Vocabulary Activities
advertisement

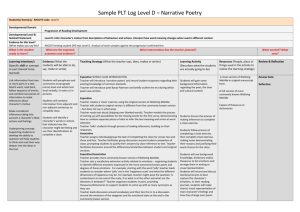
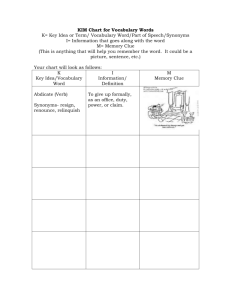
Vocabulary Activities There are a number of ways of increasing student’s vocabulary in science. 1. Vocabulary Quizzes A. Matching words to definitions: Cell Vocabulary Quiz Directions: Match the vocabulary words on the left with the definitions on the right. 1. tissue the central, essential, or highly concentrated part around which other parts are grouped. 2. vacuole a musical instrument consisting of a keyboard attached to a device that forces air through a number of pipes to produce a wide range of sounds; pipe organ. 3. chromosome a membranous enclosure within a cell that contains substances isolated from the protoplasm, such as dissolved acids. 4. chlorophyll (chlorophyl) the ground protoplasm of cells that is outside the nucleus. 5. cell membrane any of the very tiny rodlike or stringlike structures that occur in nearly all cells of plants and animals, and that process food for energy. 6. chloroplast a small spherical body in the nucleus of a cell, consisting of protein and RNA. 7. cell wall the mass of like cells in an animal or plant body, esp. as they form a specific organ: 8. nucleolus one of the tiny, threadlike, DNA-containing bodies found in the cell nuclei of all plants and animals, responsible for transmitting hereditary characteristics. 9. organ the green pigment in the leaves and stems of plants that is necessary for the production of plant food by photosynthesis. 10. cytoplasm the rigid outermost layer of a plant cell, which is made of cellulose. 11. nucleus a small oval green bit of protoplasm that contains chlorophyll and is the location of photosynthesis. 12. mitochondrion the semipermeable membrane that encloses the contents of a cell; plasma membrane. You can find further examples at http://www.teach-nology.com/worksheets/language_arts/vocab/ 1 B. Science Hangman Always a fun activity. A sample: What word is this? Clue: The thick covering around a plant cell membrane. What word is this? Clue: State in which an atom has a higher potential energy than its ground state. What word is this? Clue: The outer layer of the Earth that makes up the continents and the ocean floors. There are websites with activities in all science subjects, such as: http://education.jlab.org/vocabhangman/index.html http://www.eram.k12.ny.us/education/components/scrapbook/default.php?sectiondetailid=38249 http://www.quia.com/hm/158237.html 2 You can follow up the vocabulary quizzes by giving students Regents questions that contain these words to further reinforce the context of the words. 2. CLOZE ACTIVITIES What is Cloze Procedure? Cloze procedure is a technique in which words are deleted from a passage according to a wordcount formula or various other criteria. The passage is presented to students, who insert words as they read to complete and construct meaning from the text. This procedure can be used as a diagnostic reading assessment technique. What is its purpose? It is used: to identify students' knowledge and understanding of the reading process to determine which cueing systems readers effectively employ to construct meaning from print to assess the extent of students' vocabularies and knowledge of a subject to encourage students to monitor for meaning while reading to encourage students to think critically and analytically about text and content How do I do it? To prepare materials for Cloze exercises, any of the following techniques may be used: 1. Select a self-contained passage of a length appropriate for the grade level of the students being assessed. Use materials easily read by the students. 2. Leave the first and last sentences and all punctuation intact. 3. Carefully select the words for omission using a word-count formula, such as every fifth word or other criteria. To assess students' knowledge of the topic or their abilities to use semantic cues, delete content words which carry meaning, such as nouns, main verbs, adjectives and adverbs. To assess students' use of syntactic cues, delete some conjunctions, prepositions and auxiliary words. 4. When preparing the final draft of the passage, make all blanks of equal length to avoid including visual clues about the lengths of omitted words. 5. Have the students read the entire passage before they fill in the blanks. 6. Encourage the students to fill each blank if possible. 7. Although there should be no time limit for this exercise, the time necessary for completion should be noted. 8. Suggest that students reread the completed passage. To be able to maintain meaning while reading a text, a student needs to be able to read over 90% of it, therefore blanking out more than 10% of the words in a Cloze passage turns it into an illegible text for many students. 3 Fill in the blanks below with words from this box: Neptune solar asteroids orbit dinosaurs Mercury gas giants Mars Jupiter water Earth Pluto nine temperature Saturn Venus planetoids comets terrestrial Uranus tail The Solar System The _______________ system is the group of planets that _____________ our Sun. There are _________________ known planets in our solar system, but some observers think they have spotted others beyond the orbit of _______________. The Terrestrial Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are called _________________ planets because they have rocky surfaces. _______________, of course, is the planet we live on. _______________ is the closest planet to the sun. ________________, which is also called the evening star, has a ______________ of 500 degrees Celsius and clouds of sulfuric acid. _________________ is known as the red planet. Recently, frozen ______________ was discovered there. The Gaseous Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are called __________________ because they are big and made mostly of gas. _______________ is the largest planet in the solar system. _________________ is famous for its rings. _______________ also has rings but is not as famous as Saturn. _____________ is named after the god of the sea. Planetoids: Asteroids and Comets There are many other ______________ in the solar system. Between Mars and Jupiter there is a belt of small rocky objects called _______________. As well, balls of ice and rock called _______________ occasionally come close to the sun creating a bright ________________ that can be seen from Earth. Some scientists think the _____________ became extinct when one of these comets came crashing into the Earth. 4 Fill in the blanks below with words from this box: evaporation evaporates heating droplets runoff rain sunny clouds heavy plants snow rivers precipitate vapor oceans hail cycle streams condenses atmosphere lakes glaciers crystals Evaporation On a warm, __________________ day, water in a glass of water seems to slowly disappear. This is because the energy from the sun is _______________ the water up and turning the liquid water into water ______________. This process is called ___________________. When the water ________________, it becomes an invisible gas in the _____________________. Evaporation takes places all over the earth, but especially in the ________________ and ________________ where there is lots of water. Condensation As the water vapor rises, it cools off and ______________________ into water _________________. If the water vapor becomes extremely cold, it will form ice ________________ instead of water droplets. As the water droplets or ice crystals grow bigger and more numerous, they form ___________________. Precipitation If water droplets or ice crystals become too _______________, they can’t stay in the air. They _________________. Water droplets precipitate as ________________ and ice crystals precipitate as _________________. Sometimes, the rain freezes before it hits the earth and precipitates as _________________. Runoff This precipitation gathers into ________________ and _________________ that flow down to the lakes and oceans. This is called __________________. Not all of the water makes it back to the oceans and lakes right away. Some of it is used by animals and ________________. Some is frozen into ___________________. Eventually, the animals and plants breathe the water out and the glaciers melt, releasing the water back into the water _______________. Further examples of Cloze Activities can be found at http://bogglesworldesl.com/cloze_activities.htm http://www.teach-nology.com/worksheets/language_arts/cloze/ You can use a number of websites to help build your own Cloze activities as well: http://www.edhelper.com/cloze.htm http://l.georges.online.fr/tools/cloze.html 5 3. WORD WHEELS After using the Cloze Activities, you can begin to get students to build word wheels. A word wheel is a way of linking definitions together in context so that students begin to make connections between key words. For instance, say we had the following words on our word wall: photosynthesis, respiration & energy. The idea is to link these words together with either words or phrases: ENERGY PHOTOSYNTHESIS is required for which is the opposite process of which produces RESPIRATION The good thing about this activity is that students can only complete it if they know the words and their context. Begin with just a linear progression of 2 or 3 words and gradually increase the number of words. Eventually you can do group work where the groups compete to see who can link the most words together. The challenge is then to see who can do this in such a way as the last word links back to the first word! You can also differentiate this activity but giving some student the phrases or linking words For example, find a sentence that contains key words from the unit: “Ribosomes are organelles within cells that are involved in making proteins.” Cut up the sentence into words or groups of words: organelles are within ribosomes that are involved in making cells proteins Give groups different combinations and ask them to write a sentence containing the word 1. All 2. Organelles; ribosomes; protein 3. Cells; protein; organelles 4. Cells; ribosomes; organelles 5. Ribosomes; that are involved in making; cells 6 4. WORD MAP Skills Objectives Use prior knowledge to fi nd word meaning. Use dictionary skills. Use word association to enhance learning. In science, students must be able to communicate ideas. An expansive vocabulary is critical to communicating those ideas effectively. A Word Map is a graphic organizer that helps students build their vocabulary. Rather than just memorize words and terms, students can use the map to help them retain learning, use vocabulary in context, and develop a framework on which to build new knowledge. A word map also works well as a prereading or postreading activity. 1. Vocabulary words are often remembered because of meaningful associations rather than repetition. To demonstrate how a word clue or association can be used, tell students that the prefix telemeans “at a distance” and is used to describe instruments thatoperate over distance. Prompt students to list words that begin with the prefix tele-, such as telephone, television, telegraph, and telephoto. Write the words on the board. Discuss how knowing the meaning of the prefix tele- offers a clue about the meaning of the word. 2. Draw a simple word map on the board, and give students a copy of the Vocabulary Word Map reproducible Distribute dictionaries, and write the following vocabulary list on the board (or use your own list): combustibility, malleability, conductivity, insulator, mixture, solution, solubility. 3. Demonstrate how to fill in the Vocabulary Word Map. Write combustibility in the center circle. Ask a volunteer to use prior knowledge to guess the word’s meaning. Write the answer in the box labeled My Definition. 4. Then have students look up the definition of combustibility in a dictionary. Have them tell you what to write in the box labeled Dictionary Definition. 7 5. Point out that a dictionary often includes the origin of the word or root word. Knowing the origin of a word can help students remember the definition. For combustibility, the origin of its root word combust means “burned up.” Write the word origin or other clues in the box labeled Word Clue. 6. Have students suggest a picture that shows the meaning of the word. Draw one of their suggestions, such as a match or campfire, in the box labeled Picture. 7. The last box labeled Association is for any clue that will help a student remember the definition of the word. For example: The b in combustibility stands for burn. Have students brainstorm several possible associations, and write one of their suggestions in the box. Review the completed map with students, and check for understanding. 8. Invite students to complete their own vocabulary word map using another word from the vocabulary list. After they finish, have students with the same vocabulary word compare their results. 9. Invite students to read their vocabulary word maps to the class. Discuss how word clues can help them remember vocabulary words. Extended Learning • Encourage students to complete word maps for new science vocabulary taught throughout the year. They can store the maps in a binder or a science portfolio. • Use pairs of index cards to create vocabulary sets, one card with the vocabulary word and one card with the definition. Give half of the class vocabulary cards and the other half definition cards. Have students take turns asking questions to find their vocabulary word or definition match. • Use a variety of word searches, crosswords, scrambled words, and other kinds of word puzzles to help students learn science vocabulary. You may go online to find resources, such as Jefferson Lab at: http://education.jlab.org/vocabhangman. 8 Name _____________________________ Date __________________ Vocabulary Word Map Directions: Write a vocabulary word in the center circle. Then fill in each book about the word 9 SCIENCE GRAPHIC ORGANIZER Name: ___________________________ Rewrite the problem in your own words. Identify facts needed to solve the problem. Put the facts in a logical order or sequence. Check to see if your answer is reasonable 10