Identifying Potential Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration
advertisement
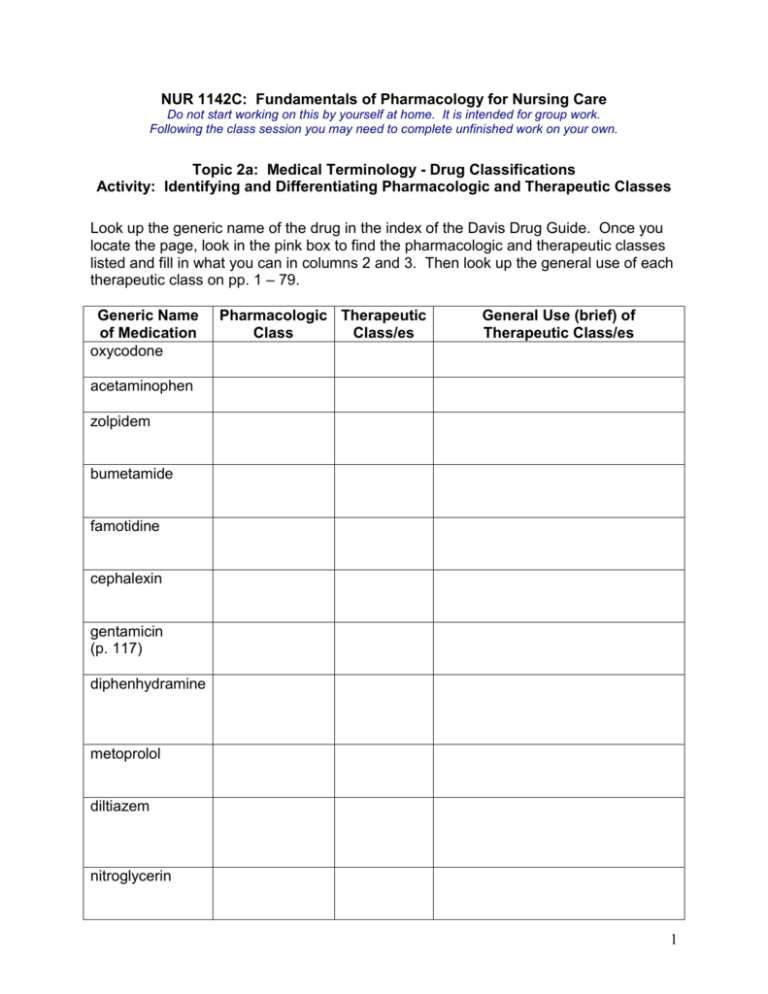
NUR 1142C: Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Nursing Care Do not start working on this by yourself at home. It is intended for group work. Following the class session you may need to complete unfinished work on your own. Topic 2a: Medical Terminology - Drug Classifications Activity: Identifying and Differentiating Pharmacologic and Therapeutic Classes Look up the generic name of the drug in the index of the Davis Drug Guide. Once you locate the page, look in the pink box to find the pharmacologic and therapeutic classes listed and fill in what you can in columns 2 and 3. Then look up the general use of each therapeutic class on pp. 1 – 79. Generic Name of Medication oxycodone Pharmacologic Therapeutic Class Class/es General Use (brief) of Therapeutic Class/es acetaminophen zolpidem bumetamide famotidine cephalexin gentamicin (p. 117) diphenhydramine metoprolol diltiazem nitroglycerin 1 Questions to consider: 1. Does every medication belong to a specified pharmacologic class? Why or why not? 2. Does every medication belong to a specified therapeutic class? Why or why not? 3. Do any medications belong to more than one therapeutic class? Why or why not? 4. Does the name of the pharmacologic class of gentamicin give you any clue what it is used for? 5. Does the name of the therapeutic class of metoprolol give you any clue what it is used for? 6. Metoprolol and diltiazem belong to common therapeutic classes but they belong to different pharmacologic classes. If you wanted or describe or explain each drug’s pharmacologic class what information from the Drug Guide would be helpful? 7. Where could you look to find the general use of an antitussive? 2 Topic 2b: Medical Terminology - Drug Forms and Routes of Administration Activity: Identifying Potential Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration Using your Davis Drug Guide, work in groups of 2 or 3 to answer these problems. Then compare your answers with your whole group once you have completed all the problems. 1. A patient has been diagnosed with angina pectoris and will be prescribed nitroglycerin upon discharge for use at home. Write down all the dosage forms this medication is supplied in. Next to the dosage form write down the route or routes this form may be given. Can you think of any reasons one dosage form or route would be preferred over another? 2. Your patient is ordered the following drugs in tablet form but is having difficulty swallowing them and asks to take them in applesauce. Identify the medications that may be crushed and/or also comes in a liquid form. Discuss when you think an action would require calling the physician for an order. Crushed or Liquid Form? Need to Call Physician? Lasix 40 mg po daily Digoxin 0.25 mg po daily Calan SR 120 mg po daily Carafate 1 g twice daily Plavix 75 mg daily Aspirin 81 mg po daily 3 3. A patient is one day post-op from an appendectomy, was NPO (nothing by mouth) for 24 hours and now is starting to take a clear liquid diet. He was receiving an antiinfective medication, cefazolin 1 g, mixed in a piggyback bag. The medication first started as a powder and the nurse needed to mix it up. After putting the proper diluent into the vial the powder dissolved completely. Take a look at the two different vials and the one ampule provided in the group materials. Discuss the following: What term would you use for the medication now in liquid form? It is now a _________________________________. How does this form differ from a suspension? Compare and contrast the properties of the vials and ampules and discuss the similarities and differences. If the physician decides to change the cefazolin from the IV route to the oral route, will the medication stay the same or need to be changed to a different yet similar medication? Could the nurse do this independently without having to wait for a physician’s order? If the IV stopped working and there was a need to give a dose of the medication by the intramuscular route would the patient be able to take the same medication? Could the nurse do this independently without having to wait for a physician’s order? 4 Topic 2c: Medical Terminology - Systems of Measurement Activity: Identifying Units of Measurement and Computing Necessary Conversions Circle all the units of measurements on the labels the following two pages. Write to the right or below the label o the abbreviation o the full name of the unit of measure o identify it as metric system, apothecary system, or household system o whether it is a weight or volume 5 6 Doctor orders cefazolin 0.5 g IM q 6 h. Does this match the unit of measure for this medication or does it require a unit conversion? Doctor orders digoxin 0.02 mg po daily. Does this match the unit of measure for this medication or does it require a unit conversion? 7 The doctor orders ampicillin and it is transcribed onto the medication administration record as pictured below. Finish timing the medication schedule using the 24-hour clock. Medication Administration Record Date Ordered Date Renewed (Assume current date) Scheduled Times Medication N D E 2301 0700 0701 1500 1501 2300 0701 1500 1501 2300 0600 Ampicillin 500 po q 6 h At 5:00 pm the nurse administers a medication for pain according to the order pictured below. Document the correct time in the correct space using the 24-hr clock. Medication Administration Record Date Ordered (Assume current date) Date Renewed Scheduled Times Medication N D E 2301 0700 1000 MDT Percocet 5 mg po q 6 h prn moderate incisional pain A full liter of IV fluid was added to the patients IV line at the time pictured below. If the liter bag of IV fluid lasts for 8 hours as expected, what time will the nurse plan to replace an empty IV bag? Express the time using both the traditional and the 24-hr clock. Intravenous Administration Record Date Ordered (Assume current date) IV Order 5% Dextrose Solution Rate 125 ml/h Time Initial 1400 MDT Site LFA Pump none Tubing Change none 8 Topic 2d: Medical Terminology - Medication Equipment Activity: Selecting and Using Most Appropriate Medication Equipment The following equations represent possible dosage calculation problems you might encounter. There is no need to be concerned about the order or medication at this time, let’s just deal with the numbers for now. 1. 10,000 divided by 5000 = Look at both the 1 mL and the 3 mL syringes. Which one can you measure the exact amount in. Draw up the correct amount of liquid into the syringe. Have your partner check it. 2. 50 divided by 200 = Look at both the 1 mL and the 3 mL syringes. Which one can you measure the exact amount in. Draw up the correct amount of liquid into the syringe. Have your partner check it. 3. 10 divided by 20 multiplied by 2 = Look at both the 1 mL and the 3 mL syringes. Find the space you think is the volume for your answer on both syringes. Can you measure the exact amount on either syringe? Draw up the correct amount of liquid into the syringe. Have your partner check it. Which syringe would you rather use to draw up this amount? Why 4. 450 divided by 330 = Look at the 3 mL syringe. Find the space you think is the volume for your answer. Can you measure the exact amount on this syringe? Round the number to a value equal to the number of decimal places possible with this syringe. 5. 2 divided by 35 = Look at the 1 mL syringe. Find the space you think is the volume for your answer. Can you measure the exact amount on this syringe? Round the number to a value equal to the number of decimal places possible with this syringe. 6. Find the two insulin syringes provided in the group materials. Compare the markings on both. What unit of measure is used. What is the maximum dose that may be drawn up in each. Observe the 25 unit marking on both and discuss observations with partner. 7. Look at the various larger syringes and medicine cups provided. Write the total volume in each piece of equipment. Describe how many decimal places may be used for accuracy. 9 Topic 2e: Medical Terminology - Medication Labels Activity: Deciphering Medication Labels Identify on the following labels: o brand name and generic name o concentration, total quantity on container o area where expiration date would be located What other useful information is also included on the label? 3/7/2016 10






