Cell Comparisons
advertisement

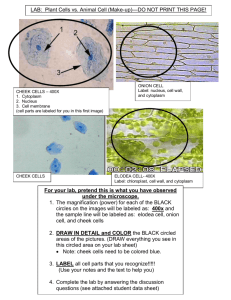
Name: ___________________________ Block: ________ Date: __________ Bio A – Cell Comparison Lab (50 points) Introduction: Ever since the first compound microscope was invented and used in the late 1500s, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of living things. After hundreds of years of research, the cell theory was developed, which in part stated that the cell is the structural and functional unit of living things. All cells contain the same basic structures, including a cell membrane, cytoplasm and DNA; however, only eukaryotic cells contain nucleus and other structures termed “organelles” to carry out cell functions. These types of cells can be classified further by the structures that they have into plant and animal cells, which have some similarities and difference due to their varied life functions. For example, plants contain thick cell walls and chloroplasts that are green and make food for the plant You will investigate the structures of 2 typical plant cells, the onion and Elodea plant, 1 animal cell, a human cheek cell, and 1 bacterial cell to compare and contrast them. Objective: To use the microscope to correctly compare, contrast, identify and explain similarities and differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Materials: Microscope Methylene blue Toothpicks Slides & Coverslips Yogurt Pipette Water Onion Colored pencils Iodine Elodea (Anacharis) Procedure: REMEMBER: Turn on your microscope and make sure that it is in low power. Clean the microscope using lens paper if it is dirty and difficult to see. Keep the diaphragm entirely open and change it if needed as you view the slides. Make sure that the stage is in the lowest position before starting. ALWAYS focus the slide under the lowest power first Human Cheek Cell 1. Use a toothpick to gently scrape some cells from the internal lining of your mouth (cheek). You will need to scrape for about 30 seconds to get enough cells. 2. Smear the toothpick on your slide to spread out the cells and saliva. 3. Add 1 drop of methylene blue to your slide. Discard the toothpick after. Place a coverslip on it on an angle to complete the wet mount. 4. Observe, draw, and label the basic structures of the cheek cells. Onion 1. Carefully peel off the thin inner layer of the onion section and place it on the slide. Add 1 drop of iodine to the onion. 2. Use a toothpick to smooth it out if needed. Then place the coverslip on the slide on an angle to avoid air bubbles. 3. Observe, draw, and label the basic structures of the onion cells. Elodea 1. Tear off 1 young leaf from the plant. 2. Make a wet mount by only using 1 drop of water (no stain needed). Cover it with a coverslip. 3. Observe, draw, and label the basic structures of the Elodea cells. Yogurt Bacteria 1. Place a tiny dab of yogurt on a slide. Make a wet mount by adding 1 drop of water and placing a coverslip on it on an angle. 2. Observe, draw, and label the basic structures of the bacterial cells. For all 4 examples, use the circles given to: - Draw the cell(s) to scale (0.5 points per) - Give it a title (example: “Onion Cell, Low Power”) (0.5 points per) - Provide a total magnification (0.5 points per) - Label all visible parts in pencil (1 point per) - Color each diagram using colored pencils (0.5 points per) 1. Title: Title: Lowest Magnification: Highest Magnification: 2. 3. 4. Title: Title: Lowest Magnification: Highest Magnification: Title: Title: Lowest Magnification: Highest Magnification: Title: Title: Lowest Magnification: Highest Magnification: Data Table 1: List the cell parts that were visible for each cell type (1 point per box) Cell Type Structures Observed Human Cheek Cells Onion Cells Elodea (Anacharis) Cells Yogurt Bacteria Directions: Answer the following analysis questions in complete sentences. 1. Why are stains such as methylene blue and iodine used when observing cells under a microscope? (1 point) Why were they not used for the Elodea leaf? (1 point) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. How does the structure (shape) of your cheek cells compare to that of the onion cells? (1 point) Explain why they are differently shaped (i.e. which structure(s) is/are responsible for this?). (1 point) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. If you were given a slide containing living cells of an unknown organism, how would you identify the cells as either plant or animal cells? (2 points) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Describe the shape and size of the yogurt bacteria. How do they differ from the other organisms viewed? (2 points) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. The mouth is the first site of chemical digestion in a human. Your saliva starts the process of breaking down the food that you eat. Keeping this in mind, what organelle do you think would be numerous inside the cells of your mouth? (1 point) Explain why. (Hint: this organelle was not seen in this lab.) (1 point) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. A. What structures (name 2) are found within the cells of eukaryotes that are NOT found within prokaryotes? (1 point) Of the cells observed which are classified as prokaryotes, and which are classified as eukaryotes? (2 points). __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ B. What other structures (name 4) might you find in prokaryotes and eukaryotes that you didn’t observe in this lab? (2 points) Why would you not see them in the lab? (1 point) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. How is the structure and organization of prokaryotic cells different from eukaryotic cells? How are they similar? Using the Venn diagram note at least 3 differences (3 pieces of information for each circle), 2 similarities in the 2 circle overlaps (any of them), and 1 similarity between all three (in the center) about how these 3 cell types are both similar and different. (6 points) Plant Cells Animal Cells Prokaryotic Cells