1 - Department of Biological Sciences
advertisement
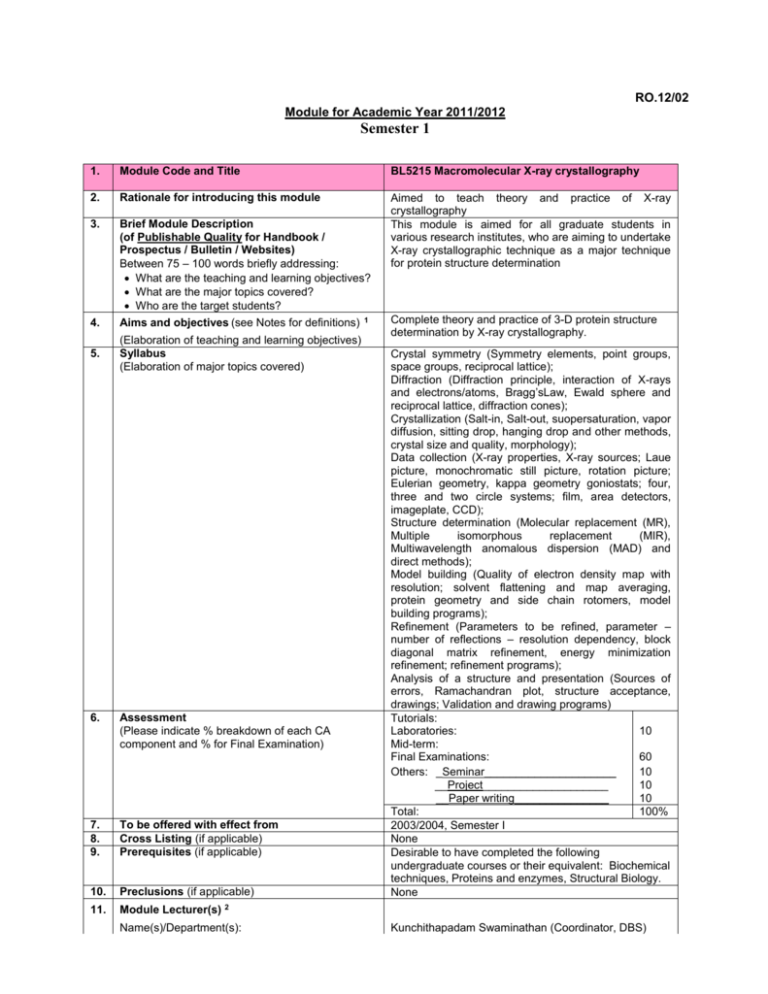
RO.12/02 Module for Academic Year 2011/2012 Semester 1 1. Module Code and Title BL5215 Macromolecular X-ray crystallography 2. Rationale for introducing this module 3. Brief Module Description (of Publishable Quality for Handbook / Prospectus / Bulletin / Websites) Between 75 – 100 words briefly addressing: What are the teaching and learning objectives? What are the major topics covered? Who are the target students? Aimed to teach theory and practice of X-ray crystallography This module is aimed for all graduate students in various research institutes, who are aiming to undertake X-ray crystallographic technique as a major technique for protein structure determination 4. Aims and objectives (see Notes for definitions) 5. (Elaboration of teaching and learning objectives) Syllabus (Elaboration of major topics covered) 6. Assessment (Please indicate % breakdown of each CA component and % for Final Examination) 7. 8. 9. To be offered with effect from Cross Listing (if applicable) Prerequisites (if applicable) 10. Preclusions (if applicable) 11. Module Lecturer(s) 2 Name(s)/Department(s): 1 Complete theory and practice of 3-D protein structure determination by X-ray crystallography. Crystal symmetry (Symmetry elements, point groups, space groups, reciprocal lattice); Diffraction (Diffraction principle, interaction of X-rays and electrons/atoms, Bragg’sLaw, Ewald sphere and reciprocal lattice, diffraction cones); Crystallization (Salt-in, Salt-out, suopersaturation, vapor diffusion, sitting drop, hanging drop and other methods, crystal size and quality, morphology); Data collection (X-ray properties, X-ray sources; Laue picture, monochromatic still picture, rotation picture; Eulerian geometry, kappa geometry goniostats; four, three and two circle systems; film, area detectors, imageplate, CCD); Structure determination (Molecular replacement (MR), Multiple isomorphous replacement (MIR), Multiwavelength anomalous dispersion (MAD) and direct methods); Model building (Quality of electron density map with resolution; solvent flattening and map averaging, protein geometry and side chain rotomers, model building programs); Refinement (Parameters to be refined, parameter – number of reflections – resolution dependency, block diagonal matrix refinement, energy minimization refinement; refinement programs); Analysis of a structure and presentation (Sources of errors, Ramachandran plot, structure acceptance, drawings; Validation and drawing programs) Tutorials: Laboratories: 10 Mid-term: Final Examinations: 60 Others: _Seminar_____________________ 10 __Project____________________ 10 __Paper writing_______________ 10 Total: 100% 2003/2004, Semester I None Desirable to have completed the following undergraduate courses or their equivalent: Biochemical techniques, Proteins and enzymes, Structural Biology. None Kunchithapadam Swaminathan (Coordinator, DBS) Hai-Wei Song (IMCB) Terje Dokland (IMCB) Prasanna Kolatkar (GIS) 12. 13. Modes of Teaching and Learning (Lectures, regular tests, Q & A, IVLE, problembased learning) Basic Reading List Compulsory reading Lectures, Practicals, Tutorial, Seminar X-Ray Structure Determination: A Practical Guide Stout, G.H. & Jensen, L.H. Wiley-Interscience, 2nd edition, 1989. Crystal Structure Analysis for Chemists and Biologists Glusker, J.P., Lewis, M. & Rossi, M. John Wiley & Sons, 1994. Supplementary reading 14. 15. 16. Maximum Class Size Modular Credits (MC) Workload Per Week See below (The workload for a 4-MC module must add up to 10 hours per week. E.g. 2 hours lecture; 1 hour tutorial; 7 hours preparatory work) 50 4 Lecture hours per week: Tutorial hours per week: Laboratory hours per week: No. of hours per week for projects, fieldwork, assignments, etc. : No. of hours per week for preparatory work 3: Total hours per week: 2 1 3 2 2 10 Notes: (Please refer to Paper R.205/02A ‘Policy on Modules’) 1 2 3 Aims specify the knowledge and abilities we expect students to acquire. Objectives are expressed in operational terms and specify what the students will be able to do at the end of the module. For regular module, at least 2 regular faculty members should be qualified to teach. No. of hours of preparatory work is the time a student is expected to spend in preparing for tutorials, projects, assignments, etc.