Earthworm Dissection Lab: Anatomy & Systems
advertisement
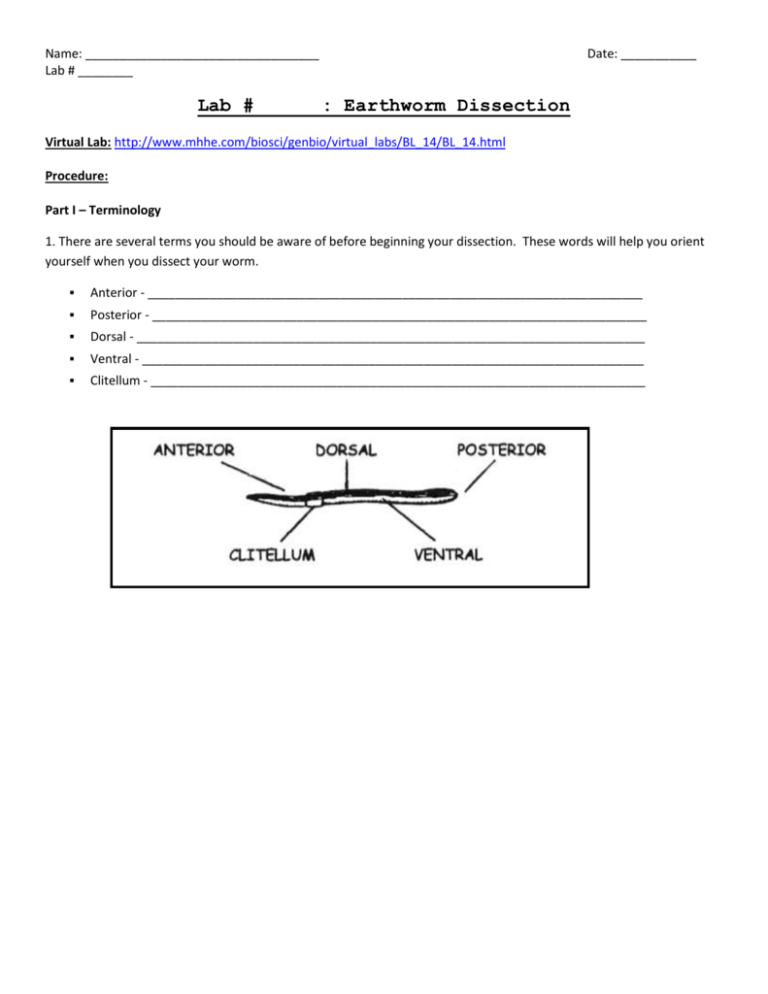
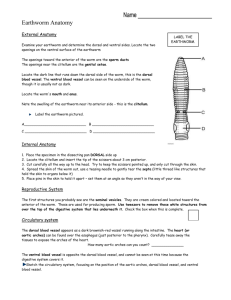
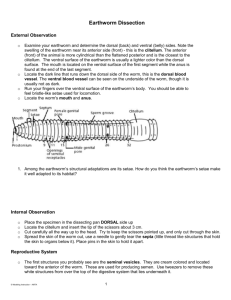
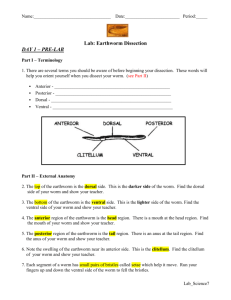
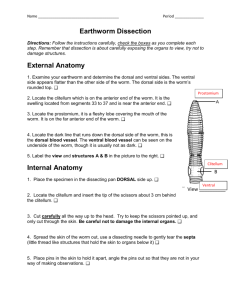
Name: __________________________________ Lab # ________ Lab # Date: ___________ : Earthworm Dissection Virtual Lab: http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/BL_14/BL_14.html Procedure: Part I – Terminology 1. There are several terms you should be aware of before beginning your dissection. These words will help you orient yourself when you dissect your worm. ▪ Anterior - ________________________________________________________________________ ▪ Posterior - ________________________________________________________________________ ▪ Dorsal - __________________________________________________________________________ ▪ Ventral - _________________________________________________________________________ ▪ Clitellum - ________________________________________________________________________ Part II. External Anatomy 1. Examine your earthworm and determine the dorsal and ventral sides. Locate the two openings on the ventral surface of the earthworm 2. The openings toward the anterior of the worm are the sperm ducts. The openings near the clitellum are the genital setae. 3. Locate the dark line that runs down the dorsal side of the worm, this is the dorsal blood vessel. The ventral blood vessel can be seen on the underside of the worm, though it is usually not as dark. 4. Locate the worm's mouth and anus. 5. Note the swelling of the earthworm near its anterior side - this is the clitellum. 6. Label the diagram to the right using the bold words above AND draw in the blood vessel. 7. Each segment of a worm has small pairs of bristles called setae which help it move. Run your fingers up and down the ventral side of the worm to fell the bristles. Part III. Internal Anatomy 1. Place the specimen in the dissecting pan DORSAL (top) side up. Push one pin through the anterior end of the worm (near the mouth) and one through the posterior. 2. Locate the clitellum and insert the tip of the scalpel/scissors about 3 cm posterior (towards the anus) 3. Cut carefully all the way up to the head. Try to keep the scissors pointed up, and only cut through the skin. 4. Spread the skin of the worm out, use a teasing needle to gently tear the septa (little thread like structures that hold the skin to organs below it) 5. Place pins in the skin to hold it apart. It should look like the diagram below: OBSERVATIONS: Reproductive System 1. Earthworms have both male and female reproductive organs, but does not fertilize itself. Earthworms reproduce sexually by lining up and exchanging sperm. The clitellum secretes mucus that picks up the egg and sperm cell forming a cocoon. The cocoon is dropped into the soil where a new earthworm develops. NOTE: The ovaries and testes are there but too small to see. An earthworm’s reproductive system has the following parts. Locate these parts & write the function: Clitellum: ______________________________________________________________________________ Seminal Vesicles: _______________________________________________________________________ Seminal Receptacles: ____________________________________________________________________ 2. The first structures you probably see are the seminal vesicles. They are located toward the anterior of the worm. These are used for producing sperm. What color are they in the earthworm? ____________________________ 3. Use tweezers to remove these structures from the worm. They lie on top of the digestive system. Circulatory system 1. Earthworm’s have a closed circulatory system which means all body fluids are contained within small tubes. An earthworm’s circulatory system has the following parts. Locate these parts on the write their function: Aortic Arches (Hearts): ____________________________________________________________________ Dorsal Blood Vessel: ______________________________________________________________________ 2. The dorsal blood vessel appears as a dark brownish-red vessel running along the intestine. The heart (or aortic arches) can be found over the esophagus (just posterior to the pharynx). Carefully tease away the tissues to expose the arches of the heart, they run across the worm. If you are careful enough, you can expose all 5 of them 3. The ventral blood vessel is opposite the dorsal blood vessel, and cannot be seen at this time because the digestive system covers it. Label the diagram below (use the bold words from above): Digestive System 1. The digestive system starts at the mouth. You will trace the organs all the way to the anus and identify each on the worm. 2. Find the mouth opening, the first part after the mouth is the pharynx, you will see stringy things attached to either side of the pharynx (pharyngeal muscles). The esophagus leads from the pharynx but you probably won’t be able to see it, since it lies underneath the heart. You will find two structures close to the clitellum. First in the order is the crop, followed by the gizzard. The gizzard leads to the intestine which is as long as the worm and ends at the anus. After you have located the parts of the earthworm’s digestive system, describe their functions: Mouth: __________________________________________________________________________________ Pharynx: __________________________________________________________________________________ Esophagus: ________________________________________________________________________________ Crop: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Gizzard: __________________________________________________________________________________ Intestine: __________________________________________________________________________________ Nervous System 1. Earthworms have a simple nervous system which allows the worm to sense its surrounding. The brain is very small and usually hard to see. A nerve cord is located on the ventral side. Locate the nerve cord & write the function. ▪ Ventral Nerve Cord: __________________________________________________________________ Label the following diagram of the earthworm using the word bank: 2. ____ 3. ____ 8. ____ 4. ____ 1. ____ 5. ____ 6. ____ 7. ____ 15. ___ 10. ____ 14. ____ 13.____ 12.____ 11. ____ a. Mouth h. Dorsal Blood Vessel b. Pharynx i. Ventral Blood Vessel c. Esophagus j. Clitellum d. Crop k. Seminal Vesicles e. Gizzard l. Seminal Receptacles f. Intestine m. Ventral Nerve Cord g. Aortic Arches (Hearts) n. Brain h. Dorsal Blood Vessel i. Ventral Blood Vessel j. Clitellum k. Seminal Vesicles l. Seminal Receptacles m. Ventral Nerve Cord n. Brain 9. ____