SNC 1D
advertisement
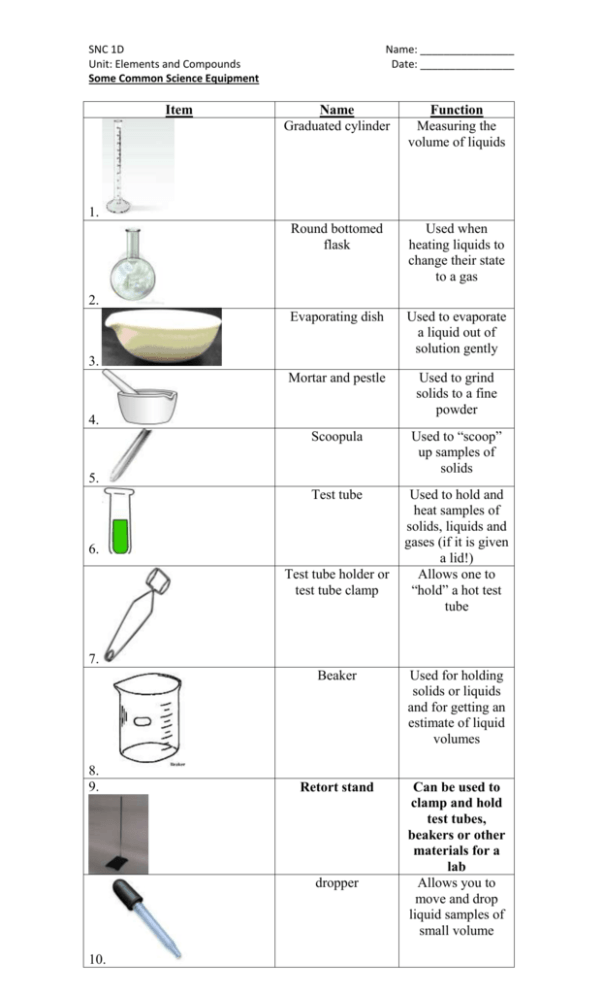
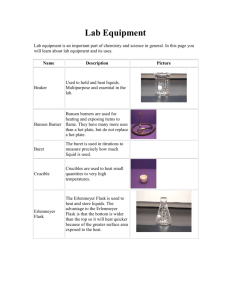
SNC 1D Unit: Elements and Compounds Some Common Science Equipment Item Name: ________________ Date: ________________ Name Graduated cylinder Function Measuring the volume of liquids Round bottomed flask Used when heating liquids to change their state to a gas Evaporating dish Used to evaporate a liquid out of solution gently Mortar and pestle Used to grind solids to a fine powder Scoopula Used to “scoop” up samples of solids Test tube Used to hold and heat samples of solids, liquids and gases (if it is given a lid!) Allows one to “hold” a hot test tube 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Test tube holder or test tube clamp 7. 8. 9. Beaker Used for holding solids or liquids and for getting an estimate of liquid volumes Retort stand Can be used to clamp and hold test tubes, beakers or other materials for a lab Allows you to move and drop liquid samples of small volume dropper 10. Item Name Microscope slide Function Used to mount a specimen on to view it under a microscope Tweezers or forceps Used to pick up small items or in a dissection to move tissue Test tube rack Holds several test tubes upright for use Erlenmeyer flask Narrow at the top to prevent liquids from splashing during heating; often used instead of a beaker Used to plug the top of a test tube or a flask 11. 12. 13. 14. Rubber stoppers 15. Ring clamp 16. Funnel 17. Cover glass 18. Specimen jar 19. 20. 2 pronged clamp Clamps onto a retort stand to allow other things to be added to a set up Can help transferring a liquid from a large to a small container; can help to filter mixtures and separate out undissolved bits Prevents evaporation by covering a container of liquid Glass container for storing samples Used to hold glassware in place when it is attached to a retort stand Lab Safety Examine the diagram below. Use the information within the diagram to fill in the table. A Description of an Unsafe Name of the Person What Should Be Done Practice for the Laboratory Involved Instead http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/safety.gif Safety Symbols and MSDS Information Read over page xvii near the front of the textbook. Two types of safety symbols are discussed: (1) symbols used in your textbook (ON Science 9 Safety Symbols) and (2) WHMIS Symbols. You need to be able to recognize all of these and understand what each one means. A Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) contains information about the composition and properties of a chemical substance as well as steps for handling and storing it safely. A MSDS sheet for a particular substance has to be rewritten every 3 years. You may run across two "sizes" of MSDS Forms in Canada. The more common one is the 9 Section Form. There is also a newer 16 Section Form. The 16 sections in the newer MSDS forms are; 1. Product and Supplier Information 2. Hazards Identification 3. Composition / Information on Ingredients 4. First Aid Measures 5. Fire & Explosion 6. Accidental Release Measures 7. Handling & Storage 8. Exposure Controls / Personal Protection 9. Physical & Chemical Properties 10. Stability and Reactivity 11. Toxicological Information 12. Ecological Information 13. Disposal Considerations 14. Transportation 15. Regulatory Information 16. Other Here is an sample of the more common 9 section MSDS form. http://www.firesafetraining.com/WHMISMSDS.html Do the “Instant Practice – Safety Symbols” question at the bottom of page xvii in the textbook. Do questions #1, 2, 3 at the bottom of page xvii in the textbook. Practice recognizing what each of the symbols from page xvii mean.