Chapter_26_Reading_Guiderevised
advertisement

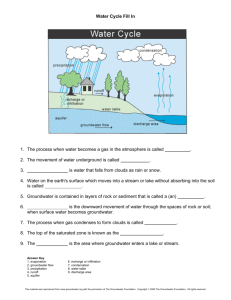
Name: ___________________ Introduction: pg. 497 1. All the fresh water that is not locked up in glaciers makes up ___________________________ of the water on earth. 2. Surface fresh water does what 2 things? a. b. 3. Only water supply that is safe for drinking without being treated? ___________ __________ 4. Ground water is _________ times greater than all surface fresh water supplies. 5. How many gallons of ground water are pumped each day? _______________________ 6. Ground water makes up _______ % of the nations drinking water. 26.1 Watersheds and Rivers pp.502-504 15. How is a river different than a lake? 16. Define what a drainage basin, or watershed is Draw a side view of a watershed 17. Use a line and arrow to place each term below in Fig. 26-6 mouth meander decreasing velocity headwaters cut bank riffle 26.1 Stream Features pp.505-506 18. Use a line and arrow to show the two best locations on this stretch of river to locate a mill, or turbine to generate power. 19. Explain why rivers channels meander. 21. What is the time delay between peek rainfall and peek discharge rate. “Time” is in hours. _______________ 22. Why is there a lag time between increased rainfall and increased stream discharge? 23. A rainfall increase of 3cm/hr results in a stream discharge increase of _________ cubic meters / second? 24. What practical value is there in gauging stream discharge rates? *** Complete Lab 46 – Stream Discharge Rate *** 26.1 Floodplains pg.507 25. How do floodplains form? 26. How many former river channels are in the floodplain above? ___________ 26.1 Stages Of River Development pg.507-509 27. What life stage does a river form a broad flood plain? ______________________________ 26.1 Stages Of River Development pg.507-509 28. List the main features and developments of a river next to the stages it goes through. Make sure you have at least three characteristics / features listed for each stage of development. earth math pg.509 – show your work 1. 26.2 Groundwater pp.509-519 Groundwater Recharge and the Water Table pp.509-510 29. What is the difference between infiltration and seepage? 30. What is recharge and how does it occur 31. The Water Table marks the top of which zone? _______________________________________ 32. Why does the Water Tables depth below ground vary depending on the season? Groundwater Flow pp.510-511 33. What causes groundwater to flow? ______________________________________ 34. What direction does groundwater always flow? _________________________________________________ 35. Where does groundwater eventually exit to the surface? ___________________________________________ 36. How do streams keep flowing even during dry, low precipitation times of the year? 37. Why doesn’t all groundwater travel at the same speed? 38. How does soil porosity affect the rate at which groundwater flows? *** Complete Lab. On Soil Porosity and Soil Permeability *** -- Lab is a separate handout – Aquifers and Groundwater Discharge pp.511-513 39. For each term in Fig. 26-13 below, give its definition / function. Do this to the side and below the image. 40. Explain how the well above could be an artesian well. 41. Explain what makes the aquifer above a confined aquifer. Groundwater Pollution pg.514 42. Below in Fig. 26-16 are major sources of pollution that can get into the groundwater. Think of things you have seen occur that could eventually impact our groundwater here in Des Plains and list them below. 43. Why is polluted groundwater much more difficult to try and clean up than polluted surface water? Career Connections Hydrogeologist pg.515 44. List at least 7 things a hydrogeologist would be called on to do. 45. How could you get a job as a hydrogeologist and who might you work for? *** Complete Chapter Summary and Chapter Review as assigned in class ***