chapt44 - Strive Studios
advertisement

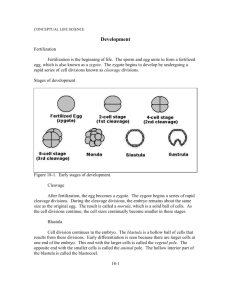
Chapter 44 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. All of the following associations are correct except: A. neural tube – brain and spinal cord B. endoderm – nervous system C. yolk sac – nourishment of embryo D. gray cresent – a complete embryo 2. Which of the following structures is made of 2 layers of cells? A. morula B. blastula C. early gastrula D. late gastrula 3. Which of the following governs the development of anterior versus posterior regions? A. homeotic genes B. bicoid genes C. morphogens D. all of these would influence the development of an anterior or posterior region of an organism. 4. How does a sperm penetrate an egg? A. Enzymes in the acrosome dissolve the jelly coating. B. The sperm melts its way inside using the nucleic acids in its DNA. C. The forward pressure of the flagellum forces it through the vitelline membrane. D. Spermatids are wedge shaped and are chemically attracted to the inside of the vitelline membrane. E. The haploid set of chromosomes match across the membrane, and this triggers the membrane to dissolve. 5. Generally, only one sperm fertilizes an egg because A. sperm are so few that two are unlikely to arrive at the same time. B. sperm compete against one another before entering, and only the most fit one is accepted. C. one small entry hole called the blastopore allows only one sperm to fit through and then seals. D. many sperm enter but only one set of chromosomes can fuse with the egg nucleus; the other sperm are absorbed. E. when the first sperm membrane fuses with the egg membrane, it forms the fertilization membrane and forms a barrier to any other sperm. 6. What would prevent one species' sperm from fertilizing another species' egg? A. The chemical and other behavioral cues for mating are unlikely to lead to insemination by a male of another species. B. The reactions between the sperm acrosome and the surface of the egg are generally species-specific. C. Any successful fertilization would require a successful match of chromosomes and genes to produce a viable zygote. D. All of the choices are correct. E. None of the choices is correct. 7. A fertilized egg undergoes cell division without further growth in the process called A. cleavage B. gastrulation C. differentiation D. morphogenesis E. embryology 8. Early stages of human development resemble those of the chick embryo because A. they contain the same amount of yolk. B. birds, mammals, and reptiles are closely related and share this evolutionary feature. C. all vertebrates avoid the morula stage. D. mammals evolved from ancient birds. E. both are warm-blooded. 9. The coelomic cavity is derived from the A. blastocoel. B. folding of the neural tube. C. splitting of the mesoderm. D. elimination of the yolk sac nutrients. E. space left after organs develop. 10. In humans implantation begins at the end of the A. fertilization. B. first week. C. second week. D. second month. E. fourth month. 11. During the formation of an embryo, a solid ball of cells with a hollow cavity inside is termed a A. morula. B. blastula. C. blastocoel. D. gastrula. E. neurula. 12. Which association is incorrect? A. gastrula–blastopore B. blastula–blastocoel C. gut–archenteron D. primitive streak–morula E. cleavage–zygote 13. Which of these best represents morphogenesis? A. cells divide and get larger B. cells become specialized in structure and function C. body parts are shaped and patterned into a specific form D. All of the choices are correct. E. None of the choices is correct. 14. During gastrulation in vertebrates, the pore created by invagination will become the A. brain. B. heart. C. mouth. D. anus. E. ear. 15. Which of these best represents differentiation? A. cells divide and get larger B. cells become specialized in structure and function C. body parts are shaped and patterned into a specific form D. All of the choices are correct. E. None of the choices is correct. 16. Which of these best represents development? A. cells divide and get larger B. cells become specialized in structure and function C. body parts are shaped and patterned into a specific form D. All of the choices are correct. E. None of the choices is correct. 17. Which of these best represents growth? A. cells divide and get larger B. cells become specialized in structure and function C. body parts are shaped and patterned into a specific form D. All of the choices are correct. E. None of the choices is correct. 18. Which statement is NOT true about homeotic genes? A. They have been found in almost all eukaryotic organisms. B. They are master genes that control all other genes in the organism. C. Each homeotic gene has a variable region and a sequence called the homeobox that is very similar in all such genes. D. They are sequentially arranged on the chromosome in the same sequence they are activated during development of the embryo in Drosophila. E. All homeotic genes are thought to be derived from an original DNA sequence that has been highly conserved in evolution because of its importance to animal development. 19. The presence of the same homeotic genes in a wide range of organisms for producing set patterns is an indication that A. evolution solved certain developmental problems just once. B. all organisms are composed of exactly the same proteins. C. the same homeotic mutations are likely to appear in all organisms. D. essentially we can complete the genome mapping of all animals in a short time. E. structures remain fairly constant, but regulation of animal development varies widely across the kingdom. 20. In a chordate embryo, which of these stages occurs first? A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. cleavage 21. In a chordate embryo, which of these stages occurs second? A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. cleavage 22. In a chordate embryo, which of these stages occurs third? A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. cleavage 23. The neural tube of vertebrates develops during morphogenesis of the nervous system by the A. folding of ectoderm tissue. B. migration of mesoderm cells. C. fusion of ectoderm and mesoderm. D. contraction of the endoderm away from the mesoderm. E. extension of endoderm into a thin spinal column. 24. Which system below develops first in the embryo? A. reproductive B. circulatory C. excretory D. respiratory E. nervous 25. The egg from a ___ will form a gray crescent after fertilization. A. fish B. frog C. reptile D. chicken E. human 26. Which of the following describes the process in which cells become specialized in structure and function? A. development B. growth C. differentiation D. morphogenesis E. embryology 27. During development, which of the following describes the correct sequence? A. growth, differentiation, morphogenesis B. differentiation, growth, morphogenesis C. differentiation, morphogenesis, growth D. morphogenesis, differentiation, growth E. growth, morphogenesis, differentiation 28. Morphogenesis is A. the total life cycle of any animal. B. a process by which tissues are shaped into organs. C. the mechanism by which gametes are formed. D. a study of the beginning and ending of life. E. the study of aging. 29. Which of the following is NOT correct? A. Embryonic nuclei are totipotent. B. Differentiation is due to parceling out of genes into various embryonic cells. C. The contents of the cytoplasm of an egg are not distributed uniformly. D. If an egg from a frog divides without receiving the gray crescent, it will not become a tadpole. E. Differentiation is influenced by chemical signals given off by neighboring cells. 30. The Latin root words for "lead" and "into" are the basis for the term A. homeobox. B. cleavage. C. gastrulation. D. induction. E. morphogenesis. 31. The process in which neighboring cells influence the development of each other, either by direct contact or by production of chemical signals, is A. neurulation. B. gastrulation. C. induction. D. maternal determinants. E. homeotic pattern formation. 32. The formation of the lens of the vertebrate eye from a skin layer in contact with an outgrowth of the embryonic brain is an example of A. cellular aggregation. B. induction. C. morphogenesis. D. gastrulation. E. neurulation. 33. In a chordate embryo, which of these stages occurs last? A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. cleavage 34. Which of the following is NOT a chordate embryo? A. lancelet B. frog C. human D. starfish E. chick 35. Which stage would show the development of the ectoderm and endoderm germ layers? A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. cleavage 36. Which stage would show the development of the mesoderm germ layer? A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. cleavage 37. Which stage would show the development of the notochord? A. gastrulation B. neurulation C. blastulation D. cleavage 38. Somites, which form segmental muscles and vertebrae, develop from which germ layer? A. epiderm B. ectoderm C. endoderm D. mesoderm E. myoderm 39. The nervous system develops from which germ layer? A. epiderm B. ectoderm C. endoderm D. mesoderm E. myoderm 40. Proteins that influence morphogenesis are A. homeobox genes. B. mutagens. C. morphogens. D. trophoblasts. E. blastocysts. 41. The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans is important in developmental research because it A. has a set number of body cells and we can trace each as it develops. B. is easy to culture and is transparent so we can see its development. C. has had its entire genome mapped. D. self-fertilizes so induced recessive mutations show up as homozygous recessive offspring. E. All of these are advantages in developmental research. 42. The phenomenon of apoptosis or cell death A. is a disease phenomenon and cell death is always a bad trait. B. occurs when the cellular machinery simply wears out and the cell dies from being unable to continue vital processes. C. occurs when the ability of the cell to repair DNA mutations finally fails. D. is a mechanism present in every cell but is inhibited by a master protein; when the protein is inactivated the cell death process begins and is essential for normal development. E. is not yet understood but probably involves the failure of the homeobox to correctly control development. 43. The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster is important in developmental research because it A. has a set number of body cells and we can trace each as it develops. B. allowed discovery of the bicoid gene that explains anterior-posterior orientation, morphogens that influence morphogenesis, and segmentation genes. C. has had its entire genome mapped. D. self-fertilizes so induced recessive mutations show up as homozygous recessive offspring. E. All of the choices are advantages of fruit flies in developmental research. 44. A homeotic gene codes for a ____ protein, a sequence of 60 amino acids, sets of which determine pattern formation. A. ion B. morphogenetic C. growth D. regulatory E. homeodomain 45. Genes that determine how segments develop during morphogenesis are termed ____ genes. A. induction B. cleavage C. differentiation D. homeotic E. home alone 46. Which of the following is NOT one of the extraembryonic membranes? A. chorion B. amnion C. placenta D. yolk sac E. allantois 47. Which association is incorrect? A. chorion–gas exchange B. amnion–blood vessels C. allantois–waste storage D. yolk sac–food storage 48. The Greek word for "membrane" alone is the basis for the term A. amnion. B. morula. C. chorion. D. placenta. E. umbilical. 49. The Greek word for "sausage" is the basis for the term A. amnion. B. allantois. C. chorion. D. placenta. E. umbilical 50. Which of the following is the organ of exchange between the mother and fetus? A. chorion B. amnion C. placenta D. yolk sac E. allantois 51. The allantois A. gives rise to umbilical blood vessels in humans. B. is a structure composed of two germ layers. C. lies next to the shell in chicks. D. has the same function in chicks as humans. E. becomes the chorionic villi. 52. The _____ develops into the fetal portion of the placenta. A. amnion B. archenteron C. chorion D. yolk sac E. allantois 53. Which part of the blastocyst will develop into the human embryo? A. archenteron B. blastopore C. chorion D. trophoblast E. inner cell mass 54. Which of the following serves as the site of the first production of blood cells in the embryo? A. chorion B. amnion C. placenta D. yolk sac E. allantois. 55. The Greek words for "food" and "bud" are the basis for the term A. amnion. B. morula. C. chorion. D. placenta. E. trophoblast. 56. How many days after the last menstrual period is birth of the fetus expected to occur? A. 210 B. 230 C. 255 D. 280 E. 300 57. A pregnancy test is based on the production of ___ by the ____. A. FSH, anterior pituitary B. estrogen, ovary C. progesterone, corpus luteum D. HCG, trophoblast E. GnRH, hypothalamus 58. The human blastocyst A. gives rise to umbilical blood vessels. B. contains a central cavity. C. is the expanded end of the gastrula. D. has three germ layers. E. is the fertilized egg. 59. During the ____ month, the fetal heartbeat would be developed so as to be heard by a physician with a stethoscope. A. 1st B. 2nd C. 4th D. 6th E. 8th 60. The placenta develops from A. fetal membranes only. B. uterine tissue only. C. both fetal and uterine tissue. D. separate polar bodies that develop just the placental tissues. E. None of the choices are true. 61. Which statement is NOT correct about the placenta? A. Oxygenated blood flows to the fetus via the umbilical vein. B. Fetal blood flows to maternal blood via the umbilical artery. C. Oxygen and nutrients go to the fetus from the maternal circulatory system. D. Maternal and fetal blood mix with each other. E. The placenta produces progesterone and estrogen. 62. The Latin word for "navel" is the basis for the term A. amnion. B. morula. C. chorion. D. placenta. E. umbilical. 63. If a woman takes ____ between days 27 and 40 of her pregnancy, the infant is likely to be born with deformed limbs. A. aspirin B. thalidomide C. alcohol D. marijuana E. birth control pills 64. At twenty-four weeks or about six months, a fetus has a chance of surviving, although it may have A. lung difficulties. B. kidneys that fail to function. C. an incomplete digestive system. D. problems with brain development. E. an incomplete heart and circulatory system. 65. During which stage of labor will the cervix be dilated? A. stage 1 B. stage 2 C. stage 3 D. stage 4 66. The sac that surrounds the fetus and usually ruptures just before childbirth is the A. gastrula B. allantois C. yolk sac D. amnion E. archenteron 67. Which is the proper order of embryo development? A. cleavage–morula–blastula–gastrula B. morula–cleavage–blastula–gastrula C. blastula–cleavage–morula–gastrula D. gastrula–cleavage–blastula–morula 68. The reproductive, cardiovascular, and muscular-skeletal systems develop from which of the following embryonic germ layers? A. Endoderm B. Ectoderm C. Mesoderm 69. The lining of the urinary bladder develops from the A. endoderm B. ectoderm C. mesoderm 70. Development requires which of the following? A. growth B. cellular differentiation C. morphogenesis D. all of the choices 71. That each cell contains all the instructions needed by any other specialized cell in the body is A. pattern formation. B. cytoplasmic segregation. C. totipotent. D. morphogenesis. 72. Implantation of the human embryo is at the _______ stage of development. A. zygote B. blastocyst C. morula D. none of the choices 73. Birth defects can be prevented by the mother doing all of the following except A. avoiding X-rays and pesticides. B. not smoking or drinking alcohol. C. obtaining proper nutrition. D. using aspirin and caffeine instead of illegal substances such as cocaine. 74. A very small roundworm has greatly influenced the study of the patterns of development that can be applied to higher animals as well. True False 75. Homeotic genes are called Hox genes in mammals. True False 76. Development requires growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis. True False 77. Development deals only with the growth and differentiation processes of the embryo. True False 78. The notochord during human embryonic development will later be replaced by the vertebral column. True False 79. Embryos of chordate animals may look very different from each other at the same stage of development, even though they all go through the same stages of development and have the same kinds of tissues. True False 80. During cleavage, the cells at the top of a frog egg belong to the animal pole, which contains most of the yolk of the egg. True False 81. The blastopore is the opening of the blastocoel, and in chordates it will become the anus. True False 82. In a chick, a furrow of cells called the primitive streak is the point at which invagination of cells of the embryo forms the middle ectodermal layer. True False 83. In a frog embryo, the gray crescent is important in the formation of the notochord and nervous system. True False 84. In a frog embryo, the vegetal pole of the egg becomes the endoderm. True False 85. Once the embryonic disk elongates in humans to become the primitive streak, the mesoderm forms by invagination of cells along the streak. True False 86. A coelom is defined as a body cavity that is lined by mesoderm tissue. True False 87. Embryonic development in humans occurs during the first three months. True False 88. The trophoblast is present even as germ layer formation is occurring in humans. True False 89. The human embryo becomes a fetus at the end of the second month of gestation. True False 90. The greasy, cheese-like substance that covers the developing fetus is called lanugo. True False 91. The fetal heart starts to beat about twelve weeks after fertilization. True False 92. Another term for birth is parturition. True False 93. Prevention of polyspermy depends upon changes in the plasma membrane of the egg and in the zona pellucida. True False 94. In humans the notocord is replaced by the vertebral column. True False 95. Describe the process of embryonic development from fertilization to the neurula stage. 96. Describe the difference in yolk content and its effects among embryos of the frog, the chick, and the human. 97. Describe the effects of the gray crescent in a frog embryo. 98. Describe the development of neural tissue in a chick or human embryo. 99. Explain how the homeotic genes are thought to function in development. 100. Name the four extraembryonic membranes and tell what each is or does. 101. Why does a pregnancy test kit not give a positive reading immediately after the egg is fertilized but only after it has implanted in the endometrium some days later? 102. Though (a) eggs and sperm can be harvested and fertilization can occur in a test tube, and (b) there are a few dozen cases of women with abdominal pregnancies carried through to a premature birth by Cesarean, why is it nearly impossible (and unwise) for a male to try to be pregnant? 103. Describe the different stages of development in a human. Chapter 44 KEY 1. B 2. C 3. D 4. A 5. E 6. D 7. A 8. B 9. C 10. B 11. B 12. D 13. C 14. D 15. B 16. D 17. A 18. B 19. A 20. D 21. C 22. A 23. A 24. E 25. B 26. C 27. A 28. B 29. B 30. D 31. C 32. B 33. B 34. D 35. A 36. A 37. B 38. D 39. B 40. C 41. E 42. D 43. B 44. E 45. D 46. C 47. B 48. C 49. B 50. C 51. A 52. C 53. E 54. D 55. E 56. D 57. D 58. B 59. C 60. C 61. D 62. E 63. B 64. A 65. A 66. D 67. A 68. C 69. A 70. D 71. C 72. B 73. D 74. TRUE 75. TRUE 76. TRUE 77. FALSE 78. TRUE 79. TRUE 80. FALSE 81. TRUE 82. FALSE 83. TRUE 84. TRUE 85. TRUE 86. TRUE 87. FALSE 88. TRUE 89. TRUE 90. FALSE 91. FALSE 92. TRUE 93. TRUE 94. TRUE 95. Answers will vary. 96. Answers will vary. 97. Answers will vary. 98. Answers will vary. 99. Answers will vary. 100. Answers will vary. 101. Answers will vary. 102. Answers will vary. 103. Answers will vary.