Form 2 - St Francis' Canossian College
advertisement
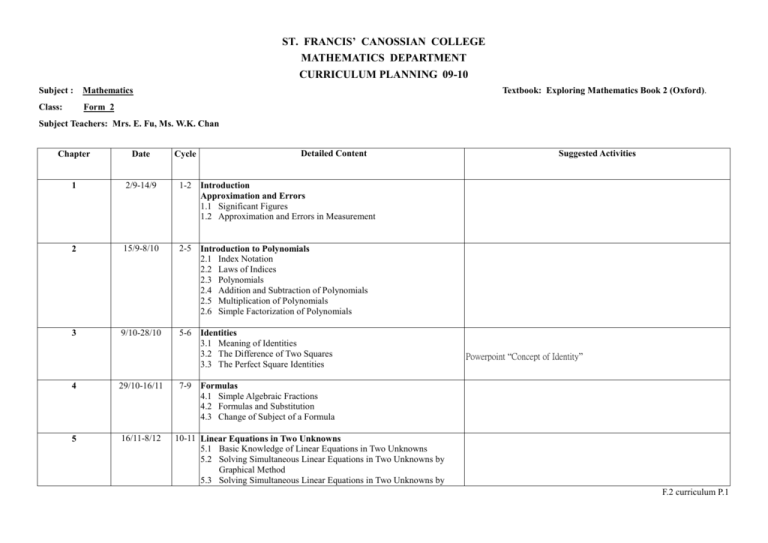
ST. FRANCIS’ CANOSSIAN COLLEGE MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT CURRICULUM PLANNING 09-10 Subject : Mathematics Class: Form 2 Textbook: Exploring Mathematics Book 2 (Oxford). Subject Teachers: Mrs. E. Fu, Ms. W.K. Chan Detailed Content Chapter Date Cycle 1 2/9-14/9 1-2 Introduction Approximation and Errors 1.1 Significant Figures 1.2 Approximation and Errors in Measurement 2 15/9-8/10 2-5 Introduction to Polynomials 2.1 Index Notation 2.2 Laws of Indices 2.3 Polynomials 2.4 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials 2.5 Multiplication of Polynomials 2.6 Simple Factorization of Polynomials 3 9/10-28/10 5-6 Identities 3.1 Meaning of Identities 3.2 The Difference of Two Squares 3.3 The Perfect Square Identities 4 29/10-16/11 5 16/11-8/12 7-9 Suggested Activities Powerpoint “Concept of Identity” Formulas 4.1 Simple Algebraic Fractions 4.2 Formulas and Substitution 4.3 Change of Subject of a Formula 10-11 Linear Equations in Two Unknowns 5.1 Basic Knowledge of Linear Equations in Two Unknowns 5.2 Solving Simultaneous Linear Equations in Two Unknowns by Graphical Method 5.3 Solving Simultaneous Linear Equations in Two Unknowns by F.2 curriculum P.1 6 9/12-21/12 22/12-3/1 4/1 – 15/1 16/1-20/1 8 21/1-1/2 9 2/2-22/2 10 12/2-20/2 23/2-9/3 11 10/3-23/3 Algebraic Method 5.4 Applications of Simultaneous Linear Equations in Two Unknowns 11-14 Rate and Ratio 6.1 Rate 6.2 Ratio X’mas holiday Mid-term Exam 6.2 Applications of Ratio Ask students to find some scale drawings from books, newspapers or internet, and then calculate the actual length of the object from the scale drawing. 14-16 Angles in Triangles and Polygons 8.1 Angles and Sides of a Triangle 8.2 Angles of a Polygon 8.2 Basic Constructions 16-17 Introduction to Deductive Geometry 9.1 Intuitive and Deductive Approaches in Studying Geometry 9.2 Deductive Approach to Properties of Geometric Figures Lunar New Year Holiday 17-19 Pythagoras’ Theorem 10.1 Square Roots 10.2 Pythagoras’ Theorem “周髀算經” (Civic Education) 10.3 Application of Pythagoras’ Theorem 10.4 Converse of Pythagoras’ Theorem 10.5 Irrational Numbers 19-20 Trigonometric Ratios 11.1 Introduction to Trigonometric Ratios 11.2 Introduction to Trigonometric Ratios 11. 3 Applications of Trigonometric Ratios F.2 curriculum P.2 12 24/3-1/4 13 2/4-10/4 11/4-19/4 20/4-6/5 7 10/5-2/6 21-22 Trigonometric Relations 12.1 Trigonometric Ratios of Some Special Angles 12.2 Finding Trigonometric Ratios Using Pythagoras’ Theorem Easter Holiday 12.3 Introduction to Trigonometric Identities 23-25 Area and Volume (II) 13.1 Circles 13.2 Arcs and Sectors 13.3 Cylinders 25-27 Handling Continuous Data 7.1 Organization of continuous Data 7.2 Presentation of Continuous Data 7.3 Cumulative Frequency 7.4 Misuses of Statistical Diagrams Class Activity: Area of Circle Powerpoint “Histogram” Powerpoint “Frequency polygon” Powerpoint “Cumulative frequency” Powerpoint “Percentile” Powerpoint “Abuses of Statistics” Project : Collect data from newspaper, magazines or internet about Environmental Pollution in Hong Kong (Civic Education) 2/6-12/6 Final Examination F.2 curriculum P.3