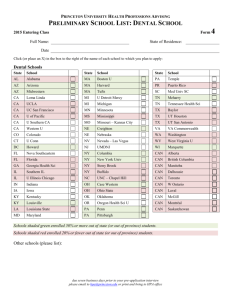
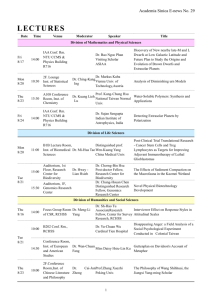
八、SCI Essential Science Indicators HOT - 图书馆
advertisement

图书情报专题研究 最新学科研究热点与前沿 2011 年第 2 期 西北工业大学图书馆 2011 年 6 月 前 言 《图书情报专题研究》的宗旨是为我校师生开展学术研究提供有价值的参 考信息。此项工作由图书馆信息咨询与情报研究部承担,根据学校所购买的数字 资源,通过分析其深层次的功能,从数据库中组织整理出了与我校学科领域相关 的最新学科热点研究论文、最新研究前沿及最新国际会议信息等,以期能对我校 师生开展学术研究、项目立项、开题等学术研究活动提供帮助。 本期,我们收集整理了如下八个方面的热点文献和前沿信息: 1.快速突破研究论文(Fast Breaking Papers),由汤姆森科技公司统计的 22 个学科全球引用率最高的高被引论文列表,每两个月按照当前引文数据进行更 新,报道在过去两个月内每个领域中引用增长率最高的一篇论文。 2.最新研究前沿(Emerging Research Fronts),由汤姆森科技公司统计的 22 个学科的最新研究领域,一个新的研究领域是由那些并没有在之前任何领域 出现过的核心论文组成,所列举出来的研究领域都是取决于其所包含的这些核心 论文的数量以及相关的引证率。 3. Elsevier Science Direct Top 25,Elsevier 数据库下载最多的 25 篇论文。 4. IEL Top20,IEL 数据库下载最多的 20 篇论文。 5. ACM 最新会议。根据 ACM 主页所提供的最新会议信息整理所得,可 供研究者参考未来将要召开的会议内容等信息。 6. AIAA 最新会议,由 AIAA 主站提供的最新会议信息,以供研究者参考 所用。 7.IEEE 最新会议,由 IEEE 主站提供的最新会议信息,供相关研究者参考 使用。 8. SCI Essential Science Indicators HOT PAPERS,SCI Essential Science Indicators 提供的最近两年的热点文章,其排名根据文章的被引频次。 如果您对我们的栏目设置、内容编排、出版方式等有好的意见和建议,欢 迎与我们联系,我们将积极采纳,使这份电子刊物以臻完善 。 图书馆 2011 年 6 月 目 录 一、快速突破研究论文(来源:http://www.sciencewatch.com/) .......1 二、最新研究前沿(来源:http://www.sciencewatch.com/) ...............3 三、Elsevier Science Direct Top 25 (工程类) ...........................................4 (来源:http://www.sciencedirect.com/) ...............................................4 四、IEL Top20(来源:http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/) ............................15 五、ACM 最新会议(来源:http://www.acm.org/) ..........................23 六、AIAA 最新会议(来源:http://www.aiaa.org/) ..........................24 七、IEEE 最新会议(来源:http://www.ieee.org/index.html) ..........27 八、SCI Essential Science Indicators HOT PAPERS(材料科学) .....30 一、快速突破研究论文(来源:http://www.sciencewatch.com/) 1. 学科领域: 生物学和生物化学(Biology & Biochemistry) 题目:Melatonin, cardiolipin and mitochondrial bioenergetics in health and disease 作者: Paradies, G;Petrosillo, G;Paradies, V;Reiter, RJ;Ruggiero, FM 出处: J PINEAL RES Volume: 48, Issue: 4, Page: 297-310, Year: MAY 2010 作者单位:* Via E Orabona 4, I-70126 Bari, Italy. * Univ Bari, Dept Biochem & Mol Biol, Bari, Italy. * Univ Bari, CNR, Inst Biomebranes & Bioenerget, Bari, Italy. * Univ Texas Hlth Sci Ctr San Antonio, Dept Cellular & Struct Biol, San Antonio, TX 78229 USA. 2. 学科领域: 化学(Chemistry) 题目: Target-Responsive Structural Switching for Nucleic Acid-Based Sensors 作者: Li, D;Song, SP;Fan, CH 出处: ACCOUNT CHEM RES Volume: 43, Issue: 5, Page: 631-641, Year: MAY 2010 作者单位:* Chinese Acad Sci, Shanghai Inst Appl Phys, Phys Biol Lab, Shanghai 201800, Peoples R China. * Chinese Acad Sci, Shanghai Inst Appl Phys, Phys Biol Lab, Shanghai 201800, Peoples R China. 3. 学科领域: 计算机科学(Computer Science) 题目: Representation of a Stochastic Traffic Bound 作者: Li, M;Zhao, W 出处: IEEE TRANS PARALL DISTRIB SYS Volume: 21, Issue: 9, Page: 1368-1372, Year: SEP 2010 作者单位:* E China Normal Univ, Sch Informat Sci & Technol, Shanghai 200241, Peoples R China. * E China Normal Univ, Sch Informat Sci & Technol, Shanghai 200241, Peoples R China. * Univ Macau, Taipa, Macau Sar, Peoples R China. 4. 学科领域: 经济和商业(Economics & Business) 题 目 :INTERNATIONAL SURVEY ON WILLINGNESS-TO-PAY (WTP) FOR ONE ADDITIONAL QALY GAINED: WHAT IS THE THRESHOLD OF COST EFFECTIVENESS? 作者: Shiroiwa, T;Sung, YK;Fukuda, T;Lang, HC;Bae, SC;Tsutani, K 出处: HEALTH ECONOMICS Volume: 19, Issue: 4, Page: 422-437, Year: APR 2010 作者单位:* Univ Tokyo, Dept Drug Policy & Management, Grad Sch Pharmaceut Sci, Bunkyo Ku, 7-3-1 Hongo, Tokyo 1130033, Japan. 1 * Univ Tokyo, Dept Drug Policy & Management, Grad Sch Pharmaceut Sci, Bunkyo Ku, Tokyo 1130033, Japan. * Hanyang Univ, Dept Rheumatol, Hosp Rheumat Dis, Seoul 133791, South Korea. * Univ Tokyo, Dept Hlth Econ & Epidemiol Res, Sch Publ Hlth, Tokyo 1130033, Japan. * Natl Yang Ming Univ, Inst Hosp & Hlth Care Adm, Sch Med, Taipei 112, Taiwan. 5.学科领域:环境生态学(Environment/Ecology) 题目: Environmental Life Cycle Comparison of Algae to Other Bioenergy Feedstocks 作者: Clarens, AF;Resurreccion, EP;White, MA;Colosi, LM 出处: ENVIRON SCI TECHNOL Volume: 44, Issue: 5, Page: 1813-1819, Year: MAR 1 2010 作者单位:* Univ Virginia, McIntire Sch Commerce, Charlottesville, VA 22904 USA. * Univ Virginia, McIntire Sch Commerce, Charlottesville, VA 22904 USA. 6.学科领域: 材料科学(Materials Science) 题目: Eccentric connectivity polynomials of fullerenes 作者: Ghorbani, M;Ashrafi, AR;Hemmasi, M 出处: OPTOELECTRON ADV MATER-RAPID Volume: 3, Issue: 12, Page: 1306-1308, Year: DEC 2009 作者单位:* Shahid Rajaei Teacher Training Univ, Fac Sci, Dept Math, Tehran 16785136, Iran. * Shahid Rajaei Teacher Training Univ, Fac Sci, Dept Math, Tehran 16785136, Iran. * Univ Kashan, Inst Nanosci & Nanotechnol, Kashan, Iran. 7. 学科领域:数学(Mathematics) 题目: AN ASYMPTOTIC ANALYSIS OF THE MEAN FIRST PASSAGE TIME FOR NARROW ESCAPE PROBLEMS: PART II: THE SPHERE 作者: Cheviakov, AF;Ward, MJ;Straube, R 出处: MULTISCALE MODEL SIMUL Volume: 8, Issue: 3, Page: 836-870, Year: 2010 作者单位:* Univ Saskatchewan, Dept Math & Stat, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5E6, Canada. * Univ Saskatchewan, Dept Math & Stat, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5E6, Canada. * Univ British Columbia, Dept Math, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z2, Canada. * Max Planck Inst Dynam Complex Tech Syst, D-39106 Magdeburg, Germany. 8. 学科领域:微生物学(Microbiology) 题目: Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 beta Modulates Host Innate Immune Response by Antagonizing IRF3 Activation 作者: Beura, LK;Sarkar, SN;Kwon, B;Subramaniam, S;Jones, C;Pattnaik, AK;Osorio, FA 出处: J VIROL Volume: 84, Issue: 3, Page: 1574-1584, Year: FEB 2010 作者单位:* Univ Pittsburgh, Inst Canc, Mol Virol Program, HCC 1-8,5117 Ctr Ave, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 USA. * Univ Pittsburgh, Inst Canc, Mol Virol Program, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 USA. * Univ Pittsburgh, Sch Med, Dept Microbiol & Mol Genet, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 USA. 2 * Univ Nebraska, Nebraska Ctr Virol, Lincoln, NE 68583 USA. * Univ Nebraska, Sch Vet & Biomed Sci, Lincoln, NE 68583 USA. 9. 学科领域:物理学(Physics) 题目: REVIEW OF PARTICLE PHYSICS 作者: Nakamura, K, et al. 出处: J PHYS G-NUCL PARTICLE PHYS Volume: 37, Issue: 7A, Page: art., Year: no.-075021 JUL 2010 作者单位:* Univ Tokyo, IPMU, Kashiwa, Chiba 2778583, Japan. * Univ Tokyo, IPMU, Kashiwa, Chiba 2778583, Japan. * High Energy Accelerator Res Org, KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3050801, Japan. 10. 学科领域:社会科学(Social Sciences, general) 题目: A National Strategy To Put Accountable Care Into Practice 作者: McClellan, M;McKethan, AN;Lewis, JL;Roski, J;Fisher, ES 出处: HEALTH AFFAIR Volume: 29, Issue: 5, Page: 982-990, Year: MAY-JUN 2010 作者单位:* Brookings Inst, Engelberg Ctr Hlth Care Reform, Washington, DC 20036 USA. * Brookings Inst, Engelberg Ctr Hlth Care Reform, Washington, DC 20036 USA. * Dartmouth Inst Hlth Policy & Clin Practice, Ctr Hlth Policy Res, Hanover, NH USA. * Dartmouth Med Sch, Hanover, NH USA. 二、最新研究前沿(来源:http://www.sciencewatch.com/) 1.学科领域:Biology & Biochemistry 研 究 前 沿 名 称 : Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells; Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modified; Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Akt Dramatically Repair Infarcted Myocardium; Akt-Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Cardiac Protection; Mesenchymal Stem Cell Homing 2. 学科领域:Chemistry 研 究 前 沿 名 称 : Porous Metal-Organic Framework [Zn4o(Ntb)(2)]; Guest-Induced Drastic Single-Crystal-To-Single-Crystal Transformations; Metal-Organic Porous Solid; Highly Porous; Redox Active Pillared Bilayer Open Framework 3. 学科领域:Computer Science 研究前沿名称:Molecular Dynamics Simulations; Amber Biomolecular Simulation Programs; Multiple Amber Force Fields; All-Atom Equilibrium Ensemble Simulations; Automatic Atom Type 3 4. 学科领域:Economics & Business 研 究 前 沿 名 称 : Monetary Incentives; Social Image; Image Motivation; Wage Inequality; Performance Pay 5. 学科前沿:Engineering 研究前沿名称:Hyperspectral Image Classification; Hyperspectral Data; Svms; Hyperspectral Image Data; Hyperspectral Images Using Minimum Spanning Forest Grown; Nearest Neighbor Classification 6. 学科领域:Environment/ Ecology 研 究 前 沿 名 称 : Social-Ecological System Resilience; Social-Ecological Resilience; Urban Environmental Education; Resilience Systems Framework; Exploring Learning Opportunities 7. 学科领域: Materials & Science 研究前沿名称:Crystalline Diblock Conjugated Copolymers; Crystalline Random Conjugated Copolymers; All-Conjugated Block Copolymers; Block Copolymer Templates; Bulk Heterojunction Solar Cells Using Block Copoly(3-Alkylthiophene)S 8. 学科领域:Mathematics 研究前沿名称:Multidimensional Partial Differential Equations; Separated Representations; Applications; Non Incremental Strategies; Kinetic Theory Modeling 9. 学科领域:Microbiology 研究前沿名称:Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1; Human Immunodeficiency Virus Transfer; Membrane Nanotubes Physically Connect T Cells; Virological Synapse-Mediated Spread; Biofilm-Like Extracellular Viral Assemblies Mediate Htlv-1 Cell-To-Cell Transmission 10.学科领域:Physics 研究前沿名称:Charged Lifshitz Black Holes; Analytic Lifshitz Black Holes; Higher Dimensions 三、Elsevier Science Direct Top 25 (工程类) (来源:http://www.sciencedirect.com/) 1. 题名:Carbon nanotube-polymer composites: Chemistry, processing, mechanical and electrical properties • Review article 出处:Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 35, Issue 3, March 2010, Pages 357-401 作者:Spitalsky, Z.; Tasis, D.; Papagelis, K.; Galiotis, C. 摘要:Carbon nanotubes have long been recognized as the stiffest and strongest man-made 4 material known to date. In addition, their high electrical conductivity has roused interest in the area of electrical appliances and communication related applications. However, due to their miniscule size, the excellent properties of these nanostructures can only be exploited if they are homogeneously embedded into light-weight matrices as those offered by a whole series of engineering polymers. We review the present state of polymer nanocomposites research in which the fillers are carbon nanotubes. In order to enhance their chemical affinity to engineering polymer matrices, chemical modification of the graphitic sidewalls and tips is necessary. In this review, an extended account of the various chemical strategies for grafting polymers onto carbon nanotubes and the manufacturing of carbon nanotube/polymer nanocomposites is given. The mechanical and electrical properties to date of a whole range of nanocomposites of various carbon nanotube contents are also reviewed in an attempt to facilitate progress in this emerging area. 2. 题 名 : Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications • Review article 出处:Biomaterials, Volume 26, Issue 18, June 2005, Pages 3995-4021 作者:Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. 摘要:Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) with appropriate surface chemistry have been widely used experimentally for numerous in vivo applications such as magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement, tissue repair, immunoassay, detoxification of biological fluids, hyperthermia, drug delivery and in cell separation, etc. All these biomedical and bioengineering applications require that these nanoparticles have high magnetization values and size smaller than 100 nm with overall narrow particle size distribution, so that the particles have uniform physical and chemical properties. In addition, these applications need special surface coating of the magnetic particles, which has to be not only non-toxic and biocompatible but also allow a targetable delivery with particle localization in a specific area. To this end, most work in this field has been done in improving the biocompatibility of the materials, but only a few scientific investigations and developments have been carried out in improving the quality of magnetic particles, their size distribution, their shape and surface in addition to characterizing them to get a protocol for the quality control of these particles. Nature of surface coatings and their subsequent geometric arrangement on the nanoparticles determine not only the overall size of the colloid but also play a significant role in biokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles in the body. The types of specific coating, or derivatization, for these nanoparticles depend on the end application and should be chosen by keeping a particular application in mind, whether it be aimed at inflammation response or anti-cancer agents. Magnetic nanoparticles can bind to drugs, proteins, enzymes, antibodies, or nucleotides and can be directed to an organ, tissue, or tumour using an external magnetic field or can be heated in alternating magnetic fields for use in hyperthermia. This review discusses the synthetic chemistry, fluid stabilization and surface modification of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, as well as their use for above biomedical applications. 3. 题名:Replication of homologous optical and hydrophobic features by templating wings of butterflies Morpho menelaus • Article 出处:Optics Communications, Volume 284, Issue 9, May 2011, Pages 2376-2381 作者:Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Hu, X.; Dong, B.; Shi, W.; Xie, Y.; Ye, X. 5 摘要:The revealed “Christmas-tree” nanostructures in the cover and ground scales of the butterfly Morpho menelaus are responsible for the observed iridescent blue color and the diffraction pattern of the wings. The aspect ratio of nanostructures in ground scales is more than 5 times higher than that of Morpho peleides cover scales. Inspired by the butterfly, artificial nanostructures are fabricated successfully by templating the scales imbricating in the wings with low-temperature atomic layer deposition (ALD) methods. Through structural characterizations and optical measurements, we reveal that the hybrid structures inherit not only the morphology of the scales with high fidelity but also the homologous optical features including iridescence and diffraction. Besides, water contact angle measurements on both uncoated and coated wings show hydrophobic results. The integration of bio-templates and ALD methods provide a potential route to fabricate the nanostructures with multi-functional features, which may be especially crucial in the applications of innovative functional optical devices. 4. 题名:TiO"2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena • Review article 出处:Surface Science Reports, Volume 63, Issue 12, December 2008, Pages 515-582 作者:Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X.; Tryk, D.A. 摘要:The field of photocatalysis can be traced back more than 80 years to early observations of the chalking of titania-based paints and to studies of the darkening of metal oxides in contact with organic compounds in sunlight. During the past 20 years, it has become an extremely well researched field due to practical interest in air and water remediation, self-cleaning surfaces, and self-sterilizing surfaces. During the same period, there has also been a strong effort to use photocatalysis for light-assisted production of hydrogen. The fundamental aspects of photocatalysis on the most studied photocatalyst, titania, are still being actively researched and have recently become quite well understood. The mechanisms by which certain types of organic compounds are decomposed completely to carbon dioxide and water, for example, have been delineated. However, certain aspects, such as the photo-induced wetting phenomenon, remain controversial, with some groups maintaining that the effect is a simple one in which organic contaminants are decomposed, while other groups maintain that there are additional effects in which the intrinsic surface properties are modified by light. During the past several years, powerful tools such as surface spectroscopic techniques and scanning probe techniques performed on single crystals in ultra-high vacuum, and ultrafast pulsed laser spectroscopic techniques have been brought to bear on these problems, and new insights have become possible. Quantum chemical calculations have also provided new insights. New materials have recently been developed based on titania, and the sensitivity to visible light has improved. The new information available is staggering, but we hope to offer an overview of some of the recent highlights, as well as to review some of the origins and indicate some possible new directions. 5. 题名:Recent advances in graphene based polymer composites • Review article 出处:Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 35, Issue 11, November 2010, Pages 1350-1375 作者:Kuilla, T.; Bhadra, S.; Yao, D.; Kim, N.H.; Bose, S.; Lee, J.H. 摘要:This paper reviews recent advances in the modification of graphene and the fabrication of graphene-based polymer nanocomposites. Recently, graphene has attracted both academic and industrial interest because it can produce a dramatic improvement in properties at very low filler content. The modification of graphene/graphene oxide and the utilization of these materials in the 6 fabrication of nanocomposites with different polymer matrixes have been explored. Different organic polymers have been used to fabricate graphene filled polymer nanocomposites by a range of methods. In the case of modified graphene-based polymer nanocomposites, the percolation threshold can be achieved at a very lower filler loading. Herein, the structure, preparation and properties of polymer/graphene nanocomposites are discussed in general along with detailed examples drawn from the scientific literature. 6. 题名:Recent developments in cathode materials for lithium ion batteries • Review article 出处:Journal of Power Sources, Volume 195, Issue 4, February 2010, Pages 939-954 作者:Fergus, J.W. 摘要:One of the challenges for improving the performance of lithium ion batteries to meet increasingly demanding requirements for energy storage is the development of suitable cathode materials. Cathode materials must be able to accept and release lithium ions repeatedly (for recharging) and quickly (for high current). Transition metal oxides based on the α-NaFeO2, spinel and olivine structures have shown promise, but improvements are needed to reduce cost and extend effective lifetime. In this paper, recent developments in cathode materials for lithium ion batteries are reviewed. This includes comparison of the performance characteristics of the promising cathode materials and approaches for improving their performances. 7. 题名:Graphene-based polymer nanocomposites • Review article 出处:Polymer, Volume 52, Issue 1, January 2011, Pages 5-25 作者:Potts, J.R.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. 摘要:Graphene-based materials are single- or few-layer platelets that can be produced in bulk quantities by chemical methods. Herein, we present a survey of the literature on polymer nanocomposites with graphene-based fillers including recent work using graphite nanoplatelet fillers. A variety of routes used to produce graphene-based materials are reviewed, along with methods for dispersing these materials in various polymer matrices. We also review the rheological, electrical, mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of these composites, and how each of these composite properties is dependent upon the intrinsic properties of graphene-based materials and their state of dispersion in the matrix. An overview of potential applications for these composites and current challenges in the field are provided for perspective and to potentially guide future progress on the development of these promising materials. 8. 题名:Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide • Article 出处:Carbon, Volume 45, Issue 7, June 2007, Pages 1558-1565 作者:Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. 摘要:Reduction of a colloidal suspension of exfoliated graphene oxide sheets in water with hydrazine hydrate results in their aggregation and subsequent formation of a high-surface-area carbon material which consists of thin graphene-based sheets. The reduced material was characterized by elemental analysis, thermo-gravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and by electrical conductivity measurements. 7 9. 题名:The surface science of titanium dioxide • Review article 出处:Surface Science Reports, Volume 48, Issue 5-8, January 2003, Pages 53-229 作者:Diebold, U. 摘要:Titanium dioxide is the most investigated single-crystalline system in the surface science of metal oxides, and the literature on rutile (1 1 0), (1 0 0), (0 0 1), and anatase surfaces is reviewed. This paper starts with a summary of the wide variety of technical fields where TiO2 is of importance. The bulk structure and bulk defects (as far as relevant to the surface properties) are briefly reviewed. Rules to predict stable oxide surfaces are exemplified on rutile (1 1 0). The surface structure of rutile (1 1 0) is discussed in some detail. Theoretically predicted and experimentally determined relaxations of surface geometries are compared, and defects (step edge orientations, point and line defects, impurities, surface manifestations of crystallographic shear planes—CSPs) are discussed, as well as the image contrast in scanning tunneling microscopy (STM). The controversy about the correct model for the (1×2) reconstruction appears to be settled. Different surface preparation methods, such as reoxidation of reduced crystals, can cause a drastic effect on surface geometries and morphology, and recommendations for preparing different TiO2(1 1 0) surfaces are given. The structure of the TiO2(1 0 0)-(1×1) surface is discussed and the proposed models for the (1×3) reconstruction are critically reviewed. Very recent results on anatase (1 0 0) and (1 0 1) surfaces are included. The electronic structure of stoichiometric TiO2 surfaces is now well understood. Surface defects can be detected with a variety of surface spectroscopies. The vibrational structure is dominated by strong Fuchs–Kliewer phonons, and high-resolution electron energy loss spectra often need to be deconvoluted in order to render useful information about adsorbed molecules. The growth of metals (Li, Na, K, Cs, Ca, Al, Ti, V, Nb, Cr, Mo, Mn, Fe, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au) as well as some metal oxides on TiO2 is reviewed. The tendency to ‘wet’ the overlayer, the growth morphology, the epitaxial relationship, and the strength of the interfacial oxidation/reduction reaction all follow clear trends across the periodic table, with the reactivity of the overlayer metal towards oxygen being the most decisive factor. Alkali atoms form ordered superstructures at low coverages. Recent progress in understanding the surface structure of metals in the ‘strong-metal support interaction’ (SMSI) state is summarized. Literature is reviewed on the adsorption and reaction of a wide variety of inorganic molecules (H2, O2, H2O, CO, CO2, N2, NH3, NOx, sulfur- and halogen-containing molecules, rare gases) as well as organic molecules (carboxylic acids, alcohols, aldehydes and ketones, alkynes, pyridine and its derivates, silanes, methyl halides). The application of TiO2-based systems in photo-active devices is discussed, and the results on UHV-based photocatalytic studies are summarized. The review ends with a brief conclusion and outlook of TiO2-based surface science for the future. 10. 题名:Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation • Review article 出处:Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 34, Issue 7, July 2009, Pages 641-678 作者:Pillai, C.K.S.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. 摘要:Chitin and chitosan (CS) are biopolymers having immense structural possibilities for chemical and mechanical modifications to generate novel properties, functions and applications especially in biomedical area. Despite its huge availability, the utilization of chitin has been 8 restricted by its intractability and insolubility. The fact that chitin is as an effective material for sutures essentially because of its biocompatibility, biodegradability and non-toxicity together with its antimicrobial activity and low immunogenicity, points to immense potential for future development. This review discusses the various attempts reported on solving this problem from the point of view of the chemistry and the structure of these polymers highlighting the drawbacks and advantages of each method and proposes that based on considerations of structure–property relations, it is possible to obtain chitin fibers with improved strength by making use of their nanostructures and/or mesophase properties of chitin. 11. 题名:Carbonaceous nanomaterials for the enhancement of TiO"2 photocatalysis • Review article 出处:Carbon, Volume 49, Issue 3, March 2011, Pages 741-772 作者:Leary, R.; Westwood, A. 摘要:Semiconductor photocatalysis has important applications such as achieving sustainable energy generation and treating environmental pollution. TiO2 has been the most widely-researched photocatalyst, but suffers from low efficiency and narrow light response range. Combining TiO2 with carbonaceous nanomaterials is being increasingly investigated as a means to increase photocatalytic activity, and demonstrations of enhancement are plentiful. This review surveys the literature and highlights recent progress in the development of nanocarbon-TiO2 photocatalysts, covering activated carbon, carbon doping, carbon nanotubes, [60]-fullerenes, graphene, thin layer carbon coating, nanometric carbon black and more recently developed morphologies. Mechanisms of enhancement, synthesis routes and future applications are summarised and discussed. New insight and enhanced photocatalytic activity may be provided by novel nanocarbon-TiO2 systems. Ongoing challenges and possible new directions are outlined. 12. 题名:Graphene and graphite nanoribbons: Morphology, properties, synthesis, defects and applications • Review article 出处:Nano Today, Volume 5, Issue 4, August 2010, Pages 351-372 作者:Terrones, M.; Botello-Mendez, A.R.; Campos-Delgado, J.; Lopez-Urias, F.; Vega-Cantu, Y.I.; Rodriguez-Macias, F.J.; Elias, A.L.; Munoz-Sandoval, E.; Cano-Marquez, A.G.; Charlier, J.C.; Terrones, H. 摘要:Carbon is a unique and very versatile element which is capable of forming different architectures at the nanoscale. Over the last 20 years, new members of the carbon nanostructure family arose, and more are coming. This review provides a brief overview on carbon nanostructures ranging from C60 to graphene, passing through carbon nanotubes. It provides the reader with important definitions in carbon nanoscience and concentrates on novel one- and two-dimensional layered carbon (sp2 hybridized), including graphene and nanoribbons. This account presents the latest advances in their synthesis and characterization, and discusses new perspectives of tailoring their electronic, chemical, mechanical and magnetic properties based on defect control engineering. It is foreseen that some of the structures discussed in the review will have important applications in areas related to electronics, spintronics, composites, medicine and many others. 13. 题名:Fabrication and processing of polymer solar cells: A review of printing and coating 9 techniques • Review article 出处:Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, Volume 93, Issue 4, April 2009, Pages 394-412 作者:Krebs, F.C. 摘要:Polymer solar cells are reviewed in the context of the processing techniques leading to complete devices. A distinction is made between the film-forming techniques that are used currently such as spincoating, doctor blading and casting and the, from a processing point of view, more desirable film-forming techniques such as slot-die coating, gravure coating, knife-over-edge coating, off-set coating, spray coating and printing techniques such as ink jet printing, pad printing and screen printing. The former are used almost exclusively and are not suited for high-volume production whereas the latter are highly suited, but little explored in the context of polymer solar cells. A further distinction is made between printing and coating when a film is formed. The entire process leading to polymer solar cells is broken down into the individual steps and the available techniques and materials for each step are described with focus on the particular advantages and disadvantages associated with each case. 14. 题名:Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials • Review article 出处:Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 32, Issue 8-9, August 2007, Pages 762-798 作者:Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. 摘要:During the past two decades significant advances have been made in the development of biodegradable polymeric materials for biomedical applications. Degradable polymeric biomaterials are preferred candidates for developing therapeutic devices such as temporary prostheses, three-dimensional porous structures as scaffolds for tissue engineering and as controlled/sustained release drug delivery vehicles. Each of these applications demands materials with specific physical, chemical, biological, biomechanical and degradation properties to provide efficient therapy. Consequently, a wide range of natural or synthetic polymers capable of undergoing degradation by hydrolytic or enzymatic route are being investigated for biomedical applications. This review summarizes the main advances published over the last 15 years, outlining the synthesis, biodegradability and biomedical applications of biodegradable synthetic and natural polymers. 15. 题 名 : A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites • Article 出处:Composites Science and Technology, Volume 63, Issue 15, November 2003, Pages 2223-2253 作者:Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. 摘要:Electrospinning has been recognized as an efficient technique for the fabrication of polymer nanofibers. Various polymers have been successfully electrospun into ultrafine fibers in recent years mostly in solvent solution and some in melt form. Potential applications based on such fibers specifically their use as reinforcement in nanocomposite development have been realized. In this paper, a comprehensive review is presented on the researches and developments related to electrospun polymer nanofibers including processing, structure and property characterization, applications, and modeling and simulations. Information of those polymers together with their processing conditions for electrospinning of ultrafine fibers has been summarized in the paper. Other issues regarding the technology limitations, research challenges, and future trends are also 10 discussed. 16. 题名:Transparent conductors as solar energy materials: A panoramic review • Review article 出处:Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, Volume 91, Issue 17, October 2007, Pages 1529-1598 作者:Granqvist, C.G. 摘要:Transparent conductors (TCs) have a multitude of applications for solar energy utilization and for energy savings, especially in buildings. The largest of these applications, in terms of area, make use of the fact that the TCs have low infrared emittance and hence can be used to improve the thermal properties of modern fenestration. Depending on whether the TCs are reflecting or not in the near infrared pertinent to solar irradiation, the TCs can serve in “solar control” or “low-emittance” windows. Other applications rely on the electrical conductivity of the TCs, which make them useful as current collectors in solar cells and for inserting and extracting electrical charge in electrochromic “smart windows” capable of combining energy efficiency and indoor comfort in buildings. This Review takes a “panoramic” view on TCs and discusses their properties from the perspective of the radiative properties in our ambience. This approach leads naturally to considerations of spectral selectivity, angular selectivity, and temporal variability of TCs, as covered in three subsequent sections. The spectrally selective materials are thin films based on metals (normally gold or titanium nitride) or wide band gap semiconductors with heavy doping (normally based on indium, tin, or zinc). Their applications to energy-efficient windows are covered in detail, experimentally as well as theoretically, and briefer discussions are given applications to solar cells and solar collectors. Photocatalytic properties and super-hydrophilicity are touched upon. Angular selective TCs, for which the angular properties are caused by inclined columnar nanostructures, are then covered. A discussion of TC-like materials with thermochromic and electrochromic properties follows in the final part. Detailed treatments are given for thermochromic materials based on vanadium dioxide and for electrochromic multi-layer structures (incorporating TCs as essential components). The reference list is extensive and aims at giving an easy entrance to the many varied aspects of TCs. 17. 题名:Lithium batteries: Status, prospects and future • Review article 出处:Journal of Power Sources, Volume 195, Issue 9, May 2010, Pages 2419-2430 作者:Scrosati, B.; Garche, J. 摘要:Lithium batteries are characterized by high specific energy, high efficiency and long life. These unique properties have made lithium batteries the power sources of choice for the consumer electronics market with a production of the order of billions of units per year. These batteries are also expected to find a prominent role as ideal electrochemical storage systems in renewable energy plants, as well as power systems for sustainable vehicles, such as hybrid and electric vehicles. However, scaling up the lithium battery technology for these applications is still problematic since issues such as safety, costs, wide operational temperature and materials availability, are still to be resolved. This review focuses first on the present status of lithium battery technology, then on its near future development and finally it examines important new directions aimed at achieving quantum jumps in energy and power content. 18. 题名:Polymer nanotechnology: Nanocomposites • Review article 11 出处:Polymer, Volume 49, Issue 15, July 2008, Pages 3187-3204 作者:Paul, D.R.; Robeson, L.M. 摘要:In the large field of nanotechnology, polymer matrix based nanocomposites have become a prominent area of current research and development. Exfoliated clay-based nanocomposites have dominated the polymer literature but there are a large number of other significant areas of current and emerging interest. This review will detail the technology involved with exfoliated clay-based nanocomposites and also include other important areas including barrier properties, flammability resistance, biomedical applications, electrical/electronic/optoelectronic applications and fuel cell interests. The important question of the “nano-effect” of nanoparticle or fiber inclusion relative to their larger scale counterparts is addressed relative to crystallization and glass transition behavior. Of course, other polymer (and composite)-based properties derive benefits from nanoscale filler or fiber addition and these are addressed. 19. 题名:Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: a review from preparation to processing • Review article 出处:Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 28, Issue 11, November 2003, Pages 1539-1641 作者:Sinha Ray, S.; Okamoto, M. 摘要:A review is given of the academic and industrial aspects of the preparation, characterization, materials properties, crystallization behavior, melt rheology, and processing of polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites. These materials are attracting considerable interest in polymer science research. Hectorite and montmorillonite are among the most commonly used smectite-type layered silicates for the preparation of nanocomposites. Smectites are a valuable mineral class for industrial applications because of their high cation exchange capacities, surface area, surface reactivity, adsorptive properties, and, in the case of hectorite, high viscosity and transparency in solution. In their pristine form they are hydrophilic in nature, and this property makes them very difficult to disperse into a polymer matrix. The most common way to remove this difficulty is to replace interlayer cations with quarternized ammonium or phosphonium cations, preferably with long alkyl chains. A wide range of polymer matrices is covered in this review, with special emphasis on biodegradable polymers. In general, polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites are of three different types, namely (1) intercalated nanocomposites, for which insertion of polymer chains into a layered silicate structure occurs in a crystallographically regular fashion, with a repeat distance of few nanometers, regardless of polymer to clay ratio, (2) flocculated nanocomposites, for which intercalated and stacked silicate layers flocculated to some extent due to the hydroxylated edge–edge interactions of the silicate layers, and (3) exfoliated nanocomposites, for which the individual silicate layers are separated in the polymer matrix by average distances that depend only on the clay loading. This new family of composite materials frequently exhibits remarkable improvements of material properties when compared with the matrix polymers alone or conventional micro- and macro-composite materials. Improvements can include a high storage modulus, both in solid and melt states, increased tensile and flexural properties, a decrease in gas permeability and flammability, increased heat distortion temperature, an increase in the biodegradability rate of biodegradable polymers, and so forth. 20. 题名:Hollow polymeric nanostructures-Synthesis, morphology and function • Review article 12 出处:Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 36, Issue 1, January 2011, Pages 127-167 作者:Fu, G.D.; Li, G.L.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T. 摘要:The development of reliable synthetic routes to polymeric nanostructures of well-defined composition, morphology and function is of scientific importance and technological interest. The generation of functional hollow polymeric nanostructures, hollow nanospheres and nanotubes in particular, can be achieved through direct and template-directed synthesis, core–shell precursors, and self-assembly of copolymers and polymer conjugates, as well as from dendrimers. The ability to prepare precursor macromolecules of well-defined structure and architecture has been substantially enhanced by recent advances in controlled radical polymerizations. The application and potential application of the hollow polymeric nanospheres and nanotubes as nanoreactors, and in diagnostics, encapsulation, controlled release, and other stimuli-responsive systems are also described. 21. 题名:Polymer nanocomposites based on functionalized carbon nanotubes • Review article 出处:Progress in Polymer Science, Volume 35, Issue 7, July 2010, Pages 837-867 作者:Sahoo, N.G.; Rana, S.; Cho, J.W.; Li, L.; Chan, S.H. 摘要:Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) exhibit excellent mechanical, electrical, and magnetic properties as well as nanometer scale diameter and high aspect ratio, which make them an ideal reinforcing agent for high strength polymer composites. However, since CNTs usually form stabilized bundles due to Van der Waals interactions, are extremely difficult to disperse and align in a polymer matrix. The biggest issues in the preparation of CNT-reinforced composites reside in efficient dispersion of CNTs into a polymer matrix, the assessment of the dispersion, and the alignment and control of the CNTs in the matrix. There are several methods for the dispersion of nanotubes in the polymer matrix such as solution mixing, melt mixing, electrospinning, in-situ polymerization and chemical functionalization of the carbon nanotubes, etc. These methods and preparation of high performance CNT-polymer composites are described in this review. A critical comparison of various CNT functionalization methods is given. In particular, CNT functionalization using click chemistry and the preparation of CNT composites employing hyperbranched polymers are stressed as potential techniques to achieve good CNT dispersion. In addition, discussions on mechanical, thermal, electrical, electrochemical and optical properties and applications of polymer/CNT composites are included. 22. 题名:A review on highly ordered, vertically oriented TiO"2 nanotube arrays: Fabrication, material properties, and solar energy applications • Review article 出处:Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, Volume 90, Issue 14, September 2006, Pages 2011-2075 作者:Mor, G.K.; Varghese, O.K.; Paulose, M.; Shankar, K.; Grimes, C.A. 摘要:We review the fabrication, properties, and solar energy applications of highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays made by anodic oxidation of titanium in fluoride-based electrolytes. The material architecture has proven to be of great interest for use in water photoelectrolysis, photocatalysis, heterojunction solar cells, and gas sensing. We examine the ability to fabricate nanotube arrays of different shape (cylindrical, tapered), pore size, length, and wall thickness by varying anodization parameters including electrolyte concentration, pH, voltage, and bath temperature, with fabrication and crystallization variables discussed in reference to a nanotube array growth model. We review 13 efforts to lower the band gap of the titania nanotubes by anionic doping. Measured optical properties are compared with computational electromagnetic simulations obtained using finite difference time domain (FDTD). The article concludes by examining various practical applications of the remarkable material architecture, including its use for water photoelectrolysis, and in heterojucntion dye-sensitized solar cells. 23. 题名:ZnS nanostructures: From synthesis to applications • Review article 出处:Progress in Materials Science, Volume 56, Issue 2, February 2011, Pages 175-287 作者:Fang, X.; Zhai, T.; Gautam, U.K.; Li, L.; Wu, L.; Bando, Y.; Golberg, D. 摘要:Zinc sulfide (ZnS) is one of the first semiconductors discovered. It has traditionally shown remarkable versatility and promise for novel fundamental properties and diverse applications. The nanoscale morphologies of ZnS have been proven to be one of the richest among all inorganic semiconductors. In this article, we provide a comprehensive review of the state-of-the-art research activities related to ZnS nanostructures. We begin with a historical background of ZnS, description of its structure, chemical and electronic properties, and its unique advantages in specific potential applications. This is followed by in-detail discussions on the recent progress in the synthesis, analysis of novel properties and potential applications, with the focus on the critical experiments determining the electrical, chemical and physical parameters of the nanostructures, and the interplay between synthetic conditions and nanoscale morphologies. Finally, we highlight the recent achievements regarding the improvement of ZnS novel properties and finding prospective applications, such as field emitters, field effect transistors (FETs), p-type conductors, catalyzators, UV-light sensors, chemical sensors (including gas sensors), biosensors, and nanogenerators. Overall this review presents a systematic investigation of the ‘synthesis-property-application’ triangle for the diverse ZnS nanostructures. 24. 题名:Small but strong: A review of the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube-polymer composites • Review article 出处:Carbon, Volume 44, Issue 9, August 2006, Pages 1624-1652 作者:Coleman, J.N.; Khan, U.; Blau, W.J.; Gun\'ko, Y.K. 摘要:The superlative mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes make them the filler material of choice for composite reinforcement. In this paper we review the progress to date in the field of mechanical reinforcement of polymers using nanotubes. Initially, the basics of fibre reinforced composites are introduced and the prerequisites for successful reinforcement discussed. The effectiveness of different processing methods is compared and the state of the art demonstrated. In addition we discuss the levels of reinforcement that have actually been achieved. While the focus will be on enhancement of Young’s modulus we will also discuss enhancement of strength and toughness. Finally we compare and tabulate these results. This leads to a discussion of the most promising processing methods for mechanical reinforcement and the outlook for the future. 25. 题名:A review on the application of inorganic nano-structured materials in the modification of textiles: Focus on anti-microbial properties • Review article 出处:Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, Volume 79, Issue 1, August 2010, Pages 5-18 作者:Dastjerdi, R.; Montazer, M. 摘要:Textiles can provide a suitable substrate to grow micro-organisms especially at appropriate 14 humidity and temperature in contact to human body. Recently, increasing public concern about hygiene has been driving many investigations for anti-microbial modification of textiles. However, using many anti-microbial agents has been avoided because of their possible harmful or toxic effects. Application of inorganic nano-particles and their nano-composites would be a good alternative. This review paper has focused on the properties and applications of inorganic nano-structured materials with good anti-microbial activity potential for textile modification. The discussed nano-structured anti-microbial agents include TiO2 nano-particles, metallic and non-metallic TiO2 nano-composites, titania nanotubes (TNTs), silver nano-particles, silver-based nano-structured materials, gold nano-particles, zinc oxide nano-particles and nano-rods, copper nano-particles, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), nano-clay and its modified forms, gallium, liposomes loaded nano-particles, metallic and inorganic dendrimers nano-composite, nano-capsules and cyclodextrins containing nano-particles. This review is also concerned with the application methods for the modification of textiles using nano-structured materials. 四、IEL Top20(来源:http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/) 1.题名:Top 11 technologies of the decade 作者:Ross, P.E. 出处:Spectrum, IEEE Volume: 48 Issue: 1 Date: Jan. 2011 Page(s):27 - 63 摘要:The most powerful technologies take a while to mature. But when they do, they can rapidly retire mainstays that are decades old. Given in this paper are the top 11 technologies of the decade which are smartphones, social networking, voice over IP, LED lighting, multicore CPU, cloud computing, drone aircraft, planetary rovers, flexible AC transmission, digital photography and class-D audio. 2.题名:IEEE Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications 出处:IEEE Std 830-1998 Digital Object Identifier : 10.1109/IEEESTD.1998.88286 摘要:The content and qualities of a good software requirements specification (SRS) are described, and several sample SRS outlines are presented. This recommended practice is aimed at specifying the requirements of software to be developed, but can also be applied to assist in the selection of in-house and commercial software products. Guidelines for compliance with IEEE/EIA Std 12207.1-1997 are also provided. 15 3.题名:Is the PHY layer dead? 作者:Dohler, M. Heath, R.W. Lozano, A. Papadias, C.B. Valenzuela, R.A. 出处:Communications Magazine, IEEE Volume: 49 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):159 - 165 摘要:This article originates from a panel with the above title, held at IEEE VTC Spring 2009, in which the authors took part. The enthusiastic response it received prompted us to discuss for a wider audience whether research at the physical layer (PHY) is still relevant to the field of wireless communications. Using cellular systems as the axis of our exposition, we exemplify areas where PHY research has indeed hit a performance wall and where any improvements are expected to be marginal. We then discuss whether the research directions taken in the past have always been the right choice and how lessons learned could influence future policy decisions. Several of the raised issues are subsequently discussed in greater details, e.g., the growing divergence between academia and industry. With this argumentation at hand, we identify areas that are either under-developed or likely to be of impact in coming years - hence corroborating the relevance and importance of PHY research. 4. 题名 : IEEE Application Guide for IEEE Std 1547, IEEE Standard for Interconnecting Distributed Resources with Electric Power Systems 出处:IEEE Std 1547.2-2008 Page(s):1 - 207 Digital Object Identifier : 10.1109/IEEESTD.2008.4816078 摘要:In this paper, technical background and application details to support understanding of IEEE Std 1547-2003 are provided. The guide facilitates the use of IEEE Std 1547-2003 by characterizing various forms of distributed resource (DR) technologies and their associated interconnection issues. It provides background and rationale of the technical requirements of IEEE Std 1547-2003. It also provides tips, techniques, and rules of thumb, and it addresses topics related to DR project implementation to enhance the user's understanding of how IEEE Std 1547-2003 may relate to those topics. This guide is intended for use by engineers, engineering consultants, and knowledgeable individuals in the field of DR. The IEEE 1547 series of standards is cited in the Federal Energy Policy Act of 2005, and this guide is one document in the IEEE 1547 series. 5.题名:Understanding Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities 作者:Grobauer, B. Walloschek, T. Stocker, E. 出处:Security & Privacy, IEEE Volume: 9 Issue: 2 Date: March-April 2011 Page(s):50 - 57 摘要:The current discourse about cloud computing security issues makes a well-founded assessment of cloud computing's security impact difficult for two primary reasons. First, as is true for many discussions about risk, basic vocabulary such as "risk," "threat," and "vulnerability" are often used as if they were interchangeable, without regard to their respective definitions. Second, not every issue that's raised is really specific to cloud computing. We can achieve an accurate understanding of the security issue "delta" that cloud computing really adds by analyzing how cloud computing influences each risk factor. One important factor concerns vulnerabilities: cloud computing makes certain well-understood vulnerabilities more significant and adds new vulnerabilities. Here, the authors define four indicators of cloud-specific vulnerabilities, introduce 16 a security-specific cloud reference architecture, and provide examples of cloud-specific vulnerabilities for each architectural component. 6.题名:Green Cloud Computing: Balancing Energy in Processing, Storage, and Transport 作者:Baliga, J. Ayre, R.W.A. Hinton, K. Tucker, R.S. 出处:Proceedings of the IEEE Volume: 99 Issue: 1 Date: Jan. 2011 Page(s):149 - 167 摘要:Network-based cloud computing is rapidly expanding as an alternative to conventional office-based computing. As cloud computing becomes more widespread, the energy consumption of the network and computing resources that underpin the cloud will grow. This is happening at a time when there is increasing attention being paid to the need to manage energy consumption across the entire information and communications technology (ICT) sector. While data center energy use has received much attention recently, there has been less attention paid to the energy consumption of the transmission and switching networks that are key to connecting users to the cloud. In this paper, we present an analysis of energy consumption in cloud computing. The analysis considers both public and private clouds, and includes energy consumption in switching and transmission as well as data processing and data storage. We show that energy consumption in transport and switching can be a significant percentage of total energy consumption in cloud computing. Cloud computing can enable more energy-efficient use of computing power, especially when the computing tasks are of low intensity or infrequent. However, under some circumstances cloud computing can consume more energy than conventional computing where each user performs all computing on their own personal computer (PC). 7.题名:A 300-GHz Fundamental Oscillator in 65-nm CMOS Technology 作者:Razavi, B. 出处:Solid-State Circuits, IEEE Journal of Volume: 46 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):894 - 903 摘要:Fundamental oscillators prove the existence of gain at high frequencies, revealing the speed limitations of other circuits in a given technology. This paper presents an oscillator topology that employs feedback from an output stage to the core, thus achieving a high speed. The behavior of the proposed oscillator is formulated and simulations are used to compare it with the conventional cross-coupled pair circuit. Three prototypes realized in 65-nm CMOS technology operate at 205 GHz, 240 GHz, and 300 GHz, each drawing 3.7 mW from a 0.8-V supply. 8.题名:A SAR-Assisted Two-Stage Pipeline ADC 作者:Lee, C.C. Flynn, M.P. 出处:Solid-State Circuits, IEEE Journal of Volume: 46 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):859 - 869 摘要:Successive approximation register (SAR) ADC architectures are popular for achieving high energy efficiency but they suffer from resolution and speed limitations. On the other hand pipeline ADC architectures can achieve high resolution and speed but have lower energy-efficiency and are more complex. We pro pose a two-stage pipeline ADC architecture with a large first-stage resolution, enabled with the help of a SAR-based sub-ADC. The prototype 12b 50 MS/s ADC achieves an ENOB of 10.4b at Nyquist, and a figure-of-merit of 52 f J/conversion-step. The ADC 17 achieves low-power, high-resolution and high-speed operation without calibration. The ADC is fabricated in 65 nm and 90 nm CMOS and occupies a core area of only 0.16 mm2. 9.题名:Emerging cognitive radio applications: A survey 作者:Jianfeng Wang Ghosh, M. Challapali, K. 出处:Communications Magazine, IEEE Volume: 49 Issue: 3 Date: March 2011 Page(s):74 - 81 摘要:Recent developments in spectrum policy and regulatory domains, notably the release of the National Broadband Plan, the publication of final rules for TV white spaces, and the ongoing proceeding for secondary use of the 2360-2400 MHz band for medical body area networks, will allow more flexible and efficient use of spectrum in the future. These important changes open up exciting opportunities for cognitive radio to enable and support a variety of emerging applications, ranging from smart grid, public safety and broadband cellular, to medical applications. This article presents a high-level view on how cognitive radio (primarily from a dynamic spectrum access perspective) would support such applications, the benefits that cognitive radio would bring, and also some challenges that are yet to be resolved. We also illustrate related standardization that uses cognitive radio technologies to support such emerging applications. 10.题名:LTE-advanced: next-generation wireless broadband technology [Invited Paper] 作者:Ghosh, A. Ratasuk, R. Mondal, B. Mangalvedhe, N. Thomas, T. 出处:Wireless Communications, IEEE Volume: 17 Issue: 3 Date: June 2010 Page(s):10 - 22 摘要:LTE Release 8 is one of the primary broadband technologies based on OFDM, which is currently being commercialized. LTE Release 8, which is mainly deployed in a macro/microcell layout, provides improved system capacity and coverage, high peak data rates, low latency, reduced operating costs, multi-antenna support, flexible bandwidth operation and seamless integration with existing systems. LTE-Advanced (also known as LTE Release 10) significantly enhances the existing LTE Release 8 and supports much higher peak rates, higher throughput and coverage, and lower latencies, resulting in a better user experience. Additionally, LTE Release 10 will support heterogeneous deployments where low-power nodes comprising picocells, femtocells, relays, remote radio heads, and so on are placed in a macrocell layout. The LTE-Advanced features enable one to meet or exceed IMT-Advanced requirements. It may also be noted that LTE Release 9 provides some minor enhancement to LTE Release 8 with respect to the air interface, and includes features like dual-layer beamforming and time-difference- of-arrival-based location techniques. In this article an overview of the techniques being considered for LTE Release 10 (aka LTEAdvanced) is discussed. This includes bandwidth extension via carrier aggregation to support deployment bandwidths up to 100 MHz, downlink spatial multiplexing including single-cell multi-user multiple-input multiple-output transmission and coordinated multi point transmission, uplink spatial multiplexing including extension to four-layer MIMO, and heterogeneous networks with emphasis on Type 1 and Type 2 relays. Finally, the performance of LTEAdvanced using IMT-A scenarios is presented and compared against IMT-A targets for full buffer and bursty traffic model. 11.题名:M2M: From mobile to embedded internet 18 作者:Geng Wu Talwar, S. Johnsson, K. Himayat, N. Johnson, K.D. 出处:Communications Magazine, IEEE Volume: 49 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):36 - 43 摘要:Is M2M hype or the future of our information society? What does it take to turn the M2M vision into reality? In this article we discuss the business motivations and technology challenges for machine-to-machine communications. We highlight key M2M application requirements and major technology gaps. We analyze the future directions of air interface technology improvements and network architectures evolution to enable the mass deployment of M2M services. In particular, we consider the salient features of M2M traffic that may not be supported efficiently by present standards, and provide an overview of potential enhancements. Finally, we discuss standards development for M2M. 12.题名:Machine-to-machine communications for home energy management system in smart grid 作者:Niyato, D. Lu Xiao Ping Wang 出处:Communications Magazine, IEEE Volume: 49 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):53 - 59 摘要:Machine-to-machine (M2M) communications have emerged as a cutting edge technology for next-generation communications, and are undergoing rapid development and inspiring numerous applications. This article presents an investigation of the application of M2M communications in the smart grid. First, an overview of M2M communications is given. The enabling technologies and open research issues of M2M communications are also discussed. Then we address the network design issue of M2M communications for a home energy management system (HEMS) in the smart grid. The network architecture for HEMS to collect status and power consumption demand from home appliances is introduced. Then the optimal HEMS traffic concentration is presented and formulated as the optimal cluster formation. A dynamic programming algorithm is applied to obtain the optimal solution. The numerical results show that the proposed optimal traffic concentration can minimize the cost of HEMS. 13.题名:Compressed sensing 作者:Donoho, D.L. 出处:Information Theory, IEEE Transactions on Volume: 52 Issue: 4 Date: April 2006 Page(s):1289 - 1306 摘要:Suppose x is an unknown vector in Ropfm (a digital image or signal); we plan to measure n general linear functionals of x and then reconstruct. If x is known to be compressible by transform coding with a known transform, and we reconstruct via the nonlinear procedure defined here, the number of measurements n can be dramatically smaller than the size m. Thus, certain natural classes of images with m pixels need only n=O(m1/4log5/2(m)) nonadaptive nonpixel samples for faithful recovery, as opposed to the usual m pixel samples. More specifically, suppose x has a sparse representation in some orthonormal basis (e.g., wavelet, Fourier) or tight frame (e.g., curvelet, Gabor)-so the coefficients belong to an lscrp ball for 0<ples1. The N most important coefficients in that expansion allow reconstruction with lscr2 error O(N1/2-1p/). It is possible to design n=O(Nlog(m)) nonadaptive measurements allowing reconstruction with accuracy comparable to that attainable with direct knowledge of the N most important coefficients. Moreover, a good approximation to those N important coefficients is extracted from the n 19 measurements by solving a linear program-Basis Pursuit in signal processing. The nonadaptive measurements have the character of "random" linear combinations of basis/frame elements. Our results use the notions of optimal recovery, of n-widths, and information-based complexity. We estimate the Gel'fand n-widths of lscrp balls in high-dimensional Euclidean space in the case 0<ples1, and give a criterion identifying near- optimal subspaces for Gel'fand n-widths. We show that "most" subspaces are near-optimal, and show that convex optimization (Basis Pursuit) is a near-optimal way to extract information derived from these near-optimal subspaces 14.题名:Toward intelligent machine-to-machine communications in smart grid 作者:Fadlullah, Z.M. Fouda, M.M. Kato, N. Takeuchi, A. Iwasaki, N. Nozaki, Y. 出处:Communications Magazine, IEEE Volume: 49 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):60 - 65 摘要:The advanced metering infrastructure of the smart grid presents the biggest growth potential in the machine-to-machine market today. Spurred by recent advances in M2M technologies, SG smart meters are expected not to require human intervention in characterizing power requirements and energy distribution. However, there are many challenges in the design of the SG communications network whereby the electrical appliances and smart meters are able to exchange information pertaining to varying power requirements. Furthermore, different types of M2M gateways are required at different points (e.g., at home, in the building, at the neighborhood, and so forth) of the SG communication network. This article surveys a number of existing communication technologies that can be adopted for M2M communication in SG. Among these, the most reliable technology to facilitate M2M communication in the SG home area network is pointed out, and its shortcoming is also noted. Furthermore, a possible solution to deal with this shortcoming to improve SG communications scalability is also presented. 15.题名:Cloud Computing Research and Development Trend 作者:Shuai Zhang Shufen Zhang Xuebin Chen Xiuzhen Huo 出处:Future Networks, 2010. ICFN '10. Second International Conference on Page(s):93 - 97 摘要:With the development of parallel computing, distributed computing, grid computing, a new computing model appeared. The concept of computing comes from grid, public computing and SaaS. It is a new method that shares basic framework. The basic principles of cloud computing is to make the computing be assigned in a great number of distributed computers, rather then local computer or remoter server. The running of the enterprise's data center is just like Internet. This makes the enterprise use the resource in the application that is needed, and access computer and storage system according to the requirement. This article introduces the background and principle of cloud computing, the character, style and actuality. This article also introduces the application field the merit of cloud computing, such as, it do not need user's high level equipment, so it reduces the user's cost. It provides secure and dependable data storage center, so user needn't do the awful things such storing data and killing virus, this kind of task can be done by professionals. It can realize data share through different equipments. It analyses some questions and hidden troubles, and puts forward some solutions, and discusses the future of cloud computing. Cloud computing is a computing style that provide power referenced with IT as a service. Users can enjoy the service even he knows nothing about the technology of cloud computing and the 20 professional knowledge in this field and the power to control it. 16.题名:A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition 作者:Rabiner, L.R. 出处:Proceedings of the IEEE Volume: 77 Issue: 2 Date: Feb 1989 Page(s):257 - 286 摘要:This tutorial provides an overview of the basic theory of hidden Markov models (HMMs) as originated by L.E. Baum and T. Petrie (1966) and gives practical details on methods of implementation of the theory along with a description of selected applications of the theory to distinct problems in speech recognition. Results from a number of original sources are combined to provide a single source of acquiring the background required to pursue further this area of research. The author first reviews the theory of discrete Markov chains and shows how the concept of hidden states, where the observation is a probabilistic function of the state, can be used effectively. The theory is illustrated with two simple examples, namely coin-tossing, and the classic balls-in-urns system. Three fundamental problems of HMMs are noted and several practical techniques for solving these problems are given. The various types of HMMs that have been studied, including ergodic as well as left-right models, are described 17.题名:Home M2M networks: Architectures, standards, and QoS improvement 作者:Yan Zhang Rong Yu Shengli Xie Wenqing Yao Yang Xiao Guizani, M. 出处:Communications Magazine, IEEE Volume: 49 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):44 - 52 摘 要 : It is envisioned that home networks will shift from current machine-to-human communications to the machine-to-machine paradigm with the rapid penetration of embedded devices in home surroundings. In this article, we first identify the fundamental challenges in home M2M networks. Then we present the architecture of home M2M networks decomposed into three subareas depending on the radio service ranges and potential applications. Finally, we focus on QoS management in home M2M networks, considering the increasing number of multimedia devices and growing visual requirements in a home area. Three standards for multimedia sharing and their QoS architectures are outlined. Cross-layer joint admission and rate control design is reported for QoS-aware multimedia sharing. This proposed strategy is aware of the QoS requirements and resilience of multimedia services. Illustrative results indicate that the joint design is able to intelligently allocate radio bandwidth based on QoS demands in resource-constrained home M2M networks. 18.题名:The Characteristics of Cloud Computing 作者:Chunye Gong Jie Liu Qiang Zhang Haitao Chen Zhenghu Gong 出处:Parallel Processing Workshops (ICPPW), 2010 39th International Conference on Page(s):275 - 279 摘要:Cloud computing emerges as one of the hottest topic in field of information technology. Cloud computing is based on several other computing research areas such as HPC, virtualization, utility computing and grid computing. In order to make clear the essential of cloud computing, we propose the characteristics of this area which make cloud computing being cloud computing and distinguish it from other research areas. The cloud computing has its own conceptional, technical, 21 economic and user experience characteristics. The service oriented, loose coupling, strong fault tolerant, business model and ease use are main characteristics of cloud computing. Clear insights into cloud computing will help the development and adoption of this evolving technology both for academe and industry. 19.题名:Data Security in the World of Cloud Computing 作者:Kaufman, L.M. 出处:Security & Privacy, IEEE Volume: 7 Issue: 4 Date: July-Aug. 2009 Page(s):61 - 64 摘要:Today, we have the ability to utilize scalable, distributed computing environments within the confines of the Internet, a practice known as cloud computing. In this new world of computing, users are universally required to accept the underlying premise of trust. Within the cloud computing world, the virtual environment lets users access computing power that exceeds that contained within their own physical worlds. Typically, users will know neither the exact location of their data nor the other sources of the data collectively stored with theirs. The data you can find in a cloud ranges from public source, which has minimal security concerns, to private data containing highly sensitive information (such as social security numbers, medical records, or shipping manifests for hazardous material). Does using a cloud environment alleviate the business entities of their responsibility to ensure that proper security measures are in place for both their data and applications, or do they share joint responsibility with service providers? The answers to this and other questions lie within the realm of yet-to-be-written law. As with most technological advances, regulators are typically in a "catch-up" mode to identify policy, governance, and law. Cloud computing presents an extension of problems heretofore experienced with the Internet. To ensure that such decisions are informed and appropriate for the cloud computing environment, the industry itself should establish coherent and effective policy and governance to identify and implement proper security methods. 20.题名:Toward ubiquitous massive accesses in 3GPP machine-to-machine communications 作者;Shao-Yu Lien Kwang-Cheng Chen Yonghua Lin 出处:Communications Magazine, IEEE Volume: 49 Issue: 4 Date: April 2011 Page(s):66 - 74 摘要:To enable full mechanical automation where each smart device can play multiple roles among sensor, decision maker, and action executor, it is essential to construct scrupulous connections among all devices. Machine-to-machine communications thus emerge to achieve ubiquitous communications among all devices. With the merit of providing higher-layer connections, scenarios of 3GPP have been regarded as the promising solution facilitating M2M communications, which is being standardized as an emphatic application to be supported by LTE-Advanced. However, distinct features in M2M communications create diverse challenges from those in human-to-human communications. To deeply understand M2M communications in 3GPP, in this article, we provide an overview of the network architecture and features of M2M communications in 3GPP, and identify potential issues on the air interface, including physical layer transmissions, the random access procedure, and radio resources allocation supporting the most critical QoS provisioning. An effective solution is further proposed to provide QoS guarantees to facilitate M2M applications with inviolable hard timing constraints. 22 五、ACM 最新会议(来源:http://www.acm.org/) 1.会议名称:K-CAP 2011 The Sixth International Conference on Knowledge Capture 会议时间:25 - 29 June 2011 会议地点:Banff, Alberta, Canada 会议简介:In today's knowledge-driven world, effective access to and use of information is a key enabler for progress. Modern technologies not only are themselves knowledge-intensive technologies, but also produce enormous amounts of new information that we must process and aggregate. These technologies require knowledge capture, which involve the extraction of useful knowledge from vast and diverse sources of information as well as its acquisition directly from users. Driven by the demands for knowledge-based applications and the unprecedented availability of information on the Web, the study of knowledge capture has a renewed importance. Researchers that work in the area of knowledge capture traditionally belong to several distinct research communities, including knowledge engineering, machine learning, natural language processing, human-computer interaction, artificial intelligence, social networks and the Semantic Web. K-CAP 2011 will provide a forum that brings together members of disparate research communities that are interested in efficiently capturing knowledge from a variety of sources and in creating representations that can be useful for reasoning, analysis, and other forms of machine processing. We solicit high-quality research papers for publication and presentation at our conference. Our aim is to promote multidisciplinary research that could lead to a new generation of tools and methodologies for knowledge capture. 2. 会议名称:DEBS '11 The 5th ACM International Conference on Distributed Event-Based Systems 会议时间:July 11 - July 15 2011 会议地点:New York NY USA 会议简介:The 5th ACM International Conference on Distributed Event-Based Systems (DEBS) builds on the success of first four editions from 2007. DEBS Conference success is rooted in five editions of the DEBS workshops held from 2002 to 2006 in companion with major conferences such as ICDCS, ICSE, and SIGMOD/PODS. The conference has received full ACM sponsorship since 2009. The objectives of the DEBS Conference are to provide a forum dedicated to the dissemination of original research, the discussion of practical insights, and the reporting on relevant experience relating to event-based computing that was previously scattered across several scientific and professional communities. The conference also aims at providing a forum for academia and industry to exchange ideas, for example, through industry papers and demo papers. The venue for the DEBS 2011 edition will be the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, NY, the headquarters for IBM Research. Yorktown Heights is located in the Lower Hudson River Valley, a historic site for the American Revolutionary War and home of some of the most famous mansions in the United States. The area is close by New York City. 23 3.会议名称:ITiCSE '11 the 16th Annual Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education 会议时间:June 27 - June 29 2011 会议地点:Darmstadt Germany 会议简介:ITiCSE 2011, the 16th Annual Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education will be held at the darmstadtium Conference Center in Darmstadt, Germany, and is hosted by the Technische Universität Darmstadt. The conference is sponsored by the ACM Special Interest Group on Computer Science Education (SIGCSE). The program of the conference will consist of keynote lectures, paper sessions, working groups, exhibits, panels, posters, courseware demonstrations, tips, techniques and courseware. The conference will begin with the Working Groups, who commence their sessions on Saturday, June 25, 2011 and will continue their work until Wednesday, June 29, 2011. The main conference starts on Monday, June 27, 2011 and ends on Wednesday, June 29, 2011. 4. 会议名称:MobiSys'11 会议时间:June 28 - July 01 2011 会议地点:Bethesda MD USA 会议简介:MobiSys 2011 seeks to present innovative and significant research on the design, implementation, usage, and evaluation of mobile computing and wireless systems, applications, and services. It is jointly sponsored by ACM SIGMOBILE and the USENIX association in cooperation with ACM SIGOPS. The conference will be held at Washington, DC, USA. The workshops will be held on June 28th and the technical program will take place on June 29th through July 1st. 六、AIAA 最新会议(来源:http://www.aiaa.org/) 1. 会议名称:41st AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 会议时间:27 - 30 Jun 2011 会议地点:Honolulu, Hawaii Venue: Sheraton Waikiki and the Hawaii Convention Center 会议简介:The 41st AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference will include papers covering all aspects of fluid dynamics, particularly those relevant to aerospace applications. Topics range from basic 24 research and development to applied and advanced technology, including novel experimental and computational observations, interdisciplinary papers that bridge theoretical, experimental, and numerical approaches, and papers that provide innovative concepts and analyses, or especially new insight into flow physics. Sessions will be planned that include papers related to low and high speed flows, instability, transition, turbulence, vortex dynamics, and various aspects of flow control. The conference is collocated with several other conferences to enable close synergism and interaction between a broad range of research disciplines in fluid dynamics, and several joint sessions on topics of broad interest will be arranged. 2. 会议名称:20th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference 会议时间:27 - 30 Jun 2011 会议地点:Honolulu, Hawaii Venue: Sheraton Waikiki and the Hawaii Convention Center 会议简介:The 20th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Conference is being held in conjunction with the 41st AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and 6th AIAA Theoretical Fluid Mechanics Conference to enable close synergism and interaction among a broad range of research disciplines in fluid dynamics. The Fluid Dynamics and the Meshing, Visualization, and Computational Environments (MVCE) Technical Committees will plan sessions covering all aspects of computational fluid dynamics particularly relevant to aerospace applications. In addition, the CFD Conference will feature the 4th AIAA CFD Student Paper Competition. 3.会议名称:29th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference 会议时间: 27 - 30 Jun 2011 会议地点: Honolulu, Hawaii Venue: Sheraton Waikiki and the Hawaii Convention Center 会议简介:TThe 29th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference provides a forum for the presentation and discussion of technical material in diverse areas of theoretical, computational, and experimental applied aerodynamics. Conference sessions will focus on technical topics in the areas of wind-tunnel and flight-testing aerodynamics, unsteady aerodynamics, subsonic, transonic, supersonic, hypersonic aerodynamics, vortical/vortex flow applications, high angle of attack and high lift aerodynamics, boundary layer transition and drag prediction, low Reynolds Number aerodynamics, airfoil/wing/configuration aerodynamics, propeller/rotorcraft aerodynamics, weapon carriage and store separation aerodynamics, innovative aerodynamic concepts/designs, aerodynamic design methodologies, active flow control applications, unmanned aerial vehicle designs/testing, missile/projectile/guided-munitions aerodynamics, aerodynamic-structural dynamics interaction, icing effects on vehicle aerodynamics, application of artificial intelligence techniques to aero problems, and application of CFD methods to aerodynamic configurations validated against experimental data. Special invited sessions will include; the prediction of sonic boom and drag for supersonic aircraft, aerodynamic efficiency and laminar flow, experimental difficulties and challenges of low Reynolds number aerodynamics, and the aerodynamic characterization of NASA’s Orion Crew Vehicle. The conference is collocated with several other conferences to enable close synergism and interaction between a broad range of research disciplines in applied aerodynamics. 25 4. 会议名称:3rd AIAA Atmospheric Space Environments Conference 会议时间:27 - 30 Jun 2011 会议地点:Honolulu, Hawaii Venue: Sheraton Waikiki and the Hawaii Convention Center 会议简介:The 3rd AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference provides a forum for presentation and discussion of scientific and technical information concerning interactions between aerospace systems and the atmospheric/ space/planetary environment. Technical sessions will focus on the areas of atmospheric environment, aviation weather and atmospheric dynamics, environmental impact of aeronautic technologies, meteorological applications to aerospace operations, meteroid and debris environment, on-orbit spacecraft-environmental interactions, satellite and ground-based measurement systems, and space environment. These sessions will provide an opportunity to share information and experiences, thereby increasing technical benefit for all attendees. 5. 会议名称:42nd AIAA Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference in conjunction with the 18th International Conference on MHD Energy Conversion (ICMHD) 会议时间:27 - 30 Jun 2011 会议地点: Honolulu, Hawaii Venue: Sheraton Waikiki and the Hawaii Convention Center 会 议 简 介 : The 42nd AIAA Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference will host the 18th International Conference on MHD Energy Conversion (ICMHD) via integration of special technical sessions within the normal conference program. The 18th ICMHD is an international technical forum encompassing all aspects of magnetohydrodynamic energy conversion science and technology. The 42nd Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference will address current basic/applied research in the areas of plasmadynamics, lasers, electromagnetics, diagnostics, and related topics in nonequilibrium reacting flows. Contributed papers will describe contemporary experimental, analytical, and computational efforts. The conference program will include recent fundamental scientific advancements as well as many interdisciplinary contributions describing state-of-art technical developments and milestone achievements. Conference sessions will focus on plasma and laser physics/chemistry/kinetics, plasma diagnostics, plasma materials processing and environmental applications, space plasma physics and applications, plasma propulsion, laser devices and applications, laser optics and fluid-optics interactions, weakly ionized gas physics and applications, and MHD energy conversion science and technology with a wide ranging international perspective. The program will also incorporate an invited lecture by the recipient of the Plasmadynamics and Lasers Award. 6. 会议名称:42nd AIAA Thermophysics Conference 会议时间:27 - 30 Jun 2011 会议地点:Honolulu, Hawaii Venue: Sheraton Waikiki and the Hawaii Convention Center 会议简介:The 42nd AIAA Thermophysics Conference will feature papers covering all aspects of heat transfer and thermophysics. Emphasis is given to aerospace applications, but is not limited to this topic area. Topics range from basic research and development to applied and advanced technology, including novel experimental and computational observations, interdisciplinary papers 26 that bridge theoretical, experimental approaches, and papers that provide innovative concepts and analyses. Conference sessions will focus on technical topic areas related to all aspects of thermal energy transfer in aerospace and mechanical engineering applications. Special sessions will address recent advances along with joint sessions with collocated conferences. The Thermophysics Award Lecture will feature an invited lecture by the 2011 Thermophysics Award recipient. Additionally, each year, the AIAA Thermophysics Technical Committee offers a Best Paper Award in both the Professional and Student Categories (with the student receiving a monetary award). Student participation is strongly encouraged. 7. 会议名称:6th AIAA Theoretical Fluid Mechanics Conference 会议时间:27 - 30 Jun 2011 会议地点:Honolulu, Hawaii Venue: Sheraton Waikiki and the Hawaii Convention Center 会议简介:The 6th triennial AIAA Theoretical Fluid Mechanics Conference is being held in conjunction with the 41st AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and the 20th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference in order to facilitate interaction between the international theoretical fluid dynamics community and the broader fluid dynamics fraternity of researchers and practitioners. Papers will describe innovative analysis methods as well as their applications leading to new insights into fundamental flow physics. Investigations that explore the use of theoretical modeling of flow problems in the aerospace and mechanical engineering industries and/or interdisciplinary applications involving aeroacoustics, flow control, combustion, aerothermodynamics, and micro/nano-fluid mechanics also will be included. In addition to the contributed papers, invited speakers will present reviews and assessments of recent progress associated with theoretical fluid dynamics. 七、IEEE 最新会议(来源:http://www.ieee.org/index.html) 1. 会议名称:2011 IEEE Technology Time Machine (TTM) 会议时间:1 Jun - 3 Jun 2011 | 会议地点:Sheraton Hong Kong Hotel Hong Kong, China 会议简介:Covered a selected set of potentially high-impact emerging technologies, their current state of maturity, and scenarios for the future. 2. 会议名称:2011 10th International Workshop on Electronics, Control, Measurement and Signals (ECMS) 27 会议时间:01 Jun - 03 Jun 2011 会议地点:Technical University of Liberec Liberec, Czech Republic 会议简介:ECMS is a traditional workshop oriented on electronics; includes the topics focused on design of electric and microelectronic circuits, measurement technology, control and signal processing. As workshop is organised by Czech, French and Spanish universities, it also put emphasis on PhD students, their presentations in front of wide expert's audience. 3. 会议名称:2011 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium - MTT 2011 会议时间: 05 Jun - 10 Jun 2011 会议地点:Baltimore Convention Center Baltimore, MD, USA 会议简介:The IEEE International Microwave Symposium (IMS) is the world s foremost conference covering the UHF, RF, wireless, microwave, millimeter-wave, terahertz, and optical frequencies; encompassing everything from basic technologies to components to systems including the latest RFIC, MIC, MEMS and filter technologies, advances in CAD, modeling, EM simulation and more. The IMS includes technical and interactive sessions, exhibits, student competitions, panels, workshops, tutorials, and networking events. 4. 会议名称:2011 7th Conference on Ph.D. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME) 会议时间: 04 Jul - 08 Jul 2011 会议地点:Hotel Carlo Magno Madonna di Campiglio, Italy 会议简介:The objectives of PRIME are: - to encourage favourable exposure to Ph. D. students in the early stages of their careers; - to benchmark Ph.D. research in a friendly and cooperative environment; - to enable sharing of students and supervisors experiences of scientific and engineering research; - to connect Ph.D. students and their supervisors with companies and research centers. 5. 会议名称:2011 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting 会议时间: 24 Jul - 29 Jul 2011 会议地点:Detroit Renaissance Center Detroit, MI, USA 会议简介:IEEE Power & Energy Annual Meeting --Papers --Awards --Plenary --Committee Meetings --Governing Board --Receptions --Tech tours --Tutorials --Companions Program 6. 会议名称:2011 16th European Conference on Networks and Optical Communications - (NOC 2011) 会议时间: 20 Jul - 22 Jul 2011 会议地点:Northumbria University Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom 会议简介:The NOC 2011conference follows recent editions held in Algarve University (Faro, 28 Portugal), Valladolid (Spain), Krems (Austria), Stockholm (Sweden), Berlin (Germany) and London (UK). It combines fibre optics systems, networks and technology within a single event, providing a forum for promotion of new opportunities from industry, institutes of technology and academia. 7. 会议名称:2011 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems Engineering (CASE) 会议时间: 30 Jul - 31 Jul 2011 会议地点:Singapore Convention Centre Singapore, Singapore 会议简介:The objective of CASE 2011 is the premier forum for the presentation of new advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied Control, Automation and Systems Engineering. The conference will bring together leading researchers, engineers and scientists in the domain of interest from around the world. 8. 会议名称:2011 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED) 会议时间: 01 Aug - 03 Aug 2011 会议地点:Fukuoka Convention Center Fukuoka, Japan 会议简介:ISLPED is the premier forum for low power design and technologies, ranging from process and circuit technologies, to simulation and synthesis tools, to system level design and optimization. 9. 会议名称:2011 20th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks ICCCN 2011 会议时间: 01 Aug - 04 Aug 2011 会议地点:Sheraton Maui Resort and Spa Lahaina, HI, USA 会议简介:Covers the following and related areas: Computer Communications and Networks, Wireless and Sensor Networks, Optical Networks, High-Speed Systems/Grid, Internet Services, Multimedia and P2P, Network Security. 10. 会议名称:2011 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA) 会议时间: 07 Aug - 10 Aug 2011 会议地点:Empark Grand Hotel, Beijing No. 69 Banjing Haidian Distric Beijing, China 会议简介: The objective of ICMA 2011 is to provide a forum for researchers, educators, engineers, and government officials involved in the general areas of mechatronics, robotics, automation and sensors to disseminate their latest research results and exchange views on the future research directions. 29 八、SCI Essential Science Indicators HOT PAPERS(材料科学) 1.被引用次数: 240 题名: Polymer-Fullerene Bulk-Heterojunction Solar Cells 作者: DENNLER G; SCHARBER MC; BRABEC CJ 出处: ADVAN MATER 21 (13): 1323-1338 APR 6 2009 地址:Konarka Austria GmbH, Altenbergerstr 69, A-4040 Linz, Austria. Konarka Austria GmbH, A-4040 Linz, Austria. 2.被引用次数: 157 题名: Towards Wafer-Size Graphene Layers By Atmospheric Pressure Graphitization Of Silicon Carbide 作者: Emtsev Kv; Bostwick A; Horn K; Jobst J; Kellogg Gl; Ley L; Mcchesney Jl; Ohta T; Reshanov Sa; Rohrl J; Rotenberg E; Schmid Ak; Waldmann D; Weber Hb; Seyller T 出处:NAT MATER 8 (3): 203-207 MAR 2009 地址: Univ Erlangen Nurnberg, Lehrstuhl Tech Phys, Erwin Rommel Str 1, D-91058 Erlangen, Germany. Univ Erlangen Nurnberg, Lehrstuhl Tech Phys, D-91058 Erlangen, Germany. Univ Calif Berkeley, Lawrence Berkeley Lab, Adv Light Source, Berkeley, CA 94720 USA. Max Planck Gesell, Fritz Haber Inst, Dept Mol Phys, D-14195 Berlin, Germany. Univ Erlangen Nurnberg, Lehrstuhl Angew Phys, D-91058 Erlangen, Germany. Sandia Natl Labs, Surface & Interface Sci Dept, Albuquerque, NM 87185 USA. Univ Calif Berkeley, Lawrence Berkeley Lab, Natl Ctr Electron Microscopy, Berkeley, CA 94720 USA. 3.被引用次数: 134 题名:: Understanding Biophysicochemical Interactions At The Nano-Bio Interface 作者: Nel Ae; Madler L; Velegol D; Xia T; Hoek Emv; Somasundaran P; Klaessig F; Castranova V; Thompson M 出处:NAT MATER 8 (7): 543-557 JUL 2009 地址: Univ Calif Los Angeles, David Geffen Sch Med, Div NanoMed, Los Angeles, CA 90095 USA. Univ Bremen, Dept Prod Engn, Fdn Inst Mat Sci IWT, D-28359 Bremen, Germany. Univ Calif Los Angeles, Calif NanoSyst Inst, Los Angeles, CA 90095 USA. Penn State Univ, Dept Chem Engn, University Pk, PA 16802 USA. Univ Calif Los Angeles, Dept Civil & Environm Engn, Los Angeles, CA 90095 USA. Columbia Univ, Dept Earth & Environm Engn, Langmuir Ctr Colloids & Interfaces, New York, NY 10027 USA. Penn Bio Nano Syst, Doylestown, PA 18902 USA. NIOSH, Morgantown, WV 26505 USA. FEI Co, Hillsboro, OR 97124 USA. 30 4.被引用次数: 134 题名:: An Optical Cloak Made Of Dielectrics 作者: Valentine J; Li Js; Zentgraf T; Bartal G; Zhang X 出处:NAT MATER 8 (7): 568-571 JUL 2009 地址: Univ Calif Berkeley, NSF Nanoscale Sci & Engn Ctr, 3112 Etcheverry Hall, Berkeley, CA 94720 USA. Univ Calif Berkeley, NSF Nanoscale Sci & Engn Ctr, Berkeley, CA 94720 USA. Lawrence Berkeley Natl Lab, Div Mat Sci, Berkeley, CA 94720 USA. 5.被引用次数: 120 题名:: Physics And Applications Of Bismuth Ferrite 作者: Catalan G; Scott Jf 出处: ADVAN MATER 21 (24): 2463-2485 JUN 26 2009 地址:Univ Cambridge, Dept Earth Sci, Downing St, Cambridge CB2 3EQ, England. Univ Cambridge, Dept Earth Sci, Cambridge CB2 3EQ, England. 6.被引用次数: 115 题名:: Ionic-Liquid Materials For The Electrochemical Challenges Of The Future 作者: Armand M; Endres F; Macfarlane Dr; Ohno H; Scrosati B 出处: NAT MATER 8 (8): 621-629 AUG 2009 地址:Univ Picardie Jules Verne, CNRS, LRCS 6007, F-80039 Amiens, France. Tech Univ Clausthal, Inst Particle Technol, D-38678 Clausthal Zellerfeld, Germany. Monash Univ, Sch Chem, Clayton, Vic 3800, Australia. Monash Univ, ARC Ctr Excellence Electromat Sci, Clayton, Vic 3800, Australia. Tokyo Univ Agr & Technol, Dept Biotechnol, Koganei, Tokyo 1848588, Japan. Univ Sapienza, Dept Chem, I-00185 Rome, Italy. 7.被引用次数: 108 题名:: Recent Progress In Polymer Solar Cells: Manipulation Of Polymer: Fullerene Morphology And The Formation Of Efficient Inverted Polymer Solar Cells 作者: Chen Lm; Hong Zr; Li G; Yang Y 出处:ADVAN MATER 21 (14-15): 1434-1449 APR 20 2009 地址:Univ Calif Los Angeles, Dept Mat Sci & Engn, Los Angeles, CA 90095 USA. Solarmer Energy Inc, El Monte, CA 91731 USA. 8.被引用次数: 102 题名:: For The Bright Future-Bulk Heterojunction Polymer Solar Cells With Power Conversion Efficiency Of 7.4% 作者: Liang Yy; Xu Z; Xia Jb; Tsai St; Wu Y; Li G; Ray C; Yu Lp 出处: ADVAN MATER 22 (20): E135-+ MAY 25 2010 地址:Univ Chicago, Dept Chem, 5735 S Ellis Ave, Chicago, IL 60637 USA. Univ Chicago, Dept Chem, Chicago, IL 60637 USA. Solarmer Energy Inc, El Monte, CA 91731 USA. 31 9.被引用次数: 100 题名:: Redox-Based Resistive Switching Memories - Nanoionic Mechanisms, Prospects, And Challenges 作者: Waser R; Dittmann R; Staikov G; Szot K 出处: ADVAN MATER 21 (25-26): 2632-+ JUL 13 2009 地址:Julich Aachen Res Alliance, Sect Fundamentals Future Informat Technol JARA FI, D-52425 Julich, Germany. KFA Julich GmbH, Forschungszentrum, Inst Festkorperforsch, D-52425 Julich, Germany. Rhein Westfal TH Aachen, Inst Werkstoffe Elektrotech 2, D-52056 Aachen, Germany. 10.被引用次数:81 题名:Biodegradable Luminescent Porous Silicon Nanoparticles For In Vivo Applications 作者: Park Jh; Gu L; Von Maltzahn G; Ruoslahti E;Etc. 出处: NAT MATER 8 (4): 331-336 APR 2009 地址: Univ Calif San Diego, Dept Chem & Biochem, La Jolla, CA 92093 USA. Univ Calif San Diego, Mat Sci & Engn Program, La Jolla, CA 92093 USA. MIT, Harvard Mit Div Hlth Sci & Technol, Cambridge, MA 02139 USA. Univ Calif Santa Barbara, Burnham Inst Med Res, Santa Barbara, CA 93106 USA. Brigham & Womens Hosp, Div Med, Boston, MA 02115 USA. Univ Calif San Diego, Dept Bioengn, La Jolla, CA 92093 USA. 11.被引用次数: 78 题名: Energy-Level Alignment At Organic/Metal And Organic/Organic Interfaces 作者: Braun S; Salaneck Wr; Fahlman M 出处: ADVAN MATER 21 (14-15): 1450-1472 APR 20 2009 地址: Linkoping Univ, Dept Phys Chem & Biol, S-58183 Linkoping, Sweden. Linkoping Univ, Dept Biol & Chem, S-58183 Linkoping, Sweden. 12.被引用次数:78 题名: Electronic And Magnetic Phase Diagram Of Beta-Fe1.01se With Superconductivity At 36.7 K Under Pressure 作者: Medvedev S; Mcqueen Tm; Troyan Ia; Palasyuk T; Eremets Mi; Cava Rj; Naghavi S; Casper F; Ksenofontov V; Wortmann G; Felser C 出处: NAT MATER 8 (8): 630-633 AUG 2009 地址: Johannes Gutenberg Univ Mainz, Inst Anorgan & Analyt Chem, D-55099 Mainz, Germany. Max Planck Inst Chem, D-55128 Mainz, Germany. Princeton Univ, Dept Chem, Princeton, NJ 08544 USA. AV Shubnikov Crystallog Inst, Moscow 119333, Russia. Polish Acad Sci, Inst Phys Chem, PL-01224 Warsaw, Poland. Univ Paderborn, Dept Phys, D-33095 Paderborn, Germany. 13.被引用次数: 72 题名:Plasmonics For Improved Photovoltaic Devices 作者: Atwater Ha; Polman A 32 出处: NAT MATER 9 (3): 205-213 MAR 2010 地址: CALTECH, Ctr Sustainable Energy Res, Pasadena, CA 91125 USA. CALTECH, Thomas J Watson Labs Appl Phys, Pasadena, CA 91125 USA. FOM Inst AMOLF, Ctr Nanophoton, NL-1098 XG Amsterdam, Netherlands. 14.被引用次数: 72 题名:Plasmonic Analogue Of Electromagnetically Induced Transparency At The Drude Damping Limit 作者: Liu N; Langguth L; Weiss T; Kastel J; Fleischhauer M; Pfau T; Giessen H 出处: NAT MATER 8 (9): 758-762 SEP 2009 地址: Univ Stuttgart, Inst Phys 4, D-70569 Stuttgart, Germany. Tech Univ Kaiserslautern, Fachbereich Phys, D-67663 Kaiserslautern, Germany. Tech Univ Kaiserslautern, Res Ctr OPTIMAS, D-67663 Kaiserslautern, Germany. Univ Stuttgart, Inst Phys 5, D-70569 Stuttgart, Germany. 15.被引用次数: 70 题名:Emerging Applications Of Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Materials 作者: Stuart Mac; Huck Wts; Genzer J; Muller M; Ober C; Stamm M; Sukhorukov Gb; Szleifer I; Tsukruk Vv; Urban M; Winnik F; Zauscher S; Luzinov I; Minko S 出处: NAT MATER 9 (2): 101-113 FEB 2010 地址: Wageningen Univ, Lab Phys Chem & Colloid Sci, Dreijenpl 6, NL-6703 HB Wageningen, Netherlands. Wageningen Univ, Lab Phys Chem & Colloid Sci, NL-6703 HB Wageningen, Netherlands. Univ Cambridge, Dept Chem, Melville Lab Polymer Synth, Cambridge CB2 1EW, England. N Carolina State Univ, Dept Chem & Biomol Engn, Raleigh, NC 27695 USA. Univ Gottingen, Inst Theoret Phys, D-37077 Gottingen, Germany. 16.被引用次数: 70 题名:A Graphene Hybrid Material Covalently Functionalized With Porphyrin: Synthesis And Optical Limiting Property 作者: Xu Yf; Liu Zb; Zhang Xl; Wang Y; Tian Jg; Huang Y; Ma Yf; Zhang Xy; Chen Ys 出处: ADVAN MATER 21 (12): 1275-+ MAR 26 2009 地址: Nankai Univ, Key Lab Weak Light Nonlinear Photon, Minist Educ, Tianjin 300457, Peoples R China. Nankai Univ, Teda Appl Phys Sch, Tianjin 300457, Peoples R China. Nankai Univ, Key Lab Funct Polymer Mat, Coll Chem, Tianjin 300071, Peoples R China. Nankai Univ, Ctr Nanoscale Sci & Technol, Coll Chem, Tianjin 300071, Peoples R China. 17.被引用次数: 61 题名: High-Performance Organic Field-Effect Transistors 作者: Braga D; Horowitz G 出处: ADVAN MATER 21 (14-15): 1473-1486 APR 20 2009 地址: Univ Paris Diderot, ITODYS, F-75205 Paris 13, France. 33 18.被引用次数: 60 题名:COMPLEXITY IN BIOMATERIALS FOR TISSUE ENGINEERING 作者: PLACE ES; EVANS ND; STEVENS MM 出处: NAT MATER 8 (6): 457-470 JUN 2009 地址: Univ London Imperial Coll Sci Technol & Med, Dept Mat, London SW7 2AZ, England. Univ London Imperial Coll Sci Technol & Med, Inst Biomed Engn, London SW7 2AZ, England. 19.被引用次数: 55 题 名 :Highly Efficient Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cell Based On Co-Sensitization Of Cds/Cdse 作者: Lee Yl; Lo Ys 出处: ADV FUNCT MATER 19 (4): 604-609 FEB 24 2009 地址: Natl Cheng Kung Univ, Dept Chem Engn, Tainan 70101, Taiwan. 20.被引用次数: 50 题名:Reduction-Sensitive Polymers And Bioconjugates For Biomedical Applications 作者: Meng Fh; Hennink We; Zhong Z 出处: BIOMATERIALS 30 (12): 2180-2198 APR 2009 地址: Soochow Univ, Biomed Polymers Lab, Coll Chem Chem Engn & Mat Sci, Ren Ai Rd 199, Suzhou 215123, Peoples R China. Soochow Univ, Biomed Polymers Lab, Coll Chem Chem Engn & Mat Sci, Suzhou 215123, Peoples R China. Soochow Univ, Jiangsu Key Lab Organ Chem, Coll Chem Chem Engn & Mat Sci, Suzhou 215123, Peoples R China. Univ Utrecht, UIPS, Dept Pharmaceut, NL-3508 TB Utrecht, Netherlands. 21.被引用次数: 46 题名:Plasmonics For Extreme Light Concentration And Manipulation 作者: Schuller Ja; Barnard Es; Cai Ws; Jun Yc; White Js; Brongersma Ml 出处: NAT MATER 9 (3): 193-204 MAR 2010 地址: Geballe Lab Adv Mat, Stanford, CA 94305 USA. 22.被引用次数: 45 题名:Atomic Structure Of Conducting Nanofilaments In Tio2 Resistive Switching Memory Authors: Kwon Dh; Kim Km; Jang Jh; Jeon Jm; Lee Mh; Kim Gh; Li Xs; Park Gs; Lee B; Han S; Kim M; Hwang Cs 出处:NAT NANOTECHNOL 5 (2): 148-153 FEB 2010 地址: Seoul Natl Univ, Dept Mat Sci & Engn, Seoul 151744, South Korea. Seoul Natl Univ, Interuniv Semicond Res Ctr, Seoul 151744, South Korea. Samsung Adv Inst Technol, Analyt Res Lab, Suwon 440600, South Korea. Ewha Womans Univ, Dept Chem, Seoul 120750, South Korea. 23.被引用次数: 45 题名:Self-Assembled Peptide-Based Hydrogels As Scaffolds For Anchorage-Dependent Cells 34 作者: Zhou M; Smith Am; Das Ak; Hodson Nw; Collins Rf; Ulijn Rv; Gough Je 出处: BIOMATERIALS 30 (13): 2523-2530 MAY 2009 地址: Univ Manchester, Sch Mat, Ctr Mat Sci, Grosvenor St, Manchester M1 7HS, Lancs, England. Univ Manchester, Sch Mat, Ctr Mat Sci, Manchester M1 7HS, Lancs, England. Univ Manchester, Manchester Interdisciplinary Bioctr, Manchester M1 7ND, Lancs, England. Univ Manchester, Manchester M13 9PT, Lancs, England. Univ Strathclyde, Dept Pure & Appl Chem, WestCHEM, Glasgow G1 1XL, Lanark, Scotland. 24.被引用次数: 43 题名:Roll-To-Roll Production Of 30-Inch Graphene Films For Transparent Electrodes 作者: Bae S; Kim H; Lee Y; Xu Xf; Park Js; Zheng Y; Balakrishnan J; Lei T; Kim Hr; Song Yi; Kim Yj; Kim Ks; Ozyilmaz B; Ahn Jh; Hong Bh; Iijima S 出处:NAT NANOTECHNOL 5 (8): 574-578 AUG 2010 地址: Sungkyunkwan Univ, SKKU Adv Inst Nanotechnol SAINT, Suwon 440746, South Korea. Sungkyunkwan Univ, Ctr Human Interface Nano Technol HINT, Suwon 440746, South Korea. Sungkyunkwan Univ, Dept Chem, Suwon 440746, South Korea. Sungkyunkwan Univ, Sch Mech Engn, Suwon 440746, South Korea. Sungkyunkwan Univ, Sch Adv Mat Sci & Engn, Suwon 440746, South Korea. Natl Univ Singapore, NanoCore & Dept Phys, Singapore 117576, Singapore. Natl Univ Singapore, NanoCore & Dept Phys, Singapore 117542, Singapore. Samsung Techwin, Digital & IT Solut Div, Songnam 462807, South Korea. Pohang Univ Sci & Technol, Dept Chem, Ctr Superfunct Mat, Pohang 790784, South Korea. Natl Inst Adv Ind Sci & Technol, Nanotube Res Ctr, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3058565, Japan. Meijo Univ, Fac Sci & Engn, Nagoya, Aichi 4688502, Japan. 25.被引用次数: 43 题名:Stretchable Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode Display Using Printable Elastic Conductors 作者: Sekitani T; Nakajima H; Maeda H; Fukushima T; Aida T; Hata K; Someya T 出处:NAT MATER 8 (6): 494-499 JUN 2009 地址: Univ Tokyo, Sch Engn, Quantum Phase Elect Ctr, Bunkyo Ku, 7-3-1 Hongo, Tokyo 1138656, Japan. Univ Tokyo, Sch Engn, Quantum Phase Elect Ctr, Bunkyo Ku, Tokyo 1138656, Japan. Dai Nippon Printing Co Ltd, R&D Ctr, Kashiwa, Chiba 2770871, Japan. RIKEN, Funct Soft Matter Engn Lab, Adv Sci Inst, Wako, Saitama 3510198, Japan. Univ Tokyo, Sch Engn, Dept Chem & Biotechnol, Bunkyo Ku, Tokyo 1138656, Japan. Japan Sci & Technol Agcy, Natl Museum Emerging Sci & Innovat, Nanospace Project, Koto Ku, Tokyo 1350064, Japan. Natl Inst Adv Ind Sci & Technol, Res Ctr Adv Carbon Mat, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3058565, Japan. Univ Tokyo, Inst Nano Quantum Informat Elect, Meguro Ku, Tokyo 1538505, Japan. Univ Tokyo, Dept Elect & Elect Engn, Bunkyo Ku, Tokyo 1138656, Japan. 35 承 办:西北工业大学图书馆信息咨询与情报研究部 审 稿:刘秋让 电 话:(029)88492928 编 辑:燕 辉 张 燕 E-mail: gyj@nwpu.edu.cn 责任编辑:郭永建 36