artesian wells, do not need a pump because of natural pressures that force the water up and out of the well. Estimated Time at End of Section Groundwater supplies are replenished, or recharged, by rain and snow melt. In some areas of the world, people face serious water shortages because groundwater is used faster than it is naturally replenished. In other areas groundwater is polluted by human activities. In areas where material above the aquifer is permeable, pollutants can readily sink into groundwater supplies. Groundwater can be polluted by landfills, septic tanks, leaky underground gas tanks, and from overuse of fertilizers and pesticides. If groundwater becomes polluted, it will no longer be safe to drink. (Source: http://www.groundwater.org/gi/gi.html) Student Practice/Engagement (Activity, reading, small group discussion, etc. - probably bulk of lesson. Include guiding ideas/questions for individual teachers to connect activity to objective) -Each group makes a model aquifer. -In a plastic bin, add gravel and sand and make one section of the bin a “lake” by pushing mass to the other side. -Rain on the land with the water bottle and watch the lake fill up. -Note where the water table level is. -Create a cap on the well pump by attaching mesh to bottom of plastic pump with rubber band. -Insert pump in the corner of high gravel and attach it to side of bin with clay. -Pump the water into a cup and note the color. -Obtain cup of red “contamination water” -Pour red water onto gravel away from pump and watch it travel to lake -Pump as red water is poured into model, assessing the water color all the time Conclusion/Wrap Up (Bring students back to lesson objective. Ask to write “what did you learn” sentence. Could be done in small or large group.) (Final time should be about 40-60 min) Worksheets/Readings Teacher Needs to Print/Copy and Number Needed of Each (1 per student for whole class, group of 3, group of 4, half of class, etc.) o Other Materials Teacher Needs to Bring to Lesson (Lab or demo materials, presentation materials, etc) Plastic bin Plastic Water Bottle Gravel Rubber Band Water(red) Clay Cup Sand Pump Mesh Fabric Classroom Resources Needed (Individual computers, overhead projector, television / DVD player, etc.) o