Animal Adaptations
advertisement

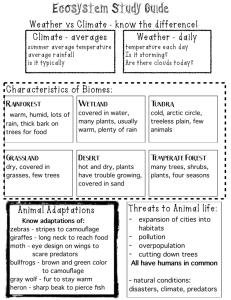
Animal Adaptations All animals live in specific habitats. These provide food, water, and shelter which animals need to survive, but there is more to survival than just the habitat! Animals also depend on adaptations of their physical features to help them obtain food, keep safe, build homes, withstand weather, and attract mates. Physical adaptations do not develop during an animal's life but over many generations. The shape of a bird's beak, the number of fingers, colour of the fur, the thickness or thinness of the fur, the shape of the nose or ears are all examples of physical adaptations which help different animals to survive. Explore these internet sites to find out about a range of animal adaptations. African Hedgehog http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azhgehog.html 1. Besides having stiff spines that stick out from their bodies and help protect them, these animals also have loose skin under those spines and powerful back muscles. Why? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html 1. From this page, click on "North America" and then click on "American alligator". 2. How are these alligators’ eyes adapted for seeing in water? Lions http://www.lpzoo.org/animals/LION-HOUSE/index.html 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the purpose of the mane on a male lion? Why are the eyes of a lion set in the front of its head rather than on the sides? A lion has heavily muscled forelimbs and shoulders. Why? Why do they have forepaws equipped with long, retractile claws? Why do they have a rough tongue? Why do they have loose belly skin? Bactrian Camel http://www.lpzoo.org/animals/FACTS/mammals/bact_camel.html 1. Camels have many adaptations that allow them to live successfully in desert conditions. List these adaptations and say how they benefit the camel. Koala http://www.seaworld.org/animal-info/animal-bytes/animalia/eumetazoa/coelomates/ deuterostomes/chordata/craniata/mammalia/diprotodontia/koala.htm 1. How are the hands of a koala adapted for life in a tree? Sea Otters http://www.mnh.si.edu/arctic/html/sea_otter.html 1. Sea otters spend almost their entire lives in water. They eat, sleep, and even have their babies in water. How is their fur adapted to keep them warm? Why is it a critical situation when otters encounter oil spills? 2. What do they eat? Burmese Python http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azpythn.html 1. How are the mouths of pythons adapted to finding prey and swallowing large prey? White-cheeked Gibbon http://www.lpzoo.org/animals/FACTS/mammals/gibbon.html 1. Why do many monkeys and apes have long arms? 2. Describe special adaptations on the hands of gibbons. South African Burrowing Bullfrog http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azsablfg.html 1. What do they eat? 2. How do they hold on to prey that is struggling to escape? California King Snake http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azkgsnke.html 1. Why can king snakes eat rattle snakes? Beaver Facts http://www.wildlife.alaska.gov/index.cfm?adfg=funfacts.beaver 1. How are beavers built for underwater work? 2. This site has additional information. White Throated Savanna Monitor http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azmonitor.html 1. How long are they? 2. What do they eat? 3. How are their mouths adapted to what they eat? Giraffe http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azgiraf.html 1. Why are giraffes able to go for long periods of time without water? 2. How are their long necks adapted to their lifestyle? Lappet-faced Vulture http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azlfvult.html 1. How are the heads of vultures adapted to what they eat? Manatees http://www.savethemanatee.org/faq.htm 1. Scroll down about 1/3 of the way down the page. What special adaptations do manatees have that that allow them to stay under water longer than the average landdwelling mammal? Wallaroo http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azwalaro.html 1. What do they eat? 2. How are their feet adapted to rock climbing? Polar Bears http://www.mnh.si.edu/arctic/html/polar_bear.html 1. Why do polar bears have such big feet? 2. How does their fur keep them warm? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html 1. From this page, click on "Australia" and then click on "Platypus". 2. How are platypuses adapted for the time they spend in water? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html 1. From this page, click on "Oceans" and then click on "Pacific walrus". 2. What do special adaptation do these walruses have that allow them to float on top of the water and sleep? Squirrel Monkey http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azsqmky.html 1. Where in the world do they live? 2. What do they eat? 3. These monkeys live in group. How does this help them? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html 1. From this page, click on "North America" and then click on "Mountain goat". 2. How are they adapted for living in the tops of high, cold mountains? 3. How are their rear ends adapted to protect themselves from other goats? Gila Monster http://www.scz.org/animals/g/gila.html 1. What do gila monsters do to avoid the heat of the day? 2. What do gila monsters do in winter months to keep warm? How do they survive during winter months with little food? Red Panda http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/mammals/redpanda/Redpandaprintout.shtml 1. How are red pandas adapted to eating bamboo? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html 1. From this page, click on "Eurasia" and then click on "Pacific walrus". 2. How are the feet of snow leopards adapted for travelling and hunting on snowy and icy ground? Canada Lynx http://www.nhm.org/cats/encyclo/canadens/ 1. What adaptations do lynxes have for manoeuvering through deep snow? Round Island Day Gecko http://www.thewildones.org/Animals/riGecko.html 1. How are their teeth adapted to what they eat? 2. How are their feet adapted to where they live? 3. What unique method do they have of defending themselves? Defensive Adaptations Many animals have developed remarkable defences to keep from being eaten. Grazing animals often feed in herds. When a predator attacks, the animals scatter and run in different directions which confuses the predator and allows the animals to escape. Some animals never venture too far from their home in underground dens or thick vegetation and can quickly hide when danger approaches. Many animals have keen senses of sight, smell, and hearing so that they can detect danger and escape. Some animals have horns or antlers to fight off predators. Some animals are active only at night when it is harder for predators to find them. Many animals rely on camouflage or the ability to blend in with their surroundings to hide from predators. A few animals are even poisonous or unpleasant-tasting, and predators soon learn to leave such animals alone. These poisonous animals are often brightly coloured too which acts as a warning to predators. Some animals use chemicals which they spray from various parts of their bodies to deter predators. A few animals rely on trickery and copy the defences of other animals to protect themselves. Western Lowland Gorilla http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/gorilla/g._gorilla_gorilla$narrative.html 1. To scare away potential sources of danger, how does an adult male gorilla communicate aggression? Tarantulas http://www.tarantulas.com/ 1. How do tarantulas protect themselves? Two and Three-Toed Sloths http://www.rossparkzoo.com/virtualtour/lowerzoo/sloth/sloth.htm 1. What are 2 ways that these sloths defend themselves? 2. What are their main predators? Afghanistan Leopard http://www.lpzoo.org/animals/FACTS/mammals/afg_leopard.html 1. How does the loose belly skin of a leopard protect it? White Throated Savanna Monitor http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azmonitor.html 1. How do these animals scare away predators? Zebras http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azebra.html 1. How do zebras defend themselves? African Hedgehog http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azhgehog.html 1. What physical feature does a hedgehog have that protects it from predators? Woma http://www.perthzoo.wa.gov.au/wildlife_facts_au_woma.html 1. What kind of animal is a woma? 2. How does it protect itself from predators? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html From this page, click on "Oceans" and then click on "Stingray". 1. How do stingrays defend themselves against predators? Lions http://www.lpzoo.org/animals/FACTS/mammals/af_lion.html 1. Why are lions a tawny brown colour? Round Island Day Gecko http://www.thewildones.org/Animals/riGecko.html 1. When in danger of becoming a predator's dinner, what does this gecko do? Bearded Dragon http://www.oaklandzoo.org/atoz/azdragon.html 1. How do they scare away predators? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html From this page, click on "Africa" and then click on "Plains zebra". 1. How do zebras warn each other of danger? Manatees http://www.seaworld.org/infobooks/Manatee/home.html 1. When confronted with danger, what do manatees generally do? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html From this page, click on "North America" and then click on "Prairie dog". 1. How do prairie dogs warn each other of danger? Kratt's Creatures http://www.pbs.org/kratts/world/index.html From this page, click on "Africa" and then click on "Cheetah". 1. What is it about baby cheetahs that makes them look bigger to predators? Finished? Go to http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topics/climate/adaptations/index.cfm