Chapter 4 Interest Rate fundamentals
advertisement

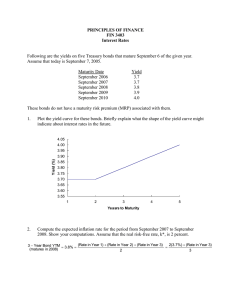
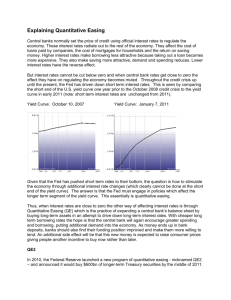
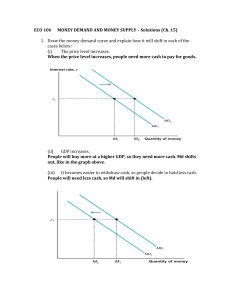
Chapter 4 Interest Rate fundamentals I. Risk Free Interest Rate a. Interest rate demanded if there were no risk b. Interest rate on short term Treasuries serves as a proxy for the risk free rate II. What determines the Risk Free Rate a. Risk free rate is determined by the supply and demand for investment money i. Supply of Investment Money 1. Money people don’t plan on spending is available for investment 2. Quantity supplied positively related to the interest rate – figure 4.2 ii. Demand for Investment Money 1. Demand depends the economic outlook 2. Quantity demanded inversely related to the interest rate – figure 4.2 iii. Interest rate and the level of investment determined by the interaction of the demand and supply of investment money b. Shifts in the supply of money – figure 4.3 i. Supply of money is controlled by the Federal Reserve 1. Monetary policy – FED policy determining the amount and growth of the money supply 2. Open Market Operation a. Primary way the FED expands or contracts the money supply b. Involves buying and selling US Treasuries i. Buy bonds – inject funds into banking system – lower interest rates ii. Sell bonds – withdraw funds from banking system – raise interest rates ii. Demand for money depends on overall economic conditions 1. Expect economic growth – demand for investment funds rises driving up interest rates 2. If demand for investment money drops interest rates drop iii. If the FED wants supply of money can overwhelm demand for money III. Term structure of interest rates a. Normally a longer term requires a higher interest rate i. People need to be paid more for tying their money up longer ii. PSECU is paying 4% on 12 and 18 month CDs iii. Why tie your money up for 18 months for same rate as 12 months b. Yield curve is a graph of interest rates against time to maturity c. Curve does not always behave normally i. Flat – interest rate the same regardless of term ii. Inverted – interest rate lower for longer term d. Yield Curve Theories i. Expectations 1. Expectation of lower rates in the future may lead to an inverted yield curve 2. Presently expect interest rates to be lower in the future ii. Liquidity Preference Theory iii. Market Segmentation Theory IV. Risk Premiums a. Nominal interest rate = risk free rate + risk premium b. Risk Premium i. Default risk 1. Bonds – Bond rating – table page 86 2. Equities a. Income statement compare debt to earnings ii. Other risks – table 4.1 V. Risk and Return a. Only get higher return for taking higher risk b. If asked to take higher risk need to receive higher return c. Evaluating this relationship is fundamental to finance VI. Interest rate sifts a. Change in risk free rate – Federal Reserve i. Mostly drives interest rate changes ii. Figure 4.9 b. Change in investors tolerance for risk i. High profile defaults ii. International affairs