Student Note Outline
advertisement

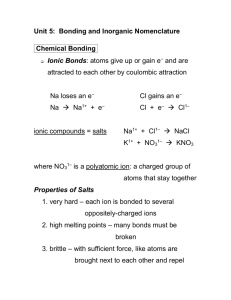
Unit 5: Bonding and Inorganic Nomenclature Name: ____________________ Chemical Bonding Ionic Bonds: species give up or gain e– and are attracted to each other by coulombic attraction ionic compounds = salts where NO3– is a polyatomic ion: oxyanions: polyatomic ions containing oxygen “Most common” oxyanions: BrO3– ClO3– PO43– IO3– NO3– SO42– CO32– If an oxyanion differs from the above by the # of O atoms, the name changes are as follows: EX. one more O = per_____ate “most common” # of O = _____ate one fewer O = _____ite two fewer O = hypo_____ite Name the following ions. SO32– BrO– NO2– ClO4– The “most common” oxyanions previously mentioned should be memorized. You should memorize the following as well: OH– CH3COO– CrO42– CN– NH4+ Cr2O72– Properties of Ionic Compounds (i.e., of Salts) 1. very hard – 2. high melting points – 3. brittle – 1 MnO4– …atoms share e– to get a full valence shell Covalent Bonds covalent compounds = molecular compounds -- have lower melting points than do ionic compounds In metals, valence shells of atoms overlap, so v.e– Metallic Bonds are free to travel between atoms through material. Properties of Metals Writing Formulas of Ionic Compounds chemical formula: To write an ionic compound’s formula, we need: 1. the two types of ions 2. the charge on each ion EX. Na+ and Ba2+ and F– Na+ O2– and Ba2+ and O2– F– charge on cation / anion “becomes” subscript of anion / cation criss-cross rule: ** Warning: EX. Al3+ and O2– In3+ and Br– Ba2+ and S2– Compounds Containing Polyatomic Ions Parentheses are req’d only when you need more than one “bunch” of a particular polyatomic ion. EX. Ba2+ and SO42– Sn4+ and SO42– Mg2+ and NO2– Fe3+ and Cr2O72– NH4+ and ClO3– NH4+ and N3– 2 Inorganic Nomenclature Ionic Compounds (cation/anion combos) Fixed-Charge Cations with Elemental Anions The fixed-charge cations are: A. To name, given the formula: 1. Use name of cation. 2. Use name of anion (it has the ending “ide”). EX. NaF Na2O BaO BaF2 B. To write formula, given the name: 1. Write symbols for the two types of ions. 2. Balance charges to write formula. EX. silver sulfide zinc phosphide calcium iodide Variable-Charge Cations with Elemental Anions The variable-charge cations are: A. To name, given the formula: 1. Figure out charge on cation. 2. Write name of cation. 3. Put Roman numerals in ( ) to show cation’s charge. 4. Write name of anion. EX. FeO CuBr Fe2O3 CuBr2 B. To find the formula, given the name: 1. Write symbols for the two types of ions. 2. Balance charges to write formula. EX. cobalt(III) chloride tin(IV) oxide 3 tin(II) oxide Compounds Containing Polyatomic Ions Insert name of ion where it should go in the compound’s name. EX. EX. Write formulas: ammonium chlorate iron(III) nitrite zinc phosphate ammonium phosphide lead(II) permanganate Write names: (NH4)3N (NH4)2SO4 U(CrO4)3 AgBrO3 Cr2(SO3)3 Covalent Compounds -- contain two types of nonmetals ** Key: What to do: EX. Use Greek prefixes to indicate 1– 6– how many atoms of each element, 2– 7– but don’t use “mono” on first element. 3– 8– 4– 9– 5– 10 – carbon dioxide N2O5 CO carbon tetrachloride dinitrogen trioxide NI3 Acid Nomenclature binary acids: acids w/H and one other element Binary Acid Nomenclature 1. Write “hydro.” 2. Write prefix of the other element, followed by “-ic acid.” HCl hydroiodic acid HBr hydrosulfuric acid 4 oxyacids: acids containing H, O, and one other element Oxyacid Nomenclature For “most common” forms of the oxyanions, write prefix of oxyanion, followed by “-ic acid.” HClO3 sulfuric acid H2CO3 phosphoric acid If an oxyacid differs from the above by the # of O atoms, the name changes are: one more O = per_____ic acid “most common” # of O = _____ic acid one fewer O = _____ous acid two fewer O = hypo_____ous acid HClO4 HClO2 phosphorous acid HClO3 HClO hypobromous acid Traditional (or Latin) System of Nomenclature …used historically (and still some today) to name compounds w/variable-charge cations To use: 1. Use Latin root of cation. 2. Use -ic ending for higher charge; -ous ending for lower charge. 3. Then say name of anion, as usual. EX. Element Latin root -ic -ous gold, Au aur- Au3+ Au+ lead, Pb plumb- Pb4+ Pb2+ tin, Sn stann- Sn4+ Sn2+ copper, Cu cupr- Cu2+ Cu+ iron, Fe ferr- Fe3+ Fe2+ Write formulas: Write names: cuprous sulfide Pb3P4 auric nitrite Pb3P2 ferrous fluoride Sn(OH)4 5 Empirical Formula and Molecular Formula Compound Molecular Formula glucose C6H12O6 propane C3H8 butane C4H10 naphthalene C10H8 sucrose C12H22O11 octane C8H18 6 Empirical Formula