THE BODY SYSTEMS TAKE HOME TEST Name: Date: ______ Part
advertisement

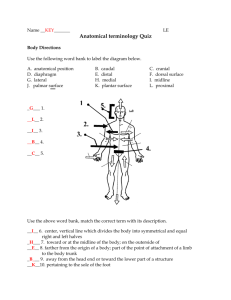
THE BODY SYSTEMS TAKE HOME TEST Name: ______________________________________________________________ Date: __________ Part I. Multiple Choice ____1. The body cavity that contains the lungs is the— a. Spinal cavity. b. Thoracic cavity. c. Cranial cavity. d. Pelvic cavity. _____2. The body cavity in which organs are the most vulnerable to injury because of a lack of protection from surrounding bones is the— a. Spinal cavity. b. Pelvic cavity. c. Thoracic cavity. d. Abdominal cavity. _____3. The bladder is located in the— a. Spinal cavity. b. Abdominal cavity. c. Thoracic cavity. d. Pelvic cavity. _____4. The brain is located in the— a. Cranial cavity. b. Spinal cavity. c. Thoracic cavity. d. Pelvic cavity. _____5. Which structure in the airway prevents food from entering the lungs when you swallow? a. Pharynx b. Epiglottis c. Trachea d. Larynx _____6. The process of breathing occurs in the— a. Respiratory system. b. Digestive system. c. Circulatory system. d. Integumentary system. _____7. Which body system regulates all other body systems through a network of nerves? a. The endocrine system b. The circulatory system c. The nervous system d. The respiratory system _____8. On a hot day, the skin of some people appears red. Which two body systems act together to make this happen? a. Musculoskeletal and endocrine b. Nervous and digestive c. Integumentary and circulatory d. Endocrine and integumentary ______9. The skin, hair and nails are part of which system: a. Musculoskeletal b. Nervous and c. Integumentary d. Endocrine _____10. The bones, liagments, muscles and tendons are part of which system: a. Musculoskeletal b. Nervous c. Integumentary d. Endocrine Part II. Matching a. Anatomy b. Body System c. Cells d. Organs e. Physiology f. Tissue g. Vital Organs h. Flexion i. Extension j. Lower Extremities k. Upper extremities l. Autonomic system _____11. This is involuntary and controls the involuntary muscles of the organs and glands. _____12. Those organs whose functions are essential to life. _____13. A collection of similar cells acting together to perform specific body functions. _____14. The study of structures, including structures that can be seen with the naked eye and seen under microscope. _____15. How living organisms function. _____16. A group of organs and other structures that work together to carry out specific functions. _____17. The basic units that combine to form all living tissue. _____18. A structure of similar tissues acting together to perform specific body functions. _____19. A term used to describe a bending movement. _____20. A term used to describe a straightening movement. _____21. This includes the shoulders, upper arms, wrists and hands. _____22. This includes the the hips, upper and lower legs, ankles and feet. Part III. True or False _____23. The muscles give the body its shape. _____24. There are four types of muscles in the body. _____25. The cardiac muscle are found in the arteries _____26. The smooth muscles are called involuntary muscles. _____27. The skeletal muscles are under control of the skeletal system. _____28. Air enters the body through the nose and mouth. _____29. The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped structure that folds down over the top of the trachea during swallowing to prevent foreign objects from entering the trachea. _____30. The upper airway includes the trachea, bronchi, lungs bronchioles, and alveoli. Part IV: Essay 30-35. Outline the anatomical difference between an adult and child/infant in the respiratory system. 36-40. Outline the four chambers of the heart and their functions. 41-45. Outline the four components of blood and describe their functions. 46-50. Outline the three types of blood vessels and their functions.