Essential Question: Why are there different types of rocks? Name
advertisement

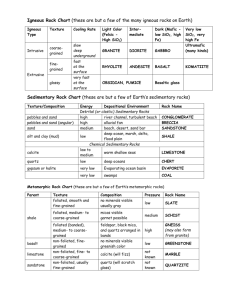
Essential Question: Why are there different types of rocks? Name: ___________________Developing Understanding:___/36 Rocky Inquiries--For each of the rock families you and your group need to do the following: -1st … define the vocab. words in YOUR NB—(write the WORD & the definition)! -2nd … answer the questions for each part (make sure you ORGANIZE & # these in your NB). -3rd … key out the samples in your boxes by filling out the tableand have them checked by the master. Two online keys to use: http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/investigations/es0610/es0610page02.cfm?chapter_no=investigation or http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/#Key **HINT: Use the resources below for help with the vocabulary words & questions: Int. Sci. (blue) Orange Textbook Purple Textbook Igneous Rocks: *page 48-51 *page 87-90 *page 118-122 Metamorphic Rocks: *page 59-61 *page 95-99 *page 125-129 Sedimentary Rocks: *page 53-56 *page 91-94 *page 95-99 Part A) Igneous Family:__/12 --Vocabulary: Felsic, Mafic, Magma, Lava, Vesicular=bubbly (air pockets) --Igneous Questions: 1) What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks? 2) What is the difference between a light colored & a dark colored igneous rock? 3) What does texture/crystal size tell you about how an igneous rock formed? 4) Explain the 3 ways a rock can melt AND how they would melt rock Part B) Sedimentary Family:___/12 --Vocabulary: Clastic Sed. Rock, Chemical Sed. Rock, Organic Sed. Rock, Strata/Stratafication, Fossil --Sedimentary Questions: 1) How do sedimentary rocks differ from igneous rocks? 2) What does the presence of sedimentary structures/appearances indicate regarding the past environmental history of an area? (think Climate) 3) Sedimentary rock is also classified by the way it forms. How do Clastic, Chemical, and Organic rocks each form? Part C) Metamorphic Family:___/12 --Vocabulary: Metamorphism, Foliated, Non-foliated. --Metamorphic Questions: 1) What are the two types metamorphism that can cause a rock to change? 2) Why do temperature and pressure increase as you/a rock go deeper down into Earth? 3) How are metamorphic rocks related to all other rocks? (think Rock Cycle) Essential Question: Why are there different types of rocks? Name: ___________________Developing Understanding:___/36 Rocky Inquiries--For each of the rock families you and your group need to do the following: -1st … define the vocab. words in YOUR NB—(write the WORD & the definition)! -2nd … answer the questions for each part (make sure you ORGANIZE & # these in your NB). -3rd … key out the samples in your boxes by filling out the tableand have them checked by the master. Two online keys to use: http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/investigations/es0610/es0610page02.cfm?chapter_no=investigation or http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/#Key **HINT: Use the resources below for help with the vocabulary words & questions: Int. Sci. (blue) Orange Textbook Purple Textbook Igneous Rocks: *page 48-51 *page 87-90 *page 118-122 Metamorphic Rocks: *page 59-61 *page 95-99 *page 125-129 Sedimentary Rocks: *page 53-56 *page 91-94 *page 95-99 Part A) Igneous Family:__/12 --Vocabulary: Felsic _________________________________________________use the Orange textbook! Mafic _________________________________________________use the Orange textbook! Magma ______________________________________________________________ Lava ________________________________________________________________ Vesicular= bubbly (air pockets)_____________________________________________ --Igneous Questions: 1) What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks? 2) What is different between a light colored & a dark colored igneous rock? 3) What does texture/crystal size tell you about how an igneous rock formed? 4) Explain the 3 ways a rock can melt AND how they would melt rock (use the orange book here). 1) _______________ how it melts the rock:_______________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 2) ________________ how it melts the rock: ______________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 3) ________________ how it melts the rock: ______________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Fill in the table below as you observe the rocks in the basket at your table: Color IGNEOUS Texture Intrusive (Dark w/green, Dark, (Glassy, Fine, Coarse, Very Intermediate, Light) Course, Vesicular or Non-Ves.) or Rock NAME Extrusive? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Part B) Sedimentary Family:___/12 --Vocabulary: Clastic Sedimentary Rock_______________________________________________________ Chemical Sedimentary Rock_____________________________________________________ Organic (Biochemical) Sedimentary Rock____________________________________________ Strata/Stratafication_________________________________________________________ Fossil_____________________________________________________________________ --Sedimentary Questions: 1) How do sedimentary rocks differ from igneous rocks? 2) What does the presence of sedimentary rock layers/structures/appearances indicate about the past history of an area? (think Climate & Environment of an area—use the Orange book!) 3) Sedimentary rock is also classified by the way it forms. How do each form? a. Clastic: b. Chemical: c. Organic/Biochemical: Fill in the table below as you observe the rocks in the basket at your table: Texture SEDIMENTARY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Grain Size Other (Clastic, Chemical, (Gravel, Sand, Organic) Silt/Mud, Clay) Characteristics Rock NAME Part C) Metamorphic Family:___/12 --Vocabulary: Metamorphism_________________________________________________________ Foliated______________________________________________________________ Non-foliated___________________________________________________________ --Metamorphic Questions: 1) What are two types of metamorphism that cause a rock to change due to heat? 2) Why do temperature and pressure increase as you/a rock go deeper down into Earth? 3) How are metamorphic rocks related to all other rocks?—think about your rock cycle! Fill in the table below as you observe the rocks in the basket at your table: METAMORPHIC 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Texture Bands, Foliated or (Grain Size: course, Layers or No Non-foliated medium Or fine Layers? Rock NAME Environment (original, squeezed, or heated)