DNA Replication and Repair
advertisement

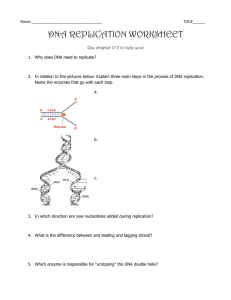
DNA Replication and Repair During cell division nucleus is divided _________________ Cytokinesis Cell is split into two cells, each daughter cell has an ____________copy of the parent’s cells __________ Each DNA strand acts as a ______________to build the complementary strand ______________ bonds between complementary bases break and DNA ___________ DNA Replicates Semi-conservatively Each DNA molecule is composed of one _________strand and one _______________________strand Meselson & Stahl Experimented with ______________(bacteria) Grew E. coli in _____________medium rich in________ Bacteria reproduced ________ generations Same bacteria is ____________to nutrient medium containing ________ M & S devised a new centrifugation method to measure __________________before and after switch to light N Experiment Samples of DNA were ________________in a solution of cesium chloride, for many hours at high speeds ____________________stops once the DNA reaches the same density in the gradient as its own M & S hypothesized that DNA strand of_______________, therefore ______________________density Process of DNA Replication Step 1: ________________the DNA Strands Begins when ____________at a specific site on DNA __________________unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between bases Strands have a natural tendency to ___________- pairing of bases Single Stranded Binding Proteins SSB’s bind to the ________________single strands and block H bonding ______________: enzyme that relieves any tension brought about by the unwinding of DNA in bacteria DNA cannot be _______________because of its large size Replication Fork The replication fork is the __________ where the DNA strands are still joined. When two replication forks are quite near each other a ______________________forms (See figure 4 page 220) Eukaryotes In eukaryotes there are ________________of replication forks, eventually bubbles become ______________and two new double-stranded daughter molecules are completely formed Building the Complementary Strands _______________________enzyme responsible for synthesizing complementary strands of DNA during DNA replication in prokaryotes ________complementary nucleotides in the ______ direction using RNA primers as starting points RNA Primer RNA Primer is a sequence of __________________which is annealed to the template because DNA polymerase III ____________________a complementary strand by itself Primase Primase is the enzyme that ____________________. RNA primer is ________________once DNA polymerase III starts elongation Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are added, the _____________obtained from breaking the bond between the P’s __________a complementary nucleotide to the elongating strand Direction DNA is always synthesized in the _________direction Therefore __________strand can be built continuously __________________- 5’ to 3’ direction - is built towards replication fork Lagging Strand The lagging strand is the strand tht is synthesized in _______fragments - known as ___________ fragments __________________is an enzyme that removes RNA primers and replaces them with the appropriate deoxyribonucleosides ______________- joins the Okazaki fragments See figure 7 page 221 Quality Control _______ DNA polymerase III and DNA polymerase I act as quality control checkers (search for _________) If error is detected either can act as an ___________ This enzyme backtracks and __________the incorrect nucleotide Review 1. How does the DNA strand unzip? 2. What does it mean when we say DNA replicates semi-conservatively? 3. How did Meselson & Stahl demonstrate this semi-conservative form of replication? 4. What is the name of the enzyme that unwinds the double helix? 5. What keeps the individual strands from annealing to each other? 6. What is the name of the enzyme that relieves any tension brought about by the unwinding of DNA? 7. What is a replication fork? 8. What is the name of the enzyme responsible for synthesizing strands of DNA during DNA replication? 9. In what direction does this enzyme add nucleotides? 10. What is a RNA primer? 11. What happens to RNA primer once DNA polymerase III starts elongation? 12. What is the difference between the leading strand and lagging strand? 13. What are the short fragments in the lagging strand called? 14. What enzyme joins the Okazaki fragments together? 15. How does the cell ensure that it has made DNA with the nucleotides in the correct sequence?