Ch. 7 Test Memory
advertisement

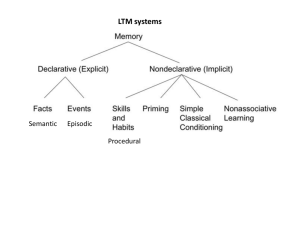
Name: ________________ Period: ____ Psychology Ch. 7 Test: Memory Directions: Choose the best answer. _________ 1. The skills needed for riding a bicycle are stored as A. implicit memories. B. episodic memories. C. semantic memories. D. echoic memories. _________ 2. Facts learned in classes at school become part of the A. implicit memory. B. episodic memory. C. semantic memory. D. iconic memory. _________ 3. Computers and people both handle information using the processes of A. implicit, semantic, and episodic memories. B. maintenance and elaborative rehearsals. C. sensory, short-term, and long-term memories. D. encoding, storage, and retrieval. _________ 4. One drawback of maintenance rehearsal is that A. it does not involve repetition. B. it does not connect memorized information to past learning. C. only the first item on the memorized list is recalled. D. only the last item on the memorized list is remembered. _________ 5. Studying for a test in the same room in which it will be held may result in a better grade because of A. iconic memory. B. state-dependent memory. C. context-dependent memory. D. eidetic memory. _________ 6. In order to remember information for a long period of time, facts must be A. stored as echoes. B. stored as icons. C. transferred from short-term memory to long-term memory. D. moved from short-term memory to sensory memory. _________ 7. The first stage of memory is A. long-term memory. B. short-term memory. C. context-dependent memory. D. sensory memory. _________ 8. We can more easily remember bits of information by organizing them into mental representations of the world called A. icons. B. echoes. C. mnemonic devices. D. schemas. _________ 9. The easiest of the three basic memory tasks is A. recall. B. recognition. C. relearning. D. chunking. _________ 10. Most people forget things because of the normal processes of A. maintenance and elaborative rehearsals. B. interference and decay. C. repression and amnesia. D. chunking and schema. _________ 11. A person trying to learn the vocabulary of a foreign language can remember the foreign words by A. maintenance rehearsal. B. constructing links to something already familiar. C. using paired associates. D. all of the above. _________ 12. Relating new information to something already known helps a person remember the new facts through A. creating an echoic memory. B. creating an iconic memory. C. elaborative rehearsal D. using a mnemonic device. _________ 13. What is the memory process that locates stored information and returns it to consciousness? A. retrieval B. storage C. encoding D. interference _________ 14. Sad feelings that trigger memories of another sad time are an example of A. state-dependent memory. B. context-dependent memory. C. echoic memory. D. sensory memory. _________ 15. Five years ago, you read the famous book, The Seven Deadly Sins. When asked to write down the list of seven sins mentioned in the book, it is very difficult. If given a list of 20 sins that include the seven sins mentioned in the book, it is much easier to pick them out and write them down. This exercise illustrates the difference between A. B. C. D. short-term memory and long-term memory recall and recognition mechanical rehearsal and elaborative rehearsal implicit memory and semantic memory 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. A C D B C C D D B B D C A A B