File
advertisement

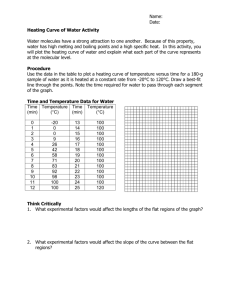
1. What is the lowest possible temperature in Kelvin units? ________________ 2. Which has the greater amount of thermal energy a. a cup of hot water b. an iceberg at the freezing point of water 3. Which of the following statements is a direct application of the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics? a. Block A has twice the temperature of Block B before they are brought into contact. Upon contact, thermal energy flows from A to B. b. A sample of gas within a cylinder with a piston is held at constant temperature and pressure while it is allowed to expand. During this process, the gas absorbs heat from its surroundings. c. The motor of a refrigerator uses electric energy to remove heat from inside the refrigerator and transfer it to the room. d. A thermometer is calibrated by placing it in an ice water bath within an adiabatic container until the thermometer is in thermal equilibrium with the ice water. 4. Conservation of Energy is another name for a. First Law of thermodynamics b. Second Law of thermodynamics c. Zeroth Law of thermodynamics d. Third Law of thermodynamics 5. The disordering effect (entropy) of heat a. increases with increasing temperature c. is constant b. decreases with increasing temperature d. increases with decreasing temperature 6. The fact that heat flows spontaneously from hot to cold is a. not always true b. the First Law of Thermodynamics c. the Second Law of Thermodynamics d. only true for isothermal processes 7. Which law of thermodynamics helps in calculating the absolute entropies of various substances at different temperatures? a. Zeroth law b. Ist law c. II law d. IIIrd law 8. Describe a reaction (chemical or physical) that is exothermic. Why is it exothermic? 9. Describe a reaction (chemical or physical) that is endothermic. Why is it endothermic? Complete the following Data Table: RXN #1: Baking soda + citric acid RXN #2: Mg + HCl Initial Temperature (oC) 2.8 oC 37.8 oC Final Temperature (oC) 21.9 oC 22.1 oC Temperature Change (oC) (Tf – Ti) ENDO or EXO a) Which reaction would feel cold to the touch? b) Which reaction gave off heat energy to the surroundings? c) Which reaction will have a negative q value? 3. Write the heat equation in the space below. a) What are the units for heat? b) What are the units for heat capacity? 4. What is the difference between heat and temperature? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the specific heat of water? 6. How much energy must be absorbed by 20.0 g of water to increase its temperature from 283.0 °C to 303.0 °C? 7. When 15.0 g of steam drops in temperature from 275.0 °C to 250.0 °C, how much heat energy is released? 8. How much energy is required to heat 120.0 g of water from 2.0 °C to 24.0 °C? 9. If 720.0 g of steam at 400.0 °C absorbs 800.0 kJ of heat energy, what will be its increase in temperature? 10. How much heat (in kJ) is given out when 85.0 g of lead cools from 200.0 °C to 10.0 °C? (Cp of lead = 0.129 J/g °C) 11. If it takes 41.72 joules to heat a piece of gold weighing 18.69 g from 10.0 °C to 27.0 °C, what is the specific heat of the gold? Heating Curve Worksheet: 2) If the specific heat of ethanol is 2.44 kj/kg, how much heat would it take to heat 250 grams of ethanol from 25˚C to 78˚C? 3) If the heat of vaporization of ethanol is 38,560 J/g, how much heat would it take to cause 250 grams of ethanol to vaporize completely? 100˚C Temperature 1) Ethyl alcohol boils at 78˚C and freezes at –114˚C. Sketch a heating curve for ethanol starting at room temperature. Label each section of the graph. 80˚C 60˚C 40˚C 20˚C Time 4) Which question above involved a calculation of a change in potential energy? 5) Which question above involved a calculation of a change in kinetic energy? 6) Data for water is shown below. If 1.00 g of steam at 150˚C is cooled to –50˚C, sketch a graph of temperature vs time for the process: a) What is the heat of the cooling steam? b) What is the heat of condensation? c) What is the heat of the cooling water? 7) Benzene melts/freezes at 5.5˚C and boils/condenses at 80.1˚C. Sketch a heating curve for benzene being heated from -40˚C to 140˚C. 8) Answer the following about the heating curve you drew. a) Where in the curve is the kinetic energy changing? b) Where in the curve is the potential energy changing? c) Where is the speed of the particles changing? d) Where are the particles breaking bonds or attractions? e) Where are the particles gaining energy?