how to perform project pert analysis manually
advertisement

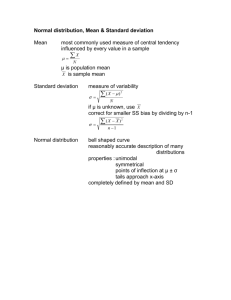
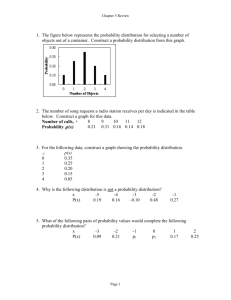
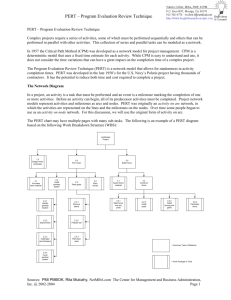
AN APPROACH TO PERFORM PROJECT PERT ANALYSIS MANUALLY One - Point estimation reflects one estimate per activity. It is based on expert judgment, experience, expert opinion or historical information. Fear of padding is always lies with onepoint estimation. Also it does not reflect risk or uncertainties associated to estimation. Therefore Three-point estimation is preferred for activity duration and cost estimation. There-point estimation ‘PERT’ uses pessimistic (P), most likely (M) and optimistic (O) for estimation. PERT is also called as ‘Weighted Average’ (not just an average). It is calculated by a formula: PERT = Author’s Profile: Yasir Masood- PMP Bsc Mechanical, Msc PERT provides the basis to calculate Activity Standard Deviation, Activity Variance and Project Variance and Project Standard Deviation. Mechatronics Engg. Expertise: Activity Standard Deviation = Project Management, Project Planning, Project Activity Variance = Risk Management, Engineering Solutions, Project Variance = Statistical Analysis & Engineering Software Project Standard Deviation = Let’s take an example of a ‘Pressure Vessel Design and Commissioning Project’ to enlighten PERT Analysis. Assume that there are four phases in a project i.e. design, fabrication, testing and commissioning. Client has given 70 days to complete the project. Project planning team asses the duration of project phases as given below: Duration Optimistic S.No. Project Phases Most Likely (O) Pessimistic PERT (P) Activity Standard Deviation Variance Project Variance Project Standard Deviation (M) Software Skills: Primavera P6, P5, Pertmaster, Ms Project, WBS Chart pro, Oracle CrystalBall, Palisade @Risk, AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Floworks, Ms Office, Ms Visio, SmartDraw, Camtasia etc. 1 Design 10 15 20 15.00 1.67 2.78 2 Fabrication 20 25 35 25.83 2.50 6.25 3 Testing 5 8 10 7.83 0.83 0.69 4 Commissioning 10 18 25 17.83 2.50 6.25 Blog: http://mechint.wordpress.com 15.97 3.995 Table -1: PERT Analysis gE n g r . Y a s i r M a s o o d – P M P , M P M I , M P M I - A G C ( y a s i r 9 1 1 0 9 @ g m a i l . c o m ) Page 1 According to calculations, project will be completed in 66.60 ~67 days. It portrays the project will be completed before the deadline. Wow sounds great! Is it the real story? Would it be the only information to rely on? Answer is no, project completion depicts only the one facade of the situation. Perhaps one requires more calculations to have a complete picture of a scenario. Therefore it is required to first find out the probability to meet the deadline on the basis of planning. Probability to finish project on deadline of 70 days can be found by ‘Z’ (Standard Normal Equation). Where ‘Z’ is the number of standard deviations the due date or target date lies from the mean or expected date. Project Standard Deviation is already calculated 3.995~4 days. So in order to calculate the probability, the standard normal equation can be applied as follows: Author’s Profile: Yasir Masood- PMP Bsc Mechanical, Msc Mechatronics Engg. Z= Expertise: = (70 days – 67 days)/4 days Project Management, Project Planning, Project = 0.75 Risk Management, Now referring to ‘Normal Curve Area Table’* to find out the area under the normal curve. From table, the probability is found 0.77337. Thus there is 77.337% chance that ‘Pressure Vessel Design and Commissioning Project’ can be completed in 70 days or less. What if to know the 99 % probability to meet the deadline? 99% chance to complete the project can be calculated by formula as given below: Due Date = Engineering Solutions, Statistical Analysis & Engineering Software Software Skills: Primavera P6, P5, Pertmaster, Ms Project, = 67 + 2.33** *4 W BS Chart pro, Oracle CrystalBall, = 67 + 9.32 = 76.32 ~ 76 Days Palisade @Risk, AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Floworks, Ms Office, Ms Visio, PERT Analsis shows there is a requirement to compress the schedule at least 6 days to meet the client’s deadline SmartDraw, Camtasia etc. Blog: http://mechint.wordpress.com * Normal Curve Area Table is also called as Distribution Table. ** At 2.33 in Normal Curve Area Table the probability is approximately 99%. gE n g r . Y a s i r M a s o o d – P M P , M P M I , M P M I - A G C ( y a s i r 9 1 1 0 9 @ g m a i l . c o m ) Page 2