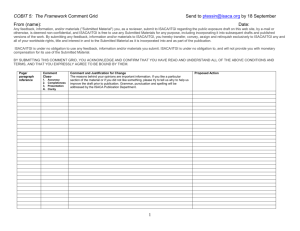
Alignment Grid for the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information Security Management
To map a program to the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information Security Management,
enter the name of the course(s) or session(s) in the program that covers each topic area or
subtopic description along with the amount of time (in hours) devoted to covering the topic in
each table. If a described topic is not covered, record a 0 (zero) in the column for contact hours.
To be in alignment with the model, the total time spent, in hours, should be at least 244 hours
and all areas in the model curriculum should have reasonable coverage. Note: When mapping a
graduate program, include the prerequisites from the undergraduate program.
Before beginning this process:
The current course syllabi should be obtained. Current and expanded course outlines provide
more detail and are better sources.
The current textbook supporting the classes and the visual media/projects used in those
classes should be accessible. For a question on content, refer to the course textbook or
PowerPoint slides.
If some of the subject matter is taught in other departments or colleges, a representative who
is knowledgeable of what is taught in those classes may need to provide assistance. For this
reason, an undergraduate program may take more time to map than a graduate program.
See if a second monitor is available; the process is facilitated by looking at the model matrix
on one and the syllabus/expanded course outline on another
The mapping process steps are listed in figure 6.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Figure 6—Mapping Process Steps
Identify all direct and support courses that apply to the program. Course syllabi are to contain at least the
following information: school name and address, course title, course number, contact hours, faculty
member names and credentials, terms offered, the purpose of the course, the objectives of the course, and
the course text.
Make sure the current syllabi or expanded course outlines and support materials for the courses are
accessible. It takes approximately 16 hours to complete the mapping, if expanded course outlines are
available from which information can be extracted.
Proceed one by one. Select the first course in the program, examine the elements and subject matter, and
map to the model. Literally, proceed week by week.
Use key words from the ISACA template subtopics to search the syllabi to identify matches. Once a match
is made, estimate the amount of time the subject was covered based on the syllabus.
If unsure of the content of the subject covered, go to the textbook and PowerPoint slides/materials used.
Note that generic titles used often cover more than what is implied.
Remember to allocate the time per course and identify the course covering each subject. For example, a
quarter system may have 10 weeks and four contact hours per week (40 hours), but some courses may have
lab or project requirements that may result in more than 40 hours.
Map course by course, and keep track of allocation. This is easiest for those familiar with the program and
who have the information available.
After completing all courses, go back and double-check that the selections/placement are the best possible
and seem reasonable.
Have a colleague check the mapping.
Submit the completed tables to ISACA for review by e-mail: sdonahue@isaca.org , fax +1.847.253.1443
or mail to the attention of the Manager of Information Security Practices at ISACA, 3701 Algonquin Road,
Suite 1010, Rolling Meadows, IL 60008, USA.
2008 ISACA. All rights reserved. Page 1
Alignment Grid for the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information Security Management
If the program is found to be in alignment with the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information
Security Management, the program may be posted on the ISACA web site and graduates of the
program will qualify for one year of work experience toward the CISM certification. The
following pages include figures 1 through 5 with blank columns added for the course and
number of hours which institutions can use to map their programs to the model curriculum.
Topics
Hours
22
Security
governance
30
Information
security
strategy
Total Hours
Figure 1—Information Security Governance Domain
Subtopics
Course Covering Topic
Effective information security
(Course number, item number on
governance
syllabus, paragraph description)
Roles and responsibilities of senior
management
Information security concepts (e.g.,
certified internal auditor [CIA] model,
borders and trust, encryption, trusted
systems, certifications, defense by
diversity, depth, obscurity, least
privilege, life cycle management,
technologies)
Information security manager
(responsibilities, senior management
commitment, reporting structures)
Scope and charter of information
security governance (laws, regulations,
policies, assurance process integration,
convergence)
Information security metrics
Views of strategy
Developing an information security
strategy aligned to business strategy
Information security strategy objectives
Architectures and frameworks (COBIT,
ISO 27002)
Determining current state of security
Strategy resources (e.g., policies,
standards, controls, education,
personnel)
Strategy constraints (e.g., regulatory,
culture, costs, resources)
Action plan for strategy
52
2008 ISACA. All rights reserved. Page 2
Hours
Alignment Grid for the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information Security Management
Topics
Hours
24
Risk
management
30
Risk
assessment
Total Hours
Figure 2—Information Risk Management
Subtopics
Course Covering Topic
Overview of risk management
Risk management strategy
Effective information security risk
management
Information security risk management
concepts (e.g., threats, vulnerabilities,
risks, attacks, BDP/DR, SLA,
governance) and technologies (e.g.,
authentication, access controls,
nonrepudiation, environmental
controls, availability/reliability
management)
Implementing risk management
Risk assessment (e.g., risk assessment
methodologies, options on handling
risk)
Controls and countermeasures
Information resource valuation
Recovery time objectives
Integration with life cycle processes
IT control baselines
Risk, monitoring and communication
54
2008 ISACA. All rights reserved. Page 3
Hours
Alignment Grid for the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information Security Management
Topics
Hours
Program
development
44
Total Hours
44
Figure 3—Information Security Program Development
Subtopics
Course Covering Topic
Effective information security program
development
Information security manager (roles,
responsibilities, obtaining senior
management commitment)
Scope and charter of information
security program development
(assurance function integration,
challenges in development)
Information security program
development objectives (goal,
objectives, outcomes, risks, testing,
standards, updating)
Defining an information security
program development road map
Information security program resources
(e.g., documentation, controls,
architecture, personnel, change
processes)
Implementing an information security
program (e.g., policies, training and
awareness, controls)
Information infrastructure, architecture,
laws, regulations and standards
Physical and environmental controls
Information security program
integration
Information security program
development metrics (e.g., strategic
alignment, value delivery, resource
management, performance)
2008 ISACA. All rights reserved. Page 4
Hours
Alignment Grid for the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information Security Management
Topics
Hours
Information
security
management
overview
11
Measuring
information
security
program
management
24
Implementing
information
security
management
23
Total Hours
58
Figure 4—Information Security Program Management
Subtopics
Course Covering Topic
Importance and outcomes of effective
security management
Organizational and individual roles and
responsibilities
Information security management
framework
Measuring information security
management performance
Common information security
management challenges
Determining the state of information
security management
Information security management
resources
Information security management
considerations
Implementing information security
management (e.g., action plans,
policies, service providers,
assessments)
2008 ISACA. All rights reserved. Page 5
Hours
Alignment Grid for the ISACA Model Curriculum for Information Security Management
Figure 5—Information Management and Response Domain
Topics
Hours
12
Incident
management
and response
overview
Defining
incident
management
procedures
12
12
Developing
an incident
response plan
Subtopics
Incident management and response
Incident management concepts
Scope and charter of incident
management
Information security manager
Incident management objectives
Incident management metrics and
indicators
Defining incident management
procedures
Incident management resources
Current state of incident response
capability
Elements of an incident response plan
(gap analysis)
Developing response and recovery
plans
Testing response and recovery plans
Course Covering Topic
Executing response and recovery
plans
Documenting events
Postincident reviews
Total Hours
36
Grand Total
244
Total hours for figures 1 through 5
2008 ISACA. All rights reserved. Page 6
Hours