Cell Lab 1 - Kirchner-WHS
advertisement

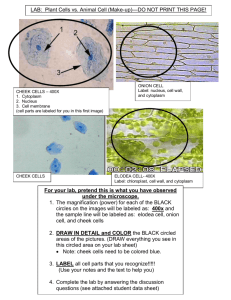
Cell Lab In this lab, you will observe various organisms ranging from single cellular organisms to the individual cells of multi-cellular organisms to identify the uniformity of cellular structures related to life functions. Cell Lab 1 Observation of Cork Cells Materials Cork, Microscope, Microscope Slide, Razor Procedure 1. Use the razor to shave some cork onto a microscope slide. Cutting off a piece of cork will not provide a thin enough specimen. 2. View the cork cells on low power. Center a group of cork cells in field of vision. 3. View the cork cells on medium power. Only use the fine adjustment knob. If needed, center cells in field of view. 4. Use colored pencils to draw what you see. Label your drawing. Labels should include the name of the specimen, magnification level, and cell parts that can be seen. 5. Observe cork cells on high power. Only use the fine adjustment knob. As you focus through the group of cells you will see different layers of cells. Questions What is the total magnification of the microscope on the following objectives? _____Low _____Medium _____High Who named the cell? _______________ What did he name it after?___________________________________________ When looking at cork cells, what cell part are you actually seeing?____________ Circle the unit of measurement that would be the most accurate in measuring cells. Meter Centimeter Millimeter Micrometer Cell Lab 2 Observation of Plant Cells Materials Elodea, Forceps, Microscope, Microscope Slide, Onion, Razor Onion Cells Procedure 1. Using a razor and forceps, remove a small piece of ONE LAYER of onion skin off of an onion and place it on a microscope slide. Avoid wrinkling the specimen. 2. View the onion cells on low power. Center the group of onion cells in field of vision. 3. View the onion cells on medium power. Only use the fine adjustment knob. If needed, center cells in field of view. 4. Use colored pencils to draw what you see. Label your drawing. Labels should include the name of the specimen, magnification level, and cell parts that can be seen. 5. Observe onion cells on high power. Only use the fine adjustment knob. As you focus through the group of cells you might see different layers of cells. Elodea Cells Procedure 1. Using forceps, tear off ONE leaf from an elodea plant and place it on a microscope slide. 2. View the leaf on low power. 3. View the elodea leaf on medium power. 4. Use colored pencils to draw what you see. Label your drawing. Labels should include the name of the specimen, magnification level, and cell parts that can be seen. 5. Observe the elodea leaf on high power. Questions 1. Who determined that all plants are composed of cells? ____________________ 2. What pigment gives the plant cells a green color? ____________________ 3. What are the green organelles seen in the elodea leaves called? ____________________ 4. What is the name of the jellylike fluid that surrounds the organelles? ____________________ 5. Why are the organelles from question 3 seen in the elodea plant but not in the onion? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Cell Lab 3 Observation of Animal Cells Materials Cover Slip, Crystal Violet Stain, Microscope, Microscope Slide, Paper Towel, Pipette, Toothpick Procedure 1. Use a toothpick to rub the inside of your cheek for 5-10 seconds. 2. Rub the end of the toothpick in the CENTER of a microscope slide. 3. Place a SMALL drop of crystal violet on the area of the slide that was rubbed by the toothpick. 4. Touch the edge of a paper towel to the stain to soak up the stain. Repeat this process until most of the stain is removed. 5. Using a pipette, place 1 drop of water on the preparation. 6. Place a cover slip on the slide. 7. View the cheek cells on lower power. Center a group of cheek cell in the field of vision. 8. View the cheek cells on medium power. If needed, center cells in the field of view. 9. Use colored pencils to draw what you see. Label your drawing. Labels should include the name of the specimen, magnification level, and cell parts that can be seen. 10. Observe cheek cells on high power. Questions 1. Who determined that all animals are composed of cells? ____________________ 2. Some cells have a darker stained area in the middle of the cell. What is the name of this organelle? Hint: Controls Cell Activities. ____________________ 3. What is the thin structure that surrounds the cheek cell? ____________________ 4. What cell part does the plant cell have that the animal cell does not? ____________________ 5. In the plants cells you observed, all the cells had a similar shape. The cheek cells were more irregular in shape. Explain why plant cells have a more definite shape than animal cells. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Cell Lab 4 Observation of Protist Cells Materials Cover Slip, Microscope, Microscope Slide, Pipette, Prepared Protist Slides, Protist Specimens Procedure 1. Using a pipette, place 2 drops of water from the euglena jar on a microscope slide. 2. Cover the preparation with a cover slip. 3. Observe the euglena on low power. 4. Observe the euglena on medium power. 5. Use colored pencils to draw what you see. Label your drawing. Labels should include the name of the specimen, magnification level, and cell parts that can be seen. 6. Observe the euglena on high power. 7. Repeat steps 1-6 using paramecium. 8. Repeat steps 1-6 using amoeba. Obtain your drops from the bottom of the jar. If you cannot find an amoeba, use the prepared slides. Questions 1. Euglena move with a whip-like extension. What is the extension called?_____________________ 2. A paramecium moves with short, hair-like extensions. What are they called?__________________ 3. What pigment gives euglena its color? _________________________ 4. Protists have membrane-bound organelles. What is their cell type?_________________________ 5. How does an amoeba move? __________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Cell Lab 5 Observation of Bacteria Cells Materials Microscope, Prepared Bacteria Slides Procedure 1. Choose either a bacillus, coccus, or spirillum slide and observe it on low power. 2. Observe the slide on medium power. 3. Observe the slide on high power. 4. Use colored pencils to draw what you see. Label your drawing. Labels should include the name of the specimen, magnification level, and cell parts that can be seen. 5. Repeat steps 1-4 for the other 2 slides. Questions Match the bacteria with its shape. A. Spiral B. Rod-shaped C. Spherical _____1. Bacillus _____2. Coccus _____3. Spirillum 4. Bacteria do not have membrane-bound organelles. What is their cell type?___________________ 5. Bacteria cells are larger than most other cells. TRUE FALSE