Components of screening exam
advertisement

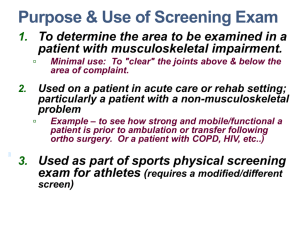
Kinesiology Lab Bilateral Upper and Lower Quarter Screening Exam: "Screen" means to broadly check, examine or test; it implies something that is done before a detailed examination. Purpose & Use To determine the area to be examined in a patient with musculoskeletal impairment. Minimal use of the screen in this type of patient is to "clear" the joints above & below the area of complaint - - to avoid missing something (ie. hip pathology often refers pain to the knee) The screen can be the neuromusculoskeletal exam on a patient in acute care or rehab setting; particularly a patient with a non-musculoskeletal problem (example – see how strong and mobile a patient is prior to ambulation or transfer following surgery; a patient with COPD, HIV, etc..) Revised/modified and used as a specific pre-participation screening exam for athletes Data / Information collected Pain – the cause (AROM, overpressure, or resistance) & location; if pain is always present, how does it change? Impairments in ROM or strength Impairments in general neurological function relative to sensation, strength, and reflexes. Place in the Physical Therapy Examination After Hx & Systems Review is performed; Prior to a detailed physical examination. Components of screening exam AROM Passive Overpressure Isometric Resistance - called gross muscle testing (not MMT); typically done with muscle in mid to shortened position. (mid to end of joint ROM) Sensory & Reflex testing Key Concepts Grade strength as painful/not painful and strong/weak; Only apply overpressure if AROM is painfree Stabilize the patient when applying resistance & overpressure Develop a personalized / systemic process – or you will be slow OR not do it at all (+) signs usually warrant further examination (bilaterally) 1 Neurological Aspect of the Screening Examination: Dermatome light-touch testing Grading: Normal, Impaired, or Absent Gross Muscle and Myotome testing Grading: judge gross strength/weakness & pain (eg. “strong-painless”, “weak-painful”, “weakpainless”, “strong-painful”) Testing Reflex (DTR) Integrity Grading scales for reflex integrity: (with such a wide, subjective range of normal; a bilateral comparison is of great importance) 0, 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+ scale; with 1+, 2+, 3+ being normal unless asymmetric (0) , (-) , (+) , (++); with (+) representing the range of normal absent, diminished (hypo), normal, hyperactive Myotome, Dermatome, DTR Chart for UE (C4 – T2 spinal nerves) Disc Root Reflex Myotome C4-C5 C5 Biceps Deltoid, (Biceps) C5-C6 C6 Brachioradialis Biceps, (Wrist Extens) C6-C7 C7 Triceps Triceps, (Wrist Flex) C7-T1 C8 -- Thumb Extension, (Grip) T1-T2 T1 -- PADS & DABS Add: C4 Derm– lateral clavicle / AC Dermatome Lateral upper arm (humeral head area) Thumb pad Middle finger pad 5th finger pad Medial arm AND T2 Derm– medial upper arm Myotome, Dermatome, DTR Chart for LE (L1 - S2 spinal nerves) Disc Root Reflex Myotome Dermatome L1-L2 L2-L3 L3-L4 L4-L5 L5-S1 -- L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 S1 --Patellar Reflex Patellar Reflex -Achilles Reflex Iliopsoas Iliopsoas Quadriceps Anterior Tibialis Extens Hallucis L. Flex Hallucis L. Inguinal area Ant-sup thigh Ant middle thigh Ant knee - suprapatellar 1st-2nd web space Lateral foot -- S2 Achilles Reflex Hamstrings Medial post thigh & calf 2 Upper Quarter Screening Examination 1) AROM & Overpressure of Cervical Spine (flexion, extension, sidebending, rotation) Lower Quarter Screening Examination A: STANDING 2) Resist C-spine rotation (C1) 1) AROM of Thoracolumbar Spine [flexion, extension, sidebending, rotation (hold pelvis)] 3) AROM & Overpressure Shoulder flexion & rotation (Apley's Scratch) B: SITTING (tripod – lean back on hands) 4) Resist Scapular elevation (C2 – C4) 2) AROM & Overpressure of Knee extension 5) Resist Shoulder abduction (C5) 3) Resist Hip flexion (L1, 2) 6) AROM & Overpressure of Elbow 4) Resist Knee extension (L3, 4) 7) Resist Elbow flexion (C6) 5) Resist Ant. Tibialis & Ext Hallucis Long. (L4, 5) 8) Resist Elbow extension (C7) 6) Resist Flex Hallucis Long (S1) 9) AROM & Overpressure of Wrist 7) Resist Knee flexion (S2) 10) AROM Hand Open/Close; Resist Thumb Extension (C8) (or grip strength) & Finger abduction (T1) C: SUPINE 8) SI Joint Compression / Distraction Stress 11) Upper Extremity Dermatomes (C4 – T2) 9) Passive SLR (Sciatic neural tension; L4,5,S1) 12) Mytotatic Stretch Reflexes (depends on findings in 1-11 above) Biceps (C5) Brachioradialis (C6) Triceps (C7) NOTE: The examination needed for detailed testing of abnormalities in sensation and/or motor function (peripheral nerve vs. spinal nerve vs. spinal cord tract vs. brain) is beyond the scope of a screening exam. 10) PROM & Overpressure of Hip 11) PROM & Overpressure of Knee Flexion 12) Lower Extremity Dermatomes (L2 – S2) 13) Mytotatic Stretch Reflexes (depends on findings in 1-12 above) Quadriceps Reflex (L3 - 4) Achilles Reflex (S1 - 2) NOTE: The examination needed for detailed testing of abnormalities in sensation and/or motor function (peripheral nerve vs. spinal nerve vs. spinal cord tract vs. brain) is beyond the scope of a screening exam. 3