Waves Lesson Worksheet
advertisement

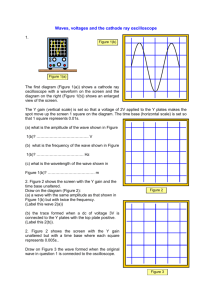
Frequency and Intensity measurement with an oscilloscope Objective: Measure sound wave frequency and Voltage with an oscilloscope. Materials: 1. Computer with speakers and software to generate different tones 2. Meter Stick 3. Microphone 4. Oscilloscope Procedure: 1) Divide into your groups and go to you station 2) Make sure the Audacity software is open on your screen. 3) Please locate the folder called “Mr. Bakunin” on the upper right corner of your computer screen. 4) Go to your “Mr. Bakunin” folder and open “freq 1” , “freq 2” and “freq 3” files in that folder by double clicking. 5) Make sure the cable coming from your microphone is connected to “Channel 1” on the oscilloscope. 6) Make sure your speaker is on (please don’t adjust the volume). 7) Place your microphone at base 1. 8) Click on the PLAY button on Audacity file called “freq 1”. This will run for 30 second. 9) Adjust the Volts/Division and Time/Division (Channel 1) on the oscilloscope until you can clearly see a wave on screen. Record the settings for time/division indicated on the oscilloscope. a. Count how many divisions there are between wave peaks. Use this to calculate the period of the sound wave. 10) Repeat steps 8-9 for files called “freq 2” and “freq 3”. 11) Go back to “freq 1”. Place your microphone at station 1 again and play “freq 1”. Adjust the Volts/Division and Time/Division (Channel 1) on the oscilloscope until you can clearly see a wave on screen. Record the settings for volts/division indicated on the oscilloscope. a. Count how many division there are from the center of your wave to the “crest” of your wave (in the vertical direction). Use this to calculate the amplitude/pressure of your wave. 12) Move the microphone to stage 2 and Play “freq 1” again. Record the settings for volts/division indicated on the oscilloscope. 13) Next, move the microphone to stage 3 and play file “freq 1” again. Record the settings for volts/division indicated on the oscilloscope. Data: microphone distance from speaker (m) Microphone Station 1 1 1 microphone distance from speaker (m) Microphone Station 1 2 3 Freq Time/Div # (sec) 1 2 3 Number of Divisions in one wave cycle Period (sec) Frequency (Hz) Freq Volt/Div # (V) 1 1 1 Number of Divisions in Amplitude Amplitude (Volts) Intensity Beat studies: 14) Pair up with your neighboring team. 15) Don’t move the computers but place your speakers at station 4. 16) Put the microphone exactly between the speakers (station 5). 17) Both teams should play 2 different frequencies simultaneously and measure the period for one beat. (Record the settings for time/division indicated on the oscilloscope.) a. Team 1: Click on the PLAY button on Audacity for “freq 1” b. Team 2: Click on the PLAY button on Audacity for “freq 2” 18) Record the beat period (you may have to adjust the triggering). Data: Freq # Team 1 Team 2 Beat 1 2 1&2 Time/Div (sec) Number of divisions in period Period (sec) Frequency (Hz) Questions: 1) Make a graph of Intensity (Volts2/ρc) versus distance – put intensity on the y-axis and distance on the x-axis. 2) How and Why does sound intensity change with distance from the speaker? Explain using your measurements. 3) Calculate the expected beat period using the frequencies you measured from “freq 1” and “freq 2”. Does your answer make sense based on the beat period you measured? 4) An oscilloscope has 10 divisions on the x-axis and a setting of 1 ms/division. Would you be able to display one full period of a 10 Hz sound wave with this oscilloscope? (show calculations) 5) What careers require the use of oscilloscopes?