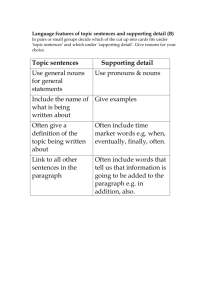
- Высшая школа Экономики, Управления и
advertisement

Ю.А. Липка-Ким И.Н. Соловьева Е.С. Эмирзиади АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК В ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОЙ СФЕРЕ Учебное пособие Чита 2012 МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования «Забайкальский государственный университет» (ФГБОУ ВПО «ЗабГУ») Ю.А. Липка-Ким И.Н. Соловьева Е.С. Эмирзиади Английский язык в профессиональной сфере Учебное пособие для студентов 1 – 2 курсов направлений 081100 – Государственное и муниципальное управление, 080100 – Экономика (финансы и кредит), 080200 – Менеджмент Чита РИК ЗабГУ 2012 1 УДК 802.0 (075) ББК 81.2Англ я7 ББК Ш13(Англ)я7 Л 613 Рецензенты: 1) к. филол.н., ст. преподаватель кафедры иностранных языков ЗабГГПУ им. Н.Г. Чернышевского Е.А. Чапаева 2) к. философ. н., доцент кафедры «Гуманитарные науки» ЗабИЖТ ИрГУПС Е.Г. Логинова Липка-Ким Ю.А. Английский язык в профессиональной сфере: учеб. пособие / Ю.А. Липка-Ким, И.Н. Соловьева, Е.С. Эмирзиади. – Чита: ЗабГУ, 2012. – 148 с. В учебном пособии представлены профессионально ориентированные аутентичные тексты с системой упражнений и заданий, направленных на формирование компетенций, необходимых для эффективной профессионально-коммуникативной деятельности менеджеров и экономистов. Учебное пособие предназначено для студентов 1 - 2 курсов направлений 081100 – Государственное и муниципальное управление, 080100 – Экономика (финансы и кредит), 080200 – Менеджмент. УДК 802.0 (075) ББК 81.2Англ я7 ББК Ш13(Англ)я7 Л 613 Утверждено и рекомендовано к изданию решением редакционноиздательского совета ЗабГУ. Ответственный за выпуск Т.Б. Макарова, зав. кафедрой регионоведения Северной Америки © Забайкальский государственный университет, 2012 © Липка-Ким Ю.А., Соловьева И.Н., Эмирзиади Е.С., 2012 2 ПРЕДИСЛОВИЕ Данное учебное пособие предназначено для студентов 1 – 2 курсов направлений 081100 – Государственное и муниципальное управление, 080100 – Экономика (финансы и кредит), 080200 – Менеджмент, а также широкого круга лиц, интересующихся экономикой и управлением и стремящихся усовершенствовать владение английским языком в данных сферах. Учебное пособие разработано в соответствии с Федеральным государственным образовательным стандартом по направлениям подготовки 081100 – Государственное и муниципальное управление, 080100 – Экономика (финансы и кредит), 080200 – Менеджмент, и может применяться как на практических занятиях по иностранному языку, так и для самостоятельной работы. Учебное пособие состоит из трех разделов: «Финансы», «Менеджмент», «Государственное управление». В них включены основные темы, составляющие содержание профессиональной деятельности специалистов в области управления и экономики. Каждый раздел включает 7 – 8 тем, которые, в свою очередь содержат следующие постоянные части: профессионально ориентированные тексты по теме, послетекстовые упражнения и задания. Упражнения и задания направлены на развитие и совершенствование навыков и умений работы с текстом, обсуждение профессионально значимых вопросов, изучение и закрепление лексики (соотнесение лексических единиц с их синонимами, определение значения лексической единицы, овладение правилами образования и сочетания слов, выбор и употребление лексической единицы), повторение и закрепление грамматики (поиск и анализ грамматических явлений, выбор и применение грамматических норм). 3 UNIT 1. FINANCE What is Finance? Finance is the science of funds management. The general areas of finance are business finance, personal finance, and public finance. Finance includes saving money and often includes lending money. The field of finance deals with the concepts of time, money, risk and how they are interrelated. It also deals with how money is spent and budgeted. One facet of finance is through individuals and business organizations, which deposit money in a bank. The bank then lends the money out to other individuals or corporations for consumption or investment and charges interest on the loans. Loans have become increasingly packaged for resale, meaning that an investor buys the loan (debt) from a bank or directly from a corporation. Bonds are debt instruments sold to investors for organizations such as companies, governments or charities. The investor can then hold the debt and collect the interest or sell the debt on a secondary market. Banks are the main facilitators of funding through the provision of credit, although private equity, mutual funds, hedge funds, and other organizations have become important as they invest in various forms of debt. Financial assets, known as investments, are financially managed with careful attention to financial risk management to control financial risk. Financial instruments allow many forms of securitized assets to be traded on securities exchanges such as stock exchanges, including debt such as bonds as well as equity in publicly traded corporations. Vocabulary funds management – управление фондами public finance – государственные финансы 4 to interrelate – находиться во взаимосвязи to budget – ассигновать, выделять денежные средства aspect – аспект, сторона, разновидность to charge – назначать цену to package for resale – оформлять для перепродажи bonds – облигации, ценные бумаги debt instruments – долговые обязательства secondary market – вторичный рынок facilitator - координатор funding – финансирование, выделение средств provision – обеспечение, предоставление private equity – прямое частное инвестирование, mutual funds – взаимный фонд, инвестиционный фонд открытого типа hedge funds – фонд использующий технику хеджирование financial risk management – управление финансовыми рисками financial instruments – финансовые документы securitized - секьюритизированный assets – активы, фонды, капитал securities - ценные бумаги securities exchange – фондовая биржа stock exchange – акционерный рынок financially – в финансовом отношении debt – долговое обязательство equity – акция, доля акционера в капитале предприятия publicly traded corporation – открытое акционерное общество 1. Write the transcription of the words and train their pronunciation. 5 science interrelate resale fund consumption provision general charge facilitator public increasingly equity field package mutual hedge securitized exchange 2. Work with the following groups of words. Define their part of speech and translate. Point out prefixes and suffixes. Memorize the words and use them in the sentences of your own. 1. Science, scientist, scientific. 2. To consume, consumer, consumption. 3. To increase, increasing, increasingly. 4. To sale, sale, resale, salesman, saleslady. 5. To provide, provision, provider. 6. To change, exchange, changeable. 3. Translate the following nouns and write their plural form. Science, fund, finance, business, company, facilitator, equity, security. 4. Translate these sentences. Define the tense form of the predicate. Compile special questions to the underlined words. 1. The general areas of finance are business finance, personal finance, and public finance. 2. Finance includes saving money and often includes lending money. 6 3. Loans have become increasingly packaged for resale. 4. The investor can then hold the debt and collect the interest. 5. Financial instruments allowed many forms of securitized assets to be traded on securities exchanges. 6. Banks became the main facilitators of funding through the provision of credit. 7. The bank lends money out to individuals or corporations for consumption or investment and charges interest on the loans. 5. Write degrees of comparisons of the following adjectives using the words much, less, the most, the least. Use them in the sentences of your own. General, personal, careful, important, expensive, profitable, successful. 6. Explain these words and word combinations in English: finance, to save money, to lend money, investor, bonds, to invest money, financial instrument. 7. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What is finance? 2. What are the general areas of finance? 3. What does finance include? 4. What are the concepts the field of finance deals with? 5. Who are the participants of financial process? 6. What does each of them do? 7. What does the resale of loans mean? 8. What are bonds? What can investors do with bonds? 9. How do banks facilitate funding? 7 10.What other facilitators appeared and why have they become important? 11. Why should financial assets be managed carefully? 12.Where can securitized assets be traded? Personal Finances Many people regard financial security as the most important thing in family finances. This is not the same thing as being rich. It means being freed from the need to think about money, living within your means. For day-to-day living you need ready cash but you also need a bit in reserve for a rainy day. The first thing to think about is your current account and how much is in it. Credit cards can be a helpful way of handling unexpected expenses, but credit is always costly, and of course it's just another form of debt. For some people, the English and the Americans, however, living on credit is a normal way of life. They believe that credit enables them to enjoy the use of goods and services before they have fully paid for them. Such people are not afraid to use consumer credit (credit from suppliers, hire purchase and loans from banks) because they have an income. If they want to buy a house they almost always borrow the money in the form of a mortgage from a building society or a mortgage bank. They pay for expensive things in installments by means of a hire purchase plan. People earn money in different ways. First of all they get an income from employment, then from keeping money in a saving account with a bank, from renting property, and from investing in shares in the stock market. People who are paid by the hour get wages. People who are paid on an annual basis get salaries and people, paid for a particular service, get fees. 8 The worst-off people are the unemployed and the homeless. For those living at a subsistence level, even buying essentials is a struggle. People on low incomes sometimes take out loans, borrow money from banks. Very often they are unable to cope with repayments and interest on loans. Banks are not willing to lend money to such people. Vocabulary finance - финансовое дело, финансы consumer credit - потребительский to regard — считать кредит financial security - финансовая обеспечение to borrow — занимать, заимствовать mortgage — закладная to be freed from — быть свободным от чего-либо building society — строительное общество means — средство, способ to pay in installments — платить в рассрочку to live within smb's means — жить по средствам hire purchase — покупка или продажа в рассрочку employment — работа, занятость in reserve — в запасе saving account — сберегательный счет current account — текущий счет to rent — сдавать в аренду credit card — кредитная карта property — собственность to handle — обращаться с чём-л., с кем-л. share — акция 9 stock market — рынок акционерного капитала debt — долг on credit — в кредит wages — заработная плата annual basis - годичная основа essentials - предметы первой необходимости salary — жалованье, оклад fee - гонорар to соре with - справиться worst-off - находящийся в худшем положении repayment - погашение (долга) interest on loan - ссудный процент subsistence level - прожиточный минимум to lend (lent, lent) - давать взаймы 1. Write the transcription and train the pronunciation of the following words. Memorize them. current unexpected subsistence reserve expenses essentials financial expensive consumer supplier mortgage annual finances debt account service purchase employment security society loan 2. Transform the following sentences into negative and translate them 1. It means being freed from the need to think about money. 10 2. Credit cards can be a helpful way of handling unexpected expenses. 3. They pay for expensive things in installments by means of a hire purchase plan. 4. The worst-off people are the unemployed and homeless. 5. He always borrows the money in the form of a mortgage from a mortgage bank. 6. He is now studying international banking and public finance. 7. The college was closed due to lack of finance. 8. Personal finances are how much money you have. 9. My finances are in a bad way now. 10. The present state of the country's finances is quite good. 3. Transform the following sentences into special questions and translate them 1. Financial security is the most important thing in the family finances. 2. Everybody needs ready cash and a bit in reserve for a rainy day. 3. Credit is always costly. 4. Many people live on credit. 5. Students must be taught how to handle their finances. 6. Some people are afraid to use consumer credit. 7. People earn money in different ways. 8. Sometimes people are unable to cope with repayments. 4. Guess what word is meant 1. Money used to run a business, an activity or a project 2. Having a lot of money or property 3. Money in the form of coins or notes 4. Available to be used in the future or when needed 11 5. Money that you spend 6. A sum of money that somebody owes 7. To make it possible for somebody to do something 8. Something that you have bought 9. Regular amount of money that a person earns, usually every week 10.Something that is needed in a particular situation or in order to do a particular thing 5. Explain the meaning of the following words: salary, the homeless, fee, the unemployed, to lend, to borrow, loan. 6. Answer the questions 1. Do you study Finance at your university? 2. Is finance one of your favorite subjects? 3. Are you going to major in finance? 4. Do you regard financial security as the most important thing in family finances? 5. Do you know how to handle your finances? 6. Do you live within your means? Do you sometimes have to borrow money? 7. Do you have the means to buy things you need? 8. Do you agree that testing is the usual means by which students' progress is measured? 9. Do small businesses have the means to develop and grow fast? 10.Do many people in Russia have bank accounts now? 11.What accounts are most popular? 12.Do you think it is easy to open a bank account? 13.Is it convenient to have a bank account? 14. Does a current account pay an interest? What about a saving account? 12 15.Is the idea of "living on credit" popular in Russia? 16.Is consumer credit used by the general public in Russia? 17.What purchases can be financed by consumer credit? How? 7. Translate into English. 1. Он получает доход от своей работы. 2. Вы получаете доход от средств, которые вы держите в банке? 3. Он не получает доход от сдачи в аренду своей собственности. 4. Дает ли вам доход вложение средств в акции? 8. Develop the following ideas. Make use of the words from the text. 1. People earn money in different ways. 2. The worst-off people are the unemployed, the homeless, and people living at a subsistence level. 9. Read the text and fill each gap with a suitable word from the list: sold, pension, costs, poverty, invested, contrast, on credit, unemployment, income. Do you agree that there is a contrast between wealth and poverty in many countries of the world? Our way of life is closely linked to our economic circumstances. In my retirement, I really have a very good life. When I retired I... my big house and bought a very small cottage. I ... the money in securities and that gives me a large part of my .... The rest comes from my ... and savings. So I'm comfortably off. In many countries there is a ... between the wealth of a small number of people and the ... of the masses. It's very difficult to manage if you are poor because everything ... much more. You have to buy .... The more things you buy on credit, the more you have to pay for them. The poorest 13 seem to suffer most in periods of recession in which output falls and ... rises. Words and word combinations you may need to link — связывать contrast — противоположность, кон траст retirement — выход на пенсию (the) rest — остаток, остальное to manage - справляться, управлять to be comfortably off — быть хорошо обеспеченным to suffer — страдать recession — спад (деловой активности) 10. Get into pairs and discuss with your partner how people can earn money. Give examples from your family's life, the life of your friends and relatives. 11. Sum up the text “Personal Finances” and work with the situation. Situation: You and your mate are going to get married. You want a flat, furniture and a TV. You are students and your families are not well off. Discuss with your mate how to solve the problems, consider the following: The flat - borrowing some money from a bank; getting a mortgage to buy a flat; renting a flat. The other things - buying furniture by hire purchase. 12. Read the text “Personal Finances” once more and give answers to the questions. 1. What do people regard as the most important thing in family life? 2. What do people need for day-to-day living? 14 3. Why do some people live on credit? 4. How do people earn money? 5. Who are the worst-off people? 6. To what people are banks unwilling to lend money? Personal Expenditure The modern market economy is populated by three types of economic agents, whose interaction constitutes economic activity: consumers, producers, and the government. The main purpose of the economy is to produce goods and services for the satisfaction of the needs of consumers. Consumers, typically representing households, spend their income to buy consumer goods and services or to save. How does a consumer distribute the income earned by him amongst a variety of goods and services offered in the market? There are different factors affecting his decisions. For instance, a fall in the price of a good or service will increase his consumption of it, while a rise in its price will have the opposite effect. Then a rise in his real income will naturally result in an increased consumption of goods and services, a fall in real income having the opposite effect1. The pattern of consumer expenditure is also influenced by tastes, consumer preferences and family circumstances. As incomes rise, expenditure on basic goods will form a smaller proportion of total spending. The terms "necessities" and "luxuries" are of little use in analyzing consumer expenditure because what are today's luxuries will probably be tomorrow's necessities. It should be stressed here, that some customers, however, want to have high-quality products even when quality means a higher price. Some 15 other customers prefer foreign products. The amount spent on goods and services and changes in this variable have a big impact on the level of economic activity: the increase in consumer spending creates new employment opportunities and causes better living standards. Note on the Text 1 ... a fall in real income having the opposite effect - ... при этом падение реального дохода будет иметь обратный результат. Vocabulary personal expenditure — личные затраты agent — агент, участник экономической деятельности market economy — рыночная экономика interaction — взаимодействие to populate — населять to constitute — составлять consumer – потребитель to result in - приводить к чему-л. producer - производитель pattern - структура, характер to represent - представлять, быть представителем consumer expenditure - затраты на потребление level - уровень opposite - противоположный, обратный household - семейная единица, домашнее хозяйство consumer preferences - предпочтения потребителей consumer goods - потребительские товары 16 basic goods - основные товары to save - экономить, копить, откладывать luxury - роскошь, предмет роскоши variable — переменная величина to distribute – распределять to have an impact - оказывать воздействие to affect - оказывать воздействие to cause — вызывать, быть причиной to effect - воздействие, влияние living standard - жизненный уровень 1. Write the transcription and train the pronunciation of the following words. Memorize them. agent whose constitute purpose typically earn distribute variety naturally increase expenditure preference quality however luxuries circumstances foreign amount variable employment caus- es opportunities higher opposite 2. Practice the reading of the following groups of words. market economy there are different factors for instance economic agents consumer expenditure real income variety of goods increase in consumer spending in analyzing a rise in its price expenditure on basic goods are of little use spend their income employment opportunities want to have 17 3. Read, translate, make the following sentences negative. 1. The modern market economy is populated by three types of economic agents. 2. Consumers spend their income to buy consumer goods and services. 3. There are different factors affecting this decision. 4. The price will have the opposite effect. 5. Some customers wanted to have high-quality products. 4. Read and translate the following sentences. Make them passive. 1. Consumers spend their income to buy consumer goods and services. 2. There are different factors affecting this decision. 3. A fall in the price of a good or service will increase the consumption of it. 4. Consumer spending creates new employment opportunities. 5. Consumer distributes the income earned by him 5. Read, translate, make the following sentences active. 1. The modern market economy is populated by three types of economic agents. 2. The pattern of consumer expenditure is also influenced by tastes, consumer preferences and family circumstances. 3. A variety of goods and services are offered in the market. 4. The decision is affected by several factors. 5. The level of economic activity is influenced by the amount spent on goods and services. 6. Compile special and negative questions to the following sentences. Translate them. 18 1. The main purpose of the economy is to produce goods and services for the satisfaction of the needs of consumers. 2. The increase in consumer spending creates new employment opportunities and causes better living standards. 3. The pattern of consumer expenditure is also influenced by tastes, consumer preferences and family circumstances. 4. The fall in the price of a good or service will increase the consumption of it. 5. Some customers want to have high-quality products. 7. Find in the text sentences containing the following Participles and translate them into Russian in writing. - ... consumers ... representing - ... the income earned by him - ... goods and services offered - ... factors affecting - ... the amount spent.... 8. Translate the phrases into English and compose sentences with them. 1. люди, зарабатывающие деньги; деньги, заработанные людьми; 2. клиент, открывающий счет в банке; счет, открытый в банке; 3. покупатель, приобретающий товар; товар, приобретенный покупателем; 4. покупатель, оплачивающий товар; товар, оплаченный покупателем; 5. лицо, берущее деньги взаймы; деньги, взятые взаймы; 6. лицо, погашающее ссуду; ссуда, погашенная клиентом. 19 9. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What economic agents interact in the market? 2. What is the main purpose of the economy? 3. How do consumers spend the income they earn? 4. How do prices influence consumers' decisions? 5. How does a rise in real income affect consumers' decisions? 6. Is it reasonable to use the terms "necessities" and "luxuries" analyzing consumer expenditure? 7. Why does consumer expenditure have a big impact on the level of economic activity? 10. Read the text. Fill in the correct form of the participle. Say how the business started. Explain the success of the business. Three years ago my aunt died ... (leaving/left) me some money in her will. I borrowed some money from my friend ... (promising/promised) to return it as soon as possible. I turned to the bank... (asked/asking) them to lend me some money. Besides, I had a saving account with the bank... (bringing/brought) me interest on my savings. The new shares ... (offered/offering) to me by my agent gave me good results that year. The dividends ... (paid/paying) to me were more than I expected. So having collected the money I was able to start my own business, making leather goods. I worked like a slave, but it was worth it. Now my business is doing quite well. I'm competing quite successfully with other firms ... (established/establishing) in the market. To be a success you must be ahead of your competitors. So I try to understand the people buying my leather goods and to study the market. I think that customers are always looking 20 for new products ... (based/ basing) on new technology I'm sure I have the capability to produce the ... (needing/needed) product. 11. Most often goods are classified as consumer goods (basic, durable, non-durable, luxury) and industrial goods. Give examples of each class. 12. Answer these questions: 1. Have you (your family) bought any durable goods lately? 2. Are you satisfied with them? 3. Have any goods you bought lately disappointed you? What goods have been the greatest disappointment to you? Describe the problem. 4. Does the purchase of durable (luxury) goods reflect the rising incomes of the population? 13. Translate into English. 1. Потребители покупают товары, чтобы удовлетворить свои потребности. 2. Потребители — это домашние хозяйства. 3. Если цены растут, то потребление товаров, как правило, снижается. 4. Несмотря на рост цен, потребление товаров длительного пользования выросло в последнее время. 5. Потребительские товары высокого качества пользуются спросом. 6. Сейчас многие семьи потребляют больше товаров высокого качества. 7. Личное потребление товаров и услуг возросло. 21 8. Производители потребительских товаров должны изучать рынок, вкусы и предпочтения потребителей. 9. Когда эта фабрика начала выпускать потребительские товары? 10.Что производит эта компания? 11.Компания увеличила производство легковых автомобилей. 12.Эта компания производит товары, которые пользуются большим спросом у населения. 13.Производство товаров длительного пользования значительно выросло в прошлом году. 14. Translate into Russian. 1. The money was distributed fairly. 2. The company distributed the annual profits to the employees. 3. Who distributes books to the students at your university? 4. How do people distribute their incomes? 5. This decision will affect his choice. 6. The goal of all producers is to affect buyer behavior. 7. Price rises affect sales. 8. How does competition affect the market? 9. Advertising affects consumers in different ways. 10.Low incomes affect people. 11.Changes in wealth can affect current consumption. 12.The pattern of consumption expenditure is affected by income. 13. Smith's ideas had an impact on the development of economics as a science. 14. Political events have an impact on the development of business and international trade. 22 15. Reduction in bank credits has a big impact on the country's economy. 16.Economic growth has an impact on consumption, production and the current standards of living. 15. Comment on the statements. 1. Political events have an impact on the development of business and international trade. 2. Economic growth has an impact on consumption, production and the current standards of living. 16. Find evidence in the text to support these statements. 1. There are different factors affecting consumer decisions and spending. 2. The amount of money spent on goods and services has a big impact on the level of economic activity. Sum up the text and discuss with your partner the factors affecting your decisions as consumers (prices, your income, quality, availability of imported goods). Eight Steps to Getting Your Finances in Order Develop a family budget. Instead of budgeting what you’d like to spend, use receipts to create a budget for what you actually spent over the last six months. One advantage of this approach is that it factors in unexpected expenses, such as car repairs, illnesses, etc., as well as predictable costs such as rent. Reduce your debt. Generally speaking, lenders look for a total debt load of no more than 36 percent of income. Since this figure includes your mortgage, which typically ranges between 25 percent and 28 percent of in23 come, you need to get the rest of installment debt—car loans, student loans, revolving balances on credit cards—down to between 8 percent and 10 percent of your total income. Get a handle on expenses. You probably know how much you spend on rent and utilities, but little expenses add up. Try writing down everything you spend for one month. You’ll probably see some great ways to save. Increase your income. It may be necessary to take on a second, part-time job to get your income at a high-enough level to qualify for the home you want. Multiple unrelated cash flows are a vital part of creating the security against losing a job, or a company going out of business. Save for a down payment. Although it’s possible to get a mortgage with only 5 percent down—or even less in some cases—you can usually get a better rate and a lower overall cost if you put down more. Shoot for saving a 20 percent down payment. Create a house fund. Don’t just plan on saving whatever’s left toward a down payment. Instead decide on a certain amount a month you want to save, then put it away as you pay your monthly bills. Keep your job. While you don’t need to be in the same job forever to qualify, having a job for less than two years may mean you have to pay a higher interest rate. Establish a good credit history. Get a credit card and make payments by the due date. Do the same for all your other bills. Pay off the entire balance promptly. Vocabulary instead of – вместо receipts – чеки по платежам 24 advantage – преимущество, достоинство approach – подход принцип, способ to factor - учитывать predictable - предсказуемый costs – издержки, затраты, расходы generally speaking – говоря вообще to look for – искать, ожидать total debt load – общая долговая нагрузка mortgage – залог, ипотека installment debt – очередной взнос to get down – снижать, спускать total income – общий доход to get a handle on – разобраться, понять utilities – коммунальные услуги to qualify – отвечать требованиям, делать способным down payment – первая выплата, взнос, аванс down – первоначальный, наличный, в качестве первонач. взноса overall cost – полная стоимость to shoot for - добиваться monthly bills – ежемесячные счета interest rate – процентная ставка to establish – создать, установить, заводить due date – установленная дата платежа to pay off – расплачиваться promptly - аккуратно, своевременно, быстро 1. Write the transcription and train the pronunciation of the following words. Memorize them. 25 receipts load installment advantage figure necessary approach typically utilities repair mortgage enough predictable range quality although overall shoot higher establish entire 2. Practice the reading of the following groups of words. last six months for a total debt rent and utilities for all your bills get a better rate at a high-enough level is that it factors in unexpected since this figure need to get certain amount whatever’s left toward 3. Compose your own sentences using the following models and the words from helpful vocabulary. Mind the tenses. 1. __________________ before ______________ . 2. __________________ after ________________ . 3. __________________ when _______________ . 4. _________________ if ___________________ . 5. _________________ till __________________ . 6. _________________ until _________________ . 7. _________________ as soon as _____________ . 26 4. Using the following models compile sentences of your own. Don’t forget to use vocabulary words. 1. You probably know how to ______________________ . 2. You probably know that _________________________ . 3. Generally speaking ______________________________. 4. ________________________ in stead of _____________. 5. Since _________________________________________ . 6. It’s possible to __________________________________ . 7. It’s impossible to ________________________________ . 8. It is not possible _________________________________ . 9. It may be necessary to _____________________________ . 5. Translate the sentences, define the tense form of the predicate and compose special questions. 1. One advantage of this approach is that it factors in unexpected expenses. 2. Lenders look for a total debt load of no more than 36 percent of income. 3. You need to get the rest of installment debt down to between 8 percent and 10 percent of your total income. 4. You’ll probably see some great ways to save. 5. It has been possible to get a mortgage with only 5 percent down. 6. He always made payments by the due date. 7. This figure includes your mortgage, which typically ranges between 25 – 28 percent of income. 8. She has decided on a certain amount a month she wants to save. 9. We will have got a better rate and a lower overall cost. 27 10. At that moment they were writing down everything they spent for one month. 6. Guess what is meant. 1. A piece of paper that you are given which shows that you have paid for something. 2. A person or organization that lends money to people on condition that they pay it back. 3. The sum total of all the money you owe: mortgage, student loans, credit cards, even loans from friends and family. 4. A legal arrangement by which you borrow money from a bank or similar organization in order to buy a house, and pay back the money over a period of years. 5. A service (such as a supply of electricity or water) that is provided to the public. 6. A first payment that you make when you buy something with an agreement to pay the rest later. 7. A small plastic card that is used to buy things that you agree to pay for later. 8. The day by which something must be done or paid. 9. A document that says how much money you owe for something you have bought or used. 10. Money that is earned from work, investments, business, etc. 7. Fill in the gaps with the appropriate word. Translate the sentences. lenders, down payment, total debt load, mortgage, interest rates, utilities, bill, income, bills, bill, earns, due date, job 28 1. Farming is his main source of …… . 2. Even on two incomes, we're having a hard time keeping up with our …. . 3. He ….. a good income as a consultant. 4. He paid the telephone …. . 5. I've been having a hard time paying the bills since I lost my … . 6. The waiter gave us our …. . 7. Add the amount I now owe to what I already owe and I will pay the … later. 8. Tomorrow's the …. for our electricity bill. (the bill must be paid by tomorrow) 9. She made a 10 percent … on the car. 10. Many of these people are in danger of having their … shut off for nonpayment. (of no longer getting electricity, water, etc., in their homes because they have not paid their bills) 11. They've taken out a 30 year …. (they will pay for their house over a period of 30 years). 12. Several … are offering very attractive …. at the moment. 8. Translate into English. 1. Маргарет собирает чеки, чтобы составить бюджет того, что она потратила за последние три месяца. Она точно (for sure) знает сколько платит за аренду и коммунальные услуги. 2. Джек ищет вторую работу. Он хочет увеличить свой доход. 3. Сергей оплатил свои счета до установленной даты. 4. Невозможно разобраться со своим бюджетом. 5. Кэйт добилась снижения процентной ставки. 6. Света создала хорошую кредитную историю, так как всегда 29 своевременно платила. 7. Я внесу большую сумму, если получу стипендию вовремя. 8. Они не смогли внести очередной взнос по кредиту, который брали на обучение. 9. К предсказуемым затратам добавляются еще и непредвиденные расходы. 10.У тебя более высокая процентная ставка по кредиту, потому что ты работаешь здесь всего полгода. 9. Answer the questions. 1. What one should do to develop a budget? 2. What is an advantage of creating a budget of what one has spent? 3. What is the difference between unexpected expenses and predictable costs? 4. What is the highest percent of one’s income the lenders look for for a total debt load? 5. How much of total income does installment debt usually constitute? 6. What is the way to find where you can save? 7. How can you increase your income? 8. What are the ways of getting a better rate and a lower overall cost? 9. Is it possible to create a house fund? What can you do to save? Do you have your own way of saving money? 10.Why is it important to make payments by the due date and to pay off the entire balance promptly? Overview of Techniques and Sectors of the Financial Industry An entity whose income exceeds its expenditure can lend or invest the excess income. On the other hand, an entity whose income is less than its ex30 penditure can raise capital by borrowing or selling equity, decreasing its expenses, or increasing its income. The lender can find a borrower, a financial intermediary such as a bank, or buy notes or bonds in the bond market. The lender receives interest, the borrower pays a higher interest than the lender receives, and the financial intermediary earns the difference for arranging the loan. A bank aggregates the activities of many borrowers and lenders. A bank accepts deposits from lenders, on which it pays interest. The bank then lends these deposits to borrowers. Banks allow borrowers and lenders, of different sizes, to coordinate their activity. Finance is used by individuals (personal finance), by governments (public finance), by businesses (corporate finance) and by a wide variety of other organizations, including schools and non-profit organizations. In general, the goals of each of the above activities are achieved through the use of appropriate financial instruments and methodologies, with consideration to their institutional setting. Finance is one of the most important aspects of business management and includes decisions related to the use and acquisition of funds for the enterprise. In corporate finance, a company's capital structure is the total mix of financing methods it uses to raise funds. One method is debt financing, which includes bank loans and bond sales. Another method is equity financing - the sale of stock by a company to investors. Possession of stock gives the investor ownership in the company in proportion to the number of shares the investor owns. In return for the stock, the company receives cash, which it may use to expand its business or to reduce its debt. Investors, in both bonds and stock, may be institutional investors - financial institutions such as investment banks and pension funds - or private individuals, called private or retail investors. 31 Vocabulary overview – обзор entity – юридическое лицо to exceed – превышать excess – дополнительный, излишний, избыточный on the one hand – с одной стороны on the other hand – с другой стороны to raise – повышать, увеличивать to borrow – занимать, одалживать borrowing – заемные операции, заем, кредит borrower – заемщик financial intermediary – финансовый посредник bond market – рынок ценных бумаг с фиксированной ставкой receive – получать, принимать to arrange – договариваться, устраивать to aggregate - cобирать, объединять, соединять, группировать to accept – принимать, признавать, акцептировать a wide variety – широкий выбор to achieve the goal - добиваться цели appropriate - соответствующий, подходящий with consideration to – учитывая consideration – рассмотрение, рассуждение institutional setting – общественный институт business management – управление коммерческими предприятиями relate to – установить связь, определять соотношение между acquisition – приобретение capital structure –структура капитала debt financing – финансирование путем получения займов, погашение 32 долга путем займа equity financing – финансирование путем выпуска акций, финанс-е за счет собственных средств possession – владение, обладание ownership – собственность, владение, право собственности to expand – расширять, развивать, увеличивать institutional investors – учреждения-вкладчики, инвестор – юридическое лицо private investors – частный инвестор pension funds – пенсионный фонд retail investors – мелкий инвестор 1. Write the transcription of the words, translate and read them correctly. overview raise goal technique intermediary pension entity receive achieve exceed arranging appropriate aggregate coordinate deposit consideration accept possession methodology acquisition share 2. Practice the reading of the following groups of words an entity whose income income exceeds lend or invest number of shares its expenditure gives the mix of financing are achieved method is use of appropriate retail investors or retail use and acquisition variety of other 33 goals of each investor ownership finance is used selling equity receives interest investor owns structure is decreasing or increasing each of the above 3. Define the tense form of the predicate and translate the sentences. Transform them into negative. 1. The lender receives interest. 2. The financial intermediary earns the difference for arranging the loan. 3. A bank aggregates the activities of many borrowers and lenders. 4. Banks allow borrowers and lenders, of different sizes, to coordinate their activity. 5. In return for the stock, the company receives cash. 4. Define the tense form of the predicate and translate the sentences. Compile general questions to the following sentences. 1. The income of the entity exceeded its expenditure. 2. The income of the entity decreased last year. 3. The lender found a borrower. 4. The bank has just accepted deposits from lenders. 5. Financial intermediary has reached the goal. 5. Pick all adjectives from the text, translate them and write the degrees of comparison. 6. Look through the last paragraph of the text, pick out the words ending in “s” and explain what it (the ending) means. 34 7. Put the following pairs of words into the possessive case where it possible. Lender/share, profit financial intermediaries/goal, schools and non- organizations/finance, entity/income, retail investors/deposits, bonds/owner, borrower/cash, institutional investors/ ownership. 8. Guess the words which are hidden in dietmeraineris nodetasirinoc nequhitec nerotodiac naiqitiusoc pateraporip garnirang nuredipetex 9. Look through the text and pick out irregular verbs. Write their forms. 10. Compose your own sentences using the words from the vocabulary list. Begin your sentences with: On the one hand__________________ . On the other hand __________________ . 11. Look through the text and pick out sentences with passive predicate. Define the tense form and translate them into Russian. Transform these sentences into active. 12. Answer the questions on the text 1. What does an entity usually do with its excess income? 1. What can an entity whose income is less than its expenditure do to raise capital? 2. What is the role of a financial intermediary? What does he earn for his work? 3. What are the main activities of the bank? 35 4. What categories of finance do you know? 5. How can they achieve their goals? 6. Why is finance considered to be one of the most important aspects of business management? 7. What financing methods does a company use to raise funds? 8. Who can function as investor? 13. Translate into English 1. Государственные финансы составляют часть финансовой системы страны. 2. В Международной финансовой индустрии в предыдущие месяцы произошло увеличение активов в фондах, инвестирующих в страны развивающихся рынков. 3. Этот рост, с одной стороны, отражал желание крупных международных инвесторов диверсифицировать валюту (diversify currency) своих вложений и уменьшить объемы вложений в американские активы, чтобы избежать падения их стоимости в случае ослабления (depreciation) доллара. 4. С другой стороны, желание инвестировать в страны развивающихся рынков является индикатором надежд на то, что роль этих стран, особенно стран БРИК (BRIC — Brazil, Russia, India, China)., в ближайшие годы возрастет и это откроет перед их экономиками новые перспективы. 5. Многие инвесторы сейчас исследуют перспективы проектов в этих странах. 6. Они ожидают, что именно их экономики возьмут на себя роль мотора экономического роста при новом экономическом порядке, который будет складываться после кризиса. 36 7. Банки готовы снижать процентные ставки для тех предприятий, которые испытывают финансовые трудности. 8. Чтобы понять, почему российские банки идут на уступки (make concessions to) своим заемщикам и каков масштаб проблемы просроченных кредитов (overdue credit), достаточно взглянуть на показатели (index) прибыли российских компаний. 9. В современных условиях предприятия самостоятельно распределяют прибыль. 10. Одним из способов увеличения капитала предприятия и привлечения дополнительных средств является эмиссия ценных бумаг (capital issue, issue of securities). 14. Compile a dialogue on the text. Use conversational phrases. 1. There is one other little thing I‘d like to add here. – Мне бы хотелось еще добавить к сказанному. 2. I’d like to draw your attention to … - Мне бы хотелось обратить ваше внимание на … 3. Excuse me for interrupting you but … - Простите, что я вас перебиваю, но… 4. I didn’t’t quite catch what you said. – Мне не совсем понятно, что вы сказали. 5. I wonder if you’d mind telling us … - Не могли бы вы рассказать нам 6. We can’t deny the fact that … - Мы не можем отрицать тот факт, что… Corporate Finance 37 Corporate finance is the field of finance dealing with financial decisions that business enterprises make and the tools and analysis used to make these decisions. The primary goal of corporate finance is to maximize corporate value managing the firm's financial risks. Although it is in principle different from managerial finance which studies the financial decisions of all firms, rather than corporations alone, the main concepts in the study of corporate finance are applicable to the financial problems of all kinds of firms. The discipline can be divided into long-term and short-term decisions and techniques. Capital investment decisions are long-term choices about which projects receive investment, whether to finance that investment with equity or debt, and when or whether to pay dividends to shareholders. On the other hand, short term decisions deal with the short-term balance of current assets and current liabilities; the focus here is on managing cash, inventories, and short-term borrowing and lending (such as the terms on credit extended to customers). The terms corporate finance and corporate financier are also associated with investment banking. The typical role of an investment bank is to evaluate the company's financial needs and raise the appropriate type of capital that best fits those needs. Thus, the terms “corporate finance” and “corporate financier” may be associated with transactions in which capital is raised in order to create, develop, grow or acquire businesses. Vocabulary tool – средство, метод, орудие primary goal – основная задача value – ценность, важность alone - только applicable – применимый, подходящий, соответствующий 38 capital investment - вложения капитала debt – заемный капитал, долговое обязательство current liabilities – краткосрочные обязательства inventories - материально-производственные запасы current assets – текущий капитал, оборотные средства to extend credit – предоставлять кредит investment banking – инвестиционный банк, to evaluate – оценивать, вычислять, давать оценку 1. Train the pronunciation of the words. field maximize value technique analysis applicable evaluate discipline choice current managerial acquire cheque liabilities enterprise associated 2. Guess what is meant! (the words are from the text) 1. a business or company 2. a device or implement, especially one held in the hand, used to carry out a particular function 3. a thing used to help perform a job 4. make as large or great as possible; make the best use of something 5. appropriate 6. a person concerned in the management of large amounts of money on behalf of governments or other large organizations 7. a bank that purchases large holdings of newly issued shares and resells them to investors 8. form an idea of the amount, number, or value of; assess 39 9. an instance of buying or selling something; the action of conducting business 10.amounts due to be paid to creditors within twelve months 11.buy or obtain (an asset or object) for oneself; learn or develop 12.a sum of money paid regularly (typically annually) by a company to its shareholders out of its profits 13.assets which a company does not use on a continuous basis, such as stocks and debts, but which can be converted into cash within one year 14. money in coins or notes, as distinct from cheques, money orders, or credit 15. the material or monetary worth of something 3. Put disjunctive questions to the following sentences and special questions to the underlined words. 1. The terms corporate finance and corporate financier are also associated with investment banking. 2. The discipline can be divided into long-term and short-term decisions and techniques. 3. The terms “corporate finance” and “corporate financier” may be associated with transactions in which capital is raised in order to create, develop, grow or acquire businesses. 4. Translate into English. 1. Вы уже решили какой проект будем финансировать? 2. Акционеры ждут выплаты дивидендов. 3. Основная цель коммерческого предприятия – получение прибыли. 40 4. Мы провели анализ предыдущих лет работы компании и полагаем, что в этом проекте следует использовать заемный капитал. 5. Оборотные средства компании позволяют ей заниматься деловыми операциями данного типа. 6. Банк предоставил кредит с высокой процентной ставкой. 7. Финансирование этого проекта позволит нам максимально увеличить прибыль компании. 8. Термин «оборотные средства» относится к мобильным активам предприятия, которые являются денежными средствами (cash assets) или могут быть обращены в них в течение года или одного производственного цикла. 9. Оборотные средства могут быть охарактеризованы с различных позиций. 10.В процессе производственной деятельности происходит постоянная трансформация отдельных элементов оборотных средств. 11.Предприятие покупает сырье и материалы, производит продукцию, затем продает ее, как правило, в кредит, в результате образуется дебиторская задолженность (receivables), которая через некоторый промежуток времени превращается в денежные средства 12.Циркуляционная природа текущих активов имеет ключевое значение в управлении оборотным капиталом. 13.Прямой связи (direct link) между оборотными средствами и кредиторской задолженностью (receivables) нет, однако считается, что у здорового предприятия текущие активы должны превышать текущие обязательства. 14.Если денежные средства, дебиторская задолженность и производственно-материальные запасы имеют низкие уровни, то вероятность неплатежеспособности (inability to pay) или нехватки (lack of) 41 средств для ведения (to carry out) рентабельной (profitable) деятельности велика. 5. Complete the dialogue and translate it into English. - Я начинаю изучать экономику. Завтра у меня первая лекция по финансам. Интересно (I wonder) что нам будут рассказывать. - Думаю, о видах финансов. Бывают … . - Интересно, чем они отличаются? - Личные финансы – это …, финансы организации - …, государственные финансы - … . - Меня больше интересуют финансы организации. Я хочу быть финансистом на предприятии. Что изучает наука корпоративное финансирование? - Она занимается … . Основная цель корпоративного финансирования - … . - А чем отличается корпоративное финансирование от административных финансов? - Административные финансы занимаются … . Кстати, корпоративные финансы делятся на … . - Что относится к долгосрочным, а что к краткосрочным операциям? - Например, … относятся к долгосрочным операциям. А краткосрочные подразумевают … . - Ты не мог бы объяснить мне, что такое текущий капитал и краткосрочные обязательства? - … . Еще с термином корпоративное финансирование связаны инвестиционные банки, потому что они занимаются увеличении ем капитала, а корпоративные финансы подразумевают совершение операций, которые позволяют увеличить капитал, чтобы … . 42 Public Finance Public finance is a field of economics concerned with paying for collective or governmental activities, and with the administration and design of those activities. The field is often divided into questions of what the government or collective organizations should do or are doing, and questions of how to pay for those activities. The broader term, public economics, and the narrower term, government finance, are also often used. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold: governmental effects on efficient allocation of resources, distribution of income, and macroeconomic stabilization The proper role of government provides a starting point for the analysis of public finance. In theory, under certain circumstances private markets will allocate goods and services among individuals efficiently. If private markets were able to provide efficient outcomes and if the distribution of income were socially acceptable, then there would be little or no scope for government. In many cases, however, conditions for private market efficiency are violated. For example, if many people can enjoy the same good at the same time, then private markets may supply too little of that good. National defense is one example of non-rival consumption, or of a public good. "Market failure" occurs when private markets do not allocate goods or services efficiently. The existence of market failure provides an efficiency-based rationale for collective or governmental provision of goods and services. Externalities, public goods, informational advantages, strong economies of scale, and network effects can cause market failures. Public 43 provision via a government or a voluntary association, however, is subject to other inefficiencies, termed "government failure." Under broad assumptions, government decisions about the efficient scope and level of activities can be efficiently separated from decisions about the design of taxation systems. In this view, public sector programs should be designed to maximize social benefits minus costs (cost-benefit analysis), and then revenues needed to pay for those expenditures should be raised through a taxation system that creates the fewest efficiency losses caused by distortion of economic activity as possible. In practice, government budgeting or public budgeting is substantially more complicated and often results in inefficient practices. Government can pay for spending by borrowing (for example, with government bonds), although borrowing is a method of distributing tax burdens through time rather than a replacement for taxes. A deficit is the difference between government spending and revenues. The accumulation of deficits over time is the total public debt. Deficit finance allows governments to smooth tax burdens over time, and gives governments an important fiscal policy tool. Deficits can also narrow the options of successor governments. Public finance is closely connected to issues of income distribution and social equity. Governments can reallocate income through transfer payments or by designing tax systems that treat high-income and lowincome households differently. The Public Choice approach to public finance seeks to explain how self-interested voters, politicians, and bureaucrats actually operate, rather than how they should operate. Vocabulary 44 concerned with – связанный (с чем-либо), занятый (чем-либо) design – проектирование, планирование, план, расчет broad – широкий narrow – узкий to narrow – уменьшать, ограничивать, сужать purview – компетенция, сфера действия threefold – втройне, состоящий из 3 частей effect – цель, результат, действие, воздействие efficient – эффективный, целесообразный efficiently – эффективно, производительно, рационально efficiency – эффективность, производительность, рентабельность distribution of income – распределение дохода allocation – ассигнование, распределение, размещение allocate –ассигновать, распределять, размещать reallocate – перераспределять proper – истинный, настоящий, provide – обеспечивать, предусматривать, снабжать circumstances – обстоятельства, материальное и финансовое положение under circumstances – при данных обстоятельствах private market – рынок частных заказов outcomes – долгосрочные результаты acceptable – приемлемый, допустимый, подходящий scope – поле деятельности. violate – нарушать, преступать, изменять enjoy – наслаждаться, вкушать, обладать supply – снабжать, поставлять national defense – национальная оборона non-rival consumption – неконкурентное потребление 45 public good – общественные блага, общественные интересы market failure – проявления неэффективности рыночного механизма, дефект рыночного регулирования occur – встречаться, возникать, происходить, случаться existence – существование, наличие rationale – логическое обоснование, основная причина public provision – государственное обеспечение товаров и услуг, производимых в частном секторе provision – обеспечение, снабжение externalities – факторы внешнего порядка advantage – преимущество, превосходство, выгода, польза economy of scale – экономия, обусловленная ростом масштаба производства network effects – эффект сетевой выгоды, сетевой эффект cause – порождать, вызывать public provision – государственное обеспечение товаров и услуг, производимых в частном секторе via – через, с помощью, по причине voluntary association – добровольное объединение however – однако, впрочем, тем не менее, не смотря на be subject to – быть подверженным, подлежать, подпадать под действие inefficiency – неэффективность, неспособность, нерентабельность government failure - проявления неэффективности государственного регулирования assumption – предположение, допущение separate – отделять, разделять, выделять public sector – государственный сектор, общественный сектор, бюджетная сфера 46 taxation system – система налогообложения public sector – государственная служба, бюджетная сфера social benefits – общественная польза, выгода; пособие по соц. страхованию benefits – льготы, услуги, суммарные выгоды, экономический эффект cost-benefit analysis – анализ затрат, оценка экономической эффективности revenues – доходные статьи, выручка, доходы losses – потеря, ущерб, убыток distortion – искажение, деформация budgeting – планирование бюджета денежных средств substantially – по существу, значительно, в основном complicated – сложный, запутанный result in – приводить к, повлечь за собой government bonds – государственные ценные бумаги, правительственные облигации tax burden – налоговое бремя replacement – замена, возмещение accumulation – накопление over time – в течении продолжительного периода deficit finance – дефицитные финансовые операции smooth – сглаживать, выравнивать, устранять fiscal policy – фискальная политика, бюджетно-налоговая политика options – выбор, право выбора, вариант действий successor – преемник, последователь social equity – социальная справедливость transfer payments – трансфертные платежи, передаточные платежи; средства на социальное обеспечение; дотация treat – обращаться, относиться 47 household – домашнее хозяйство, семья approach – подход, принцип self-interested – корыстный, эгоистичный, движимый личными интересами voter – избиратель actually – фактически, на самом деле operate - действовать 1. Train the pronunciation of the words. design resources circumstances association designed violate supply occur designing allocation existence voluntary however allocate revenue burden view reallocate efficient narrow purview threefold efficiency stabilization externalities substantially inefficiency successor acceptable enjoy non-rival failure rationale distortion accumulation assumption issue politician bureaucrat smooth 2. Read and translate the sentences. Define the tense form of the predicates. Form general questions to them and give short negative answers. 1. Public finance concerns payments for collective and governmental activities. 2. The terms public economics and government finance are often used. 3. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold. 4. The proper role of government has provided a starting point for the analyses of public finance. 48 5. Private markets will allocate goods and services among individuals efficiently. 6. Conditions for private market efficiency were violated. 7. Many people can enjoy luxurious goods. 8. Private markets allocated goods and services efficiently. 9. Government is providing goods and services efficiently. 10. Many factors can cause market failure. 11. Public provision is subject to some inefficiencies. 12. The revenue needed to pay for expenditures should be raised. 13. Public budgeting often results in inefficient practices. 14. Deficit can narrow the options of successor governments. 3. Recollect grammar theory on modal verbs and do the tasks. a) Read and translate the sentences paying attention to the use of modal verbs. 1. The field is often divided into questions of what the government or collective organizations should do or are doing, and questions of how to pay for those activities. 2. If many people can enjoy the same good at the same time, then private markets may supply too little of that good. 3. Externalities, public goods, informational advantages, strong economies of scale, and network effects can cause market failures. 4. Public sector programs should be designed to maximize social benefits minus costs, and then revenues needed to pay for those expenditures should be raised through a taxation system that creates the fewest efficiency losses caused by distortion of economic activity as possible. 49 5. Government can pay for spending by borrowing, although borrowing is a method of distributing tax burdens through time rather than a replacement for taxes. 6. Deficits can also narrow the options of successor governments. 7. Governments can reallocate income through transfer payments or by designing tax systems that treat high-income and low-income households differently. 8. The Public Choice approach to public finance seeks to explain how self-interested voters, politicians, and bureaucrats actually operate, rather than how they should operate. 9. If private markets were able to provide efficient outcomes and if the distribution of income were socially acceptable, then there would be little or no scope for government. b) Compare the sentences and explain the difference. 1. Collective organization should pay for those activities. 2. Collective organization is able to pay for those activities. 3. Collective organization is allowed to pay for those activities. 4. Collective organization is to pay for those activities. 5. Collective organization has to pay for those activities c) Translate the verbs avoiding repetition of them in English. Try to use modal equivalents instead of modal verbs from the original sentences (to be able to, to be allowed to, to have to, to be to). Translate these sentences into Russian. 1. The field может быть divided into questions of what the government or collective organizations должны do or are doing, and questions of how those activities должны быть paid for . 2. Government может pay for spending by borrowing. 50 3. Public sector programs должны быть designed to maximize social benefits. 4. Government может reallocate income through transfer payments. 5. Government придется design tax system that treats high-income and low-income households differently. 6. Externalities, public goods, informational advantages, strong economies of scale, and network effects могут cause market failures. 7. Private markets не могут provide efficient outcomes. 8. People of low-income households не могут enjoy expensive goods. 9. The distortion of economic activity может create efficiency losses. 10. The government должно pay for expenditures on public sector programs. 11. Voters могут to elect by ballot beforehand. d) Translate the following sentences into English using the words and word combinations from vocabulary list. Pay attention to the use of modal verbs. 1. Недавнее происшествие на рынке может нанести большой ущерб. 2. Тенденция к проявлению неэффективности государственного регулирования может сохраниться. 3. Добровольные объединения могут получить льготные условия (easy terms). 4. Рынок может поставлять больше товаров. 5. Нарушение социальной справедливости может вызвать революцию. 6. Коммерческое предприятие может эффективно разместить свой капитал на рынке частных заказов. 51 7. Вы можете устранить дефицит бюджета за короткое время? 8. Может ли рынок поставить больше товаров? 9. Может ли правительство оплатить расходы путем выпуска правительственных облигаций? 10. Можем ли мы надеяться на положительные долгосрочные результаты? 11. Можете ли вы дать логическое обоснование дефекта рыночного регулирования? 12. Когда вы сможете спроектировать новый бюджет? 13. При каких обстоятельствах может возникнуть дефект рыночного регулирования? 14. Не может быть, чтобы убытки были такими большими. 15. Не может быть, чтобы их сфера деятельности была такой обширной. 16. Неужели семьи с низким доходом облагаются таким высоким налогом. 17. Неужели государственное обеспечение товаров и услуг, производимых в частном секторе подвержено проявлению неэффективности государственного регулирования? 18. Неужели условия, необходимые для эффективности рынка частных заказов часто нарушаются? 19. Не могли бы вы дать оценку экономической эффективности? 20. Как можно снизить национальный долг? 21. Возможно, они снизят налоговое бремя. 22. Возможно, такое предположение социально приемлемо. 23. Должно быть составление бюджета – очень сложный процесс. 52 24. Должно быть, госфинансирование тесно связано с распределением дохода и социальным равенством. 25. Нужно эффективно размещать ресурсы. 26. Что производители должны поставлять на рынок? 27. Почему они должны увеличить социальные выплаты? 28. Где они должны разместить ресурсы? 29. Государство должно перераспределить доход посредством дотаций. 30. Государство вынуждено спроектировать новую систему налогообложения. 31. Рынки частных заказов должны эффективно распределять товары и услуги среди людей. e) Compose your own sentences in English using modal verbs and their equivalents and the words from vocabulary list. 4. Translate the following adjectives from the text into Russian and transform them into adverbs. Give their Russian equivalents. Compile 5 sentences in English with some of them. public collective efficient proper certain private national possible substantial total close narrow 5. Recollect grammar theory on degrees of comparison of adjectives and do the tasks. a) Give the comparative and superlative of the adjectives below and translate them: broad high difficult 53 good bad cold narrow comfortable clever small large big old bright hot correct low careful easy happy warm expensive cheap rich beautiful important fast talkative b) Find adjectives in the text and give their comparative and superlative degrees. c) Compile your own sentences using comparative constructions: as… as, not so … as and adjectives from the text. Model: The new governmental policy is not so efficient as the old one. The new governmental policy is as efficient as the old one. d) Use the required form of the adjectives 1. He was the (amusing) person you’ve ever met. 2. He’s far (intelligent) person than my brother. 3. She was the (practical) of the family. 4. Today I’m no (wise) than yesterday. 5. The wine is the (good) I’ve ever tasted. 6. The (near) house is three miles away. 7. The interest rate today is (high) than yesterday. 8. These shares are as (expensive) as that of our company. 9. Of the two evils let us choose the (little). 10. These are the (bad) cigarettes I’ve ever smoked. 6. a) Make these words negative adding negative prefixes in-, im-, il-, ir-, un- (efficient – inefficient). Translate them into Russian. 54 In- Im- Ir- Il- Un- visible material rational legal able adequate movable real literate acceptable competent mediate religious logical happy definite perfect relevant limitable believable different migrate regular liberal comfortable correct moderate recoverable legitimate fair expensive moral reconcilable legible easy b) Replace the words in bold type with negative ones and translate the sentences. 1. The company has not provided an adequate explanation for its actions. 2. If you signed a document, it is not wholly material whether you have read it carefully or not. 3. It is not logical to assume you can do the work of three people. 4. The Prime Minister is not competent to govern the country. 5. The company chose a simple and not expensive solution. 6. The insurance premium is not recoverable. 7. The recommendations from this report are not acceptable to many black people. 8. The president is not movable on this issue. 9. Her handwriting was so tiny it was not legible. 10. His liquid assets had to be written off as not recoverable. 11. Students viewed Latin as boring and not relevant. 12. The information you gave us was not correct. 13. The resources were not used efficiently. 55 c) Compose your own sentences in English using the words with negative prefixes and the words from vocabulary list. 7. a) Find in the text all words ending in –tion/-ion. Make corresponding verbs from these nouns and translate them into Russian. b) Translate the sentences using the verbs from the above exercise. 1. Человек, контролирующий (управляющий) работу с поставщиками был уволен за нарушение конфиденциальности (privacy). 2. Рынки частных заказов эффективно организовали размещение товаров и услуг среди потребителей. 3. Государство облагает налогом как семьи с высоким, так и с низким доходом. 4. Некоторые политики искажают факты, чтобы победить на выборах. 5. Он смог накопить крупную сумму и теперь наслаждается солнцем и морем. 6. Одежда и другие товары были распределены среди малоимущих. 7. Новые лампы потребляют меньше электричества. 8. Вместе с новым планом правительство приняло на себя огромный финансовый риск. 9. Многие служащие приняли участие в обсуждении новой пенсионной программы, но только несколько отдали ей предпочтение. c) Compose nouns from the following verbs adding to them –tion, translate them and compile your own sentences with them. Compose, produce, congratulate, examine, inform, occupy, consult, separate, adapt, expect. 56 8. Study grammar theory on conditionals and do the tasks. a) Translate the following sentences into Russian. 1. If private markets were able to provide efficient outcomes and if the distribution of income were socially acceptable, then there would be little or no scope for government. 2. If many people enjoyed the same goods at the same time, private markets would not be able to supply enough amount of that goods. 3. If you made payments by the due date and paid the entire balance promptly you would establish a good credit history. 4. If he is not very busy, he will get a handle on his expenses. 5. If I had got a part-time job, I should have increased my income. 6. If you write down everything you spend for one month, you will see some great ways to save. 7. If you had a job for more than two years you would pay a lower interest rate. 8. If I were you I would put away a certain amount of money every month. 9. If you had put down more, you would have got a better interest rate. 10. If you use receipts to create a budget for what you have actually spent over the last six months, it will help you to calculate the average amount of unexpected expenses. 11. If I were Margaret I would always pay my monthly bills. b) Translate the following sentences from Russian into English. 1. Если бы у меня были накопления, я бы наслаждалась отдыхом в Испании. 57 2. Если бы это касалось общественных организаций, то государство оплатило бы эти расходы. 3. Если компания эффективно распределит ресурсы, она получит большую прибыль. 4. Если бы люди не платили налоги, у государства было бы недостаточно средств, что бы покрыть расходы по национальной обороне. 5. Если бы частные рынки размещали товары и услуги эффективно, дефект рыночного регулирования не произошел бы. 6. Если бы программы общественного сектора были правильно спроектированы, они бы до предела увеличили общественную пользу. 7. Если бы государственное финансирование не было таким сложным процессом, оно не приводило бы к неэффективным действиям. 8. Если бы правительство оплатило расходы путем выпуска государственных облигаций, национальный долг не был бы таким высоким. 9. Если государство создаст налоговую систему, которая будет по-разному обращаться с семьями с высоким и низким доходами, уровень жизни в стране поднимется. 10. На твоем месте я бы составил оценку экономической эффективности предприятия. c) Compose your own sentences using the words from vocabulary list and above sentences as a model. 9. Study the meaning of the suffix –able. From the words bellow form adjectives adding -able. Translate the new words into Russian and compose your own sentences with these words using the vocabulary from the text. 58 Accept, comfort, allow, pay, market, credit, consume, consider, question, tax. 10. Study grammar theory on Complex Subject and do the tasks. a) Translate the following sentences into Russian paying attention to Complex Subject construction. 1. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold. 2. Government is sure to allocate resources efficiently. 3. Conditions for private market efficiency appeared to have been violated. 4. This collective organization is unlikely to pay for its expenditure. 5. Public provision via government seems to be subjected to government failure. 6. The expectation of the government is likely to come true. 7. Efficiency losses caused by distortion of economic activity turned out to be heavy. 8. Government budgeting is thought to be complicated. 9. Government is expected to pay for spending by borrowing. 10. Government is reported to have smoothed tax burden over time. b) Translate the sentences into English paying attention to Complex Subject. 1. Предполагается, что правительство со временем выровняет налоговую нагрузку. 2. Слышали, что акционеры обсуждали предстоящие (forthcoming) выборы. 3. Известно, что некоторые политики корыстные люди. 4. Сообщили, что проявление неэффективности рыночного механизма произошло из-за неумелого размещения товаров и услуг. 59 5. Говорят, что накопление дефицита на протяжении продолжительного периода составляет общий государственный долг. 6. Полагается, что государственные финансы тесно связаны с вопросами распределения дохода и социального равенства. 7. Программы государственного сектора обязательно максимально увеличат общественную пользу. 8. Рынки частных заказов, по-видимому, эффективно распределили товары и услуги среди потребителей. 9. Сообщают, что спроектирована новая система налогообложения. 10. Вчера избиратели случайно встретили политика, за которого отдали свои голоса. с) Compose your own sentences with Complex Subject. Don’t forget to use the words from vocabulary list. Mind the words for Complex Subject construction: to know, to see, to hear, to report, to think, to suppose, to expect, to say, to believe, to seem, to appear, to prove, to turn out, to happen, sure, likely, unlikely. 11. Study the meaning of the prefix re-. From the words below form the new ones adding re-. Translate them into Russian and compose your own sentences with these verbs and the vocabulary from the text. Allocate, distribute, view, create, pay, write, finance, read, examine, consider, elect, produce. 12. a) Learn the information below to get a handle on some economic terms used in the text. 60 Economy of scale means a proportionate saving in costs gained by an increased level of production. Economy of scope means a proportionate saving gained by producing two or more distinct goods, when the cost of doing so is less than that of producing each separately. Social equity implies fair access to livelihood, education, and resources; full participation in the political and cultural life of the community; and self-determination in meeting fundamental needs. As Martin Luther King observed, "where there is injustice for one, there is injustice for all." Social equity is the cornerstone of society, which cannot be maintained for a few at the expense of the many. Increased equity results in decreased spending on prisons, security enforcement, welfare, and social services. It also creates new potential markets. Social equality is a social state of affairs in which all people within a specific society or isolated group have the same status in a certain respect. Public sector, sometimes referred to as state sector, is a part of the state that deals with either the production, delivery and allocation of goods and services by and for the government or its citizens, whether national, regional or local/municipal. Government failure is a situation where government intervention in the economy to correct a market failure creates inefficiency and leads to a misallocation of scarce resources. Market failure occurs when the work of the price mechanism is imperfect and results in an inefficient or unfair allocation of resources from the perspective of society. Examples include, the education and defense markets. This is a case in which prices are unable to adequately adjust to reflect changes in supply or demand. Market failures may occur due to 61 unexpected disruptive events such as wars or natural disasters, or due to economic barriers such as trade restrictions or monopolies. Income distribution means the distribution of wages earned across a company, industry, or country. Income distribution reveals what percentage of individuals are at various wage levels, information that can reveal more about overall wage patterns (общая структура заработной платы) than average income can. Non-rival consumption occurs when the consumption of a good does not stop others from using the good e.g. air. Public goods are items which can be jointly consumed by many consumers simultaneously without any loss in quantity or quality of provision e.g. a lighthouse. Public goods are therefore goods that would not be provided in a pure free-market system (система свободного предпринимательства). This is because they display two particular characteristics: 1. Non-rivalry - consumption by one person does not reduce the amount available for others. 2. Non-excludability (неисключаемость) - once the good is provided it is impossible to stop people consuming it even if they haven't paid. An example of this is defense. It is impossible to charge people for defense as they consume it as the whole country is being defended at once. Also one person being defended does not stop others being defended. Externalities means a consequence of an industrial or commercial activity which affects other parties without this being reflected in market prices, such as the pollination (опыление) of surrounding crops by bees kept for honey. These are spillover effects (сопутствующие эффекты) of production or consumption for which no payment is made. Externalities can be positive or negative. For example all fax users gain as new users become connected (positive); and smoke from factory chimneys (negative). 62 Network effect (also called network externality or demand-side economies of scale) is the effect that one user of a good or service has on the value of that product to other people. When network effect is present, the value of a product or service is dependent on the number of others using it. Public choice theory in economics means the use of modern economic tools to study problems that traditionally are in the province of political science. Public choice seeks to understand and predict the behavior of politicians and bureaucrats in the polity by using analytical techniques developed from economics, based on the postulate of rational choice. In other words, public choice is an application of neoclassical economic tools (self interest and utility maximization) to explain political behavior. Public choice theory is about the analysis of governmental behavior, and the behavior of individuals who interact with government. The theory came about when economists looked at some apparent contradictions in human behavior. Think about it in this way - what do governments exist for? You might argue that they are there to act in the public interest. Acting in the public interest might be defined as a case where decision making is based on a principle where the maximum benefit is gained by the largest number of people. Any decision will involve some sort of cost, so there will be some people that will be affected adversely by those decisions. If those people are in the minority and the benefits to the majority outweigh those costs, a decision might then be regarded as acting in the public interest. In public choice, individuals, interest groups, bureaucrats, and politicians are assumed to seek their own self interest as in the market place. Decisions made depend on the costs and benefits of an action taken whereby each group attempts to maximize their own net benefits. 63 Benefits can take the form of monetary or non-monetary rewards and can include ideologies, goals, and cultural values. b) Translate the sentences into English paying attention to economic terms. 1. Неконкурентные товары должны быть доступны каждому независимо от возможности отдельного лица оплатить их потребление. 2. По мере роста некоторые компании изменяют производственные технологии и методы внутренней организации для того, чтобы реализовать преимущества крупного производства. Эти изменения и создают эффект экономии обусловленной ростом масштаба производства. 3. Идеалом социальной справедливости является такая система общественных институтов, которая постоянно обеспечивает справедливое распределение социально-политических прав и материальных благ. 4. Социальное равенство — общественное устройство, при котором все члены общества обладают одинаковым статусом в определенной области. 5. Изменения в области предоставления компаниями услуг имеют сильное влияние на государственный сектор. 6. Несовершенство (дефект) рынка — широко распространенный в западной экономической литературе термин, которому пока нет четкого определения. Дефект рыночного регулирования — это ситуация, когда рыночная конкуренция не ведет к экономической эффективности, вопреки тому, что следовало бы ожидать. Несовершенство рынка часто выдвигается в качестве оправдания разного рода вмеша64 тельств государства в течение экономических процессов: с точки зрения творцов экономической политики, если ресурсы распределяются неэффективно, то государство может “подправить” распределение, приблизить его к оптимуму. 7. В настоящее время бизнес сам предъявляет спрос на услуги государства, так как он в первую очередь заинтересован в преодолении рисков и неопределенности, обусловленных слабостью или неэффективностью государственного регулирования. 8. Личное (персональное) распределение доходов представляет собой их распределение между отдельными экономическими ячейками, которыми являются частные лица, семьи, домашние хозяйства. 9. Общественные блага - блага, к которым имеют доступ все индивиды. К общественным благам относятся: оборона, бесплатное образование, общедоступное посещение парков, музеев и т.п. В противоположность частным благам общественные блага: они неконкурентны - потребление такого блага одним человеком не сокращает количество блага, доступное другим; и носят неисключающий характер, что не позволяет исключить кого-либо из пользования этими благами. Эти характеристики не позволяют назначать плату за общественные блага, вследствие чего частный сектор оказывается не заинтересованным в финансировании их производства. Различают общенациональные и местные (локальные) общественные блага. 10. Сетевой эффект возникает тогда, когда выгода от товара повышается благодаря применению аналогичного товара другими людьми. Например, выгода от телефонной службы, телекса, телефакса или электронной почты проявляется, прежде всего, в случае, если ими пользуется в коммуникационных целях как можно большее количество людей. Чем шире круг абонентов, тем выше выгода отдельного 65 потребителя услуг системной технологии, так как с их ростом увеличивается и количество возможных коммуникационных связей. Так, телефон сам по себе не приносит владельцу никакой пользы, если другие лица его не имеют. 11. Факторы внешнего порядка практически не подвластны контролю со стороны товаропроизводителей, но обязательно учитываются при формировании цены на выпускаемую продукцию. 12. Теория общественного выбора - раздел экономической науки, изучающий закономерности выбора путей деятельности правительства в области экономики и то, каким образом осуществляется этот выбор под давлением демократической системы. 13. Теория общественного выбора опирается на базовую идею о том, что человек в любой области своей деятельности стремится максимизировать результат в своих собственных интересах. 13. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What does the discipline of Public Finance study? 2. Why is the purview of public finance considered to be threefold? 3. What circumstances are necessary for the efficient allocation of goods and services by private markets? 4. Give examples of private market inefficiency. 5. What is market failure? 6. When can market failure appear? What can it be caused by? 7. What is government failure? 8. Why does government budgeting often result in inefficient practices? 9. How should private sector programs be designed? 10. How can government pay for spending? 66 11. When does deficit appear? 12. What makes total public debt? 13. How can government reallocate income? 14. What is the public choice approach in economics? UNIT 2. MANAGEMENT Interpretations of Management There is a variety of views about this term. Traditionally, the term “management” refers to the set of activities, and often to the group of people, involved in four general functions, including planning, organizing, leading and coordinating activities. All these four functions are highly integrated and interrelated. Some writers, teachers and practitioners say that the above view is rather out-of-date and that management needs to focus more on leadership skills, e.g., establishing vision and goals, communicating the vision and goals, and guiding others to accomplish them. They also say that leadership must be more facilitating, participative and empowering in how visions and 67 goals are established and carried out. Some people say that this really isn’t a change in the management functions but a new look at certain aspects of management. Another common view is that “management” is getting things done through others. Yet another view, quite apart from the traditional view, asserts that the job of management is to support employees’ efforts to be fully productive members of the organizations. To most employees, the term “management” probably means the group of people (executives and other managers) who are primarily responsible for making decisions in the organization. In nonprofit organizations, the term “management” might refer to all or any of the activities of the board, executive director and/or program directors. Vocabulary management – управление, руководство. менеджмент term – термин to refer to – иметь отношение, относиться; касаться activity – деятельность to involve – привлекать, вовлекать function – функция planning – планирование organizing – организация (процесс) leading – руководство, управление coordinating – координирование interrelated – взаимосвязанный practitioner – практик, профессионал view – точка зрения, мнение, взгляд 68 to focus on – сосредоточивать, фокусировать внимание на skill – умение; навык to establish / set a goal – поставить цель, задачу vision – видение, мировоззренческая концепция to communicate – говорить, сообщать to accomplish / to achieve a goal – достигать цели to carry out – выполнять, проводить в жизнь, осуществлять common – общепринятый, распространённый to assert – утверждать, заявлять to support – поддерживать, содействовать effort – усилие, попытка employee – работник, служащий, работающий по найму executive - должностное лицо, руководитель, администратор (какого-л. учреждения) to be responsible for – быть ответственным / отвечать за to make / take a decision – принимать решение profit – выгода, прибыль nonprofit / not-for profit – некоммерческий profit / profit making organization – коммерческая организация board – правление, руководство board of directors – совет директоров executive director – исполнительный директор; управляющий program director - руководитель программы 1. Write the transcription of the words and train their pronunciation. 69 view vision through executive term goal efforts decision general guide organization board function common employee 2. Work with the following groups of words. Define their part of speech and translate. Point out prefixes and suffixes. Memorize the words and use them in the sentences of your own. 1. To manage, manager, management, managerial. 2. To act, activity, action, active, actively. 3. To lead, leader, leading, leadership. 4. To accomplish, accomplishment, accomplished. 5. To employ, employer, employee, employment, unemployment, unemployed. 6. Responsible, irresponsible, responsibility. 7. To decide, decision, decisive, indecisive, decisively, decisionmaking, decision-maker. 8. To organize, organization, organizer, organizing, organizational. 9. To profit, profit, profitable, unprofitable, profitability, for-profit, nonprofit. 3. Translate the following nouns and write their plural form. View, activity, skill, goal, employee, employer, responsibility, decisionmaker. 4. Translate these sentences. Define the tense form of the predicate. Make up disjunctive questions and special questions to the underlined words. 70 1. Four general functions of managers are planning, organizing, leading and coordinating. 2. Management needs to focus more on leadership skills. 3. Managers are responsible for decision-making in organizations. 5. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What is the traditional interpretation of the term “management”? 2. How do you understand the phrase “Management is getting things done through others”? 3. What do some writers, teachers and practitioners say about the traditional view? 4. What other interpretations of the term “management” are given in the text? 5. What does the focus on leadership skills mean? 6. Does the focus on leadership skills mean a change in the management functions? 7. What may the term “management” mean to most employees? 8. What may the term “management” refer to in nonprofit organizations? 6. Fill in the gaps with the words from the box coordinate, employees, managers, profitability, resources, efficiency … decide what will be done, who will do it, when it will be done, and what … will be used. They train and hire new …, and they … their department’s activities with other departments. Managers are the heart of a company, the force that unites everything in the organization to ensure optimum … and …. 71 What is a Manager? A number of different terms are often used instead of the term “manager”, including “director”, “administrator” and “president”. The term “manager” is used more frequently in profit-making organizations, while the others are used more widely in government and nonprofit organizations such as universities, hospitals and social work agencies. So, whom do we call a “manager”? In its broad meaning the term “manager” applies to the people who are responsible for making and carrying out decisions within a certain system. A personnel manager directly supervises people in an organization. Financial manager is a person who is responsible for finance. Sales manager is responsible for selling of goods. Marketing manager is responsible for promotion of product on the market. Almost everything a manager does involves decision-making. When a problem exists a manager has to make a decision to solve it. In decisionmaking there is always uncertainty and risk. Management is a variety of specific activities. Management is a function of planning, organizing, coordinating and directing and controlling. Any managerial system, at any managerial level, is characterized in terms of these general functions. Managing is responsible and hard job. There is a lot to be done and relatively little time to do it. In all type of organizations managerial efficiency depends on manager’s direct personal relationships, hard work on a variety of activities and preference for active tasks. The characteristics of management often vary according to national culture, which can determine how managers are trained, how they lead people and how they approach their jobs. 72 The amount of responsibility of any individual in a company depends on the position that he or she occupies in its hierarchy. Managers, for example, are responsible for leading the people directly under them, who are called subordinates. To do this successfully, they must use their authority, which is the right to take decisions and give orders. Managers often delegate authority. This means that employees at lower levels in the company hierarchy can use their initiative, i.e. make decisions without asking their manager. Vocabulary government – правительство meaning – значение, смысл to apply to = refer to within – в, внутри; в рамках (какой-л. организации) personnel manager – менеджер по персоналу, начальник отдела кадров financial manager – финансовый менеджер, финансовый директор sales manager – менеджер по продажам, заведующий отделом продаж goods – товар, товары marketing manager – менеджер по маркетингу market – рынок promotion – 1) продвижение, раскрутка, рекламирование 2) продвижение по службе, повышение в звании to solve a problem – решать, разрешать проблему variety – многообразие, разнообразие; ряд, множество in terms of – с точки зрения; в свете efficiency – эффективность, продуктивность, производительность to depend on – зависеть от according to – в соответствии с, согласно, по 73 position - положение; должность to occupy / have / hold a position — занимать должность hierarchy – иерархия subordinate – подчиненный authority – власть, полномочия to delegate authority –передавать, делегировать полномочия order – 1) порядок 2) приказ level – уровень, ступень without – без 1. Write the transcription of the words and train their pronunciation. include meaning financial specific government personnel finance efficiency agency personal product culture determine individual company hierarchy subordinates successfully authority initiative 2. Work with the following groups of words. Write the transcription of the words and train their pronunciation. Define their part of speech and translate. Point out prefixes and suffixes. Memorize the words and use one from each group in a sentence of your own. 1. To govern, governor, government, governing, governmental. 2. To mean, meaning, meaningful, meaningless. 3. To finance, finances, financial, financing. 4. To solve, solution, solvable, unsolved. 74 5. To depend, dependence, dependency, dependent, dependable, independent, independence, independently, interdependence. 6. Variety, to vary, variable, invariably. 3. Fill in the gaps with appropriate words, then translate the sentences into Russian. 1. Many different terms can be used … the term “manager”, for example, “director”, “administrator”, “president”. 2. The term “manager” is used more frequently in … organizations. 3. … manager … for supervising people in an organization. 4. … manager … for finance. 5. … manager … for selling of goods. 6. … manager … for promotion of products on the market. 7. When a problem exists a manager has to… to solve it. 8. National culture often … how managers are trained, how they lead people and how they approach their jobs. 9. The position an individual occupies in a company’s hierarchy … the amount of his or her responsibility. 10.Authority is the right to … decisions and … orders. 11.When managers delegate authority, they allow employees at … levels in the company hierarchy to make … without … their manager. 4. Write degrees of comparisons of the following adjectives. Use them in the sentences of your own, make use of different comparative constructions. Broad, responsible, hard, little, efficient, active, successful, low, high. 75 5. Make the following sentences negative and transform them into general questions. 1. The term “manager” is used in profit-making organizations. 2. The term “manager” applies to the people who are responsible for making and carrying out decisions. 3. Personnel manager is responsible for finance. 4. Manager has to make a decision to solve the problem. 5. Managerial efficiency depends on manager’s direct personal relationships. 6. National culture can determine how managers are trained, how they lead people and how they approach their jobs. 7. To lead subordinates successfully, managers must use their authority. 8. Employees at lower levels in a company can make decisions without asking their manager. 6. Read and translate the following sentences. Make them active. 1. The term “manager” is used more frequently in profit-making organizations, while the others are used more widely in government and nonprofit organizations. 2. Any managerial system, at any managerial level, is characterized in terms of these general functions. 3. The characteristics of management can be determined by national culture. 7. Read the text “What is a Manager” again and answer the questions on it. 1. What terms are used in nonprofit organizations instead of the term “manager”? 76 2. What is the manager’s role in an organization? 3. What concrete activities a financial manager (personnel manager, marketing manager, sales manager) is responsible for? 4. Prove that management is a hard and responsible job. 5. What is authority? 6. What does it mean to delegate authority? The Concept of Management and the Mission of a Manager Management is a very exciting and rewarding career. A career in management offers status, interesting work, and the satisfaction of working closely with other people. Entrepreneurs who start and run businesses by themselves do not have to manage other people. They have to manage themselves. However, if the firm has employees, then some kind of management plan is necessary. Management includes the processes or functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. For example, suppose you have created your own comic book and want to start a comic book company. Do you want to produce comic books and market them as well? Do you also want to produce cartoons, video games, and action figures based on your comic books? Because of the complexity of your business, you will need employees to help. Managers can help by supervising and directing employees. Management helps businesses focus on setting and meeting goals efficiently so that a profit can be made. The word management also refers to the people who are in charge of running a business. Managers need a thorough understanding of business operations, which involve all the activities of a company. They develop the objectives for a firm or a department and then figure out how to meet those objectives through people, work processes, and equipment. 77 Today people are considered the most important resource in companies. If they perform effectively, companies will succeed. When companies are successful, there is better utilization of resources, less stress among employees, less chaos in society, and a better quality of life for all. So, management can be defined as working with and through other people to accomplish the objectives of both the organization and its members. As we can see, the definition of management places greater emphasis on the human being in the company rather than the company itself; focuses attention on the objectives and results of the activities, rather than just the activities; points out that the accomplishment of the members’ personal objectives should be integrated with the accomplishment of the organizational objectives. We can make a conclusion that management is both a science and art, and a good manager is not just a technician, following a vocational field, but a person who is able (no matter at what level in a company) to plan, organize, staff, coordinate, motivate, lead, and control. Vocabulary career – карьера, профессия satisfaction – удовлетворение, удовольствие entrepreneur – бизнесмен, предприниматель to run a business – руководить, управлять делом, вести дело to market – продавать, сбывать to meet the goals – обеспечивать требуемые показатели to be in charge of – быть ответственным за, отвечать за; руководить чем-л. to develop – 1) развивать 2) разрабатывать, конструировать, создавать objective – задача, цель 78 to figure out – решать, разрешать (проблему); вычислять, выяснять; понимать, постигать through – через, посредством to succeed – достигать цели, преуспевать; иметь успех definition – определение emphasis – выразительность, сила, ударение to put / place emphasis on smth. — придавать особое значение чему-л., уделять большое внимание чему-л., делать акцент на чём-л. to point out – указывать; обращать (чьё-л.) внимание; отмечать, подчёркивать science – наука vocational field – сфера (область) профессиональной деятельности staffing - кадровое обеспечение, укомплектование персоналом, подбор (и расстановка) кадров 1. Write the transcription of the words and train their pronunciation. exciting rewarding career satisfaction entrepreneur firm produce objective department through equipment resource succeed chaos society emphasis result accomplishment science figure out 2. Form derivatives of the following words and translate them into Russian. Memorize the words and use one from each group in a sentence of your own. Example: to organize (организовывать, планировать) → organizer (организатор) → organization (организация) → organizing (организация, планирование) → organizational (организационный) 79 to produce, to plan, to control, to accomplish, to succeed, to supervise, to direct, to satisfy, to develop, to motivate. 3. Find in the text sentences containing modal verbs or their equivalents, translate the sentences into Russian. 4. In the following sentences determine the tense and voice form of the predicate. Make up a general and a special question to each sentence. 1. You have created your own comic book and want to start a comic book company. 2. Because of the complexity of your business, you will need employees to help. 3. Today people are considered the most important resource in companies. 4. If employees perform effectively, companies will succeed. 5. The accomplishment of the members’ personal objectives should be integrated with the accomplishment of the organizational objectives. 5. Match the phrases from column A with their Russian equivalents in column B. Make up sentences. A B 1. run a business a. управляющий 2. vocational field b. функции планирования 3. personal objectives c. цели организации 4. organizational objectives d. сфера профессиональной деятельности 5. manager 6. functions of planning e. успех 7. success f. вести дело, управлять 80 предприятием g. личные цели 6. Match the words from the box with their definitions. business, to plan, company, manager, to lead, career, status, to control, entrepreneur, management, to organize 1. the technique, practice, or science of managing, controlling or dealing with smb., smth.; 2. the members of the executive or administration of an organization or business; 3. a social or professional position, condition, or standing to which varying degrees of responsibility, privilege, and esteem are attached; 4. a profession or occupation chosen as one’s life’s work; 5. the owner or manager of a business enterprise who, by risk and initiative, attempts to make profits; 6. an affair, matter; serious work or activity; a trade or profession; an industrial, commercial, or professional operation; purchase and sale of goods and services; 7. a person who directs or manages an organization, industry, shop, etc.; a person who controls the business affairs of smb.; a person who has a talent for managing efficiently; 8. to think carefully about smth. you want to do in the future and decide exactly how you will do it; 9. to form (parts or elements of smth.) into a structured whole; coordinating; arranging methodically or in order; 10.to show the way to (an individual or a group) by going with or ahead; to guide by holding, pulling, etc.; 81 11.to command, direct, rule, regulate; 12.a business enterprise. 7. Read the text “The Concept of Management and the Mission of a Manager” again and complete the sentences. 1. Management includes the processes or functions of … . 2. Management is a very exciting and rewarding … . 3. A career in management offers … . 4. Entrepreneurs who start and run businesses by themselves do not have to manage … . 5. Management can be defined as … . 6. The word management refers to … . 7. Management is both a science and … . 8. A good manager is not just… . 9. Today people are considered the most important … . 10. A good manager is a person who is able (no matter at what level in a company) to … . 8. Express your opinion on the following. 1. “Effective managers need to be good communicators”. 2. “Effective managers need a thorough understanding of business operations”. 3. “A career in management is a very exciting and rewarding one”. What is Management? Management is a universal phenomenon. It is a very popular and widely used term. All organizations – business, political, cultural or social – are involved in management because it is the management which helps and 82 directs the various efforts towards a definite purpose. According to Harold Koontz, “Management is an art of getting things done through and with the people in formally organized groups. It is an art of creating an environment in which people can perform and individuals and can co-operate towards attainment of group goals”. According to F.W. Taylor, “Management is an art of knowing what to do, when to do and see that it is done in the best and cheapest way”. Management is a purposive activity. It is something that directs group efforts towards the attainment of certain predetermined goals. It is the process of working with and through others to effectively achieve the goals of the organization, by efficiently using limited resources in the changing world. Of course, these goals may vary from one enterprise to another. E.g.: For one enterprise it may be launching of new products by conducting market surveys and for other it may be profit maximization by minimizing cost. Management involves creating an internal environment. It is the management which puts into use the various factors of production. Therefore, it is the responsibility of management to create such conditions which are conducive to maximum efforts so that people are able to perform their task efficiently and effectively. It includes ensuring availability of raw materials, determination of wages and salaries, formulation of rules and regulations etc. Therefore, we can say that good management includes both being effective and efficient. Being effective means doing the appropriate task i.e, fitting the square pegs in square holes and round pegs in round holes. Being efficient means doing the task correctly, at least possible cost with minimum wastage of resources. 83 Vocabulary purposive – служащий для определённой цели; целевой attainment – достижение; приобретение predetermined goals – заранее заданные (установленные) цели limited resources – дефицитные / ограниченные ресурсы to launch – зд. выпускать на рынок (товар) launching – запуск (системы, программы, задачи и т. п.) to conduct market survey – проводить изучение состояния рынка internal environment – внутренняя среда (организации) to put into use – осуществлять, проводить в жизнь conducive – благоприятный, подходящий; способствующий conducive to smth. – ведущий к чему-л. wages and salaries – зарплата рабочих и служащих availability – 1) годность, полезность, пригодность 2) наличие, присутствие rules and regulations – правила и предписания effective and efficient – действенный, результативный, эффективный efficient – умелый, подготовленный, квалифицированный (о человеке); wastage of resources – потери; отходы; утечка 1. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What is Management according to Harold Koontz? 2. What is Management according to F.W. Taylor? 3. Why is management a purposive activity? 4. How can management effectively achieve the goals of the organization? 5. Why is it important for management to create an internal environment? What does it include? 6. What is meant by management being effective and efficient? 84 3. Explain these words and word combinations in English; use them in the sentences of your own: management, to co-operate, predetermined goals, profit maximization, to minimize cost, to put into use, to fit the square pegs in square holes. 3. Work with the following groups of words. Define their part of speech and translate. Point out prefixes and suffixes. Memorize the words and use them in the sentences of your own. 1. to manage, manager, management. 2. to launch, launching, launcher, launchpad. 3. to cooperate, cooperation, cooperative. 4. to effect, effective, ineffective, effectiveness. 5. to waste, wasteless, wastage. 4. Translate the following nouns and write their plural form. Use them in the sentences of your own. Phenomenon, survey, process, salary, enterprise, organization, task, purpose. 5. Translate these sentences. Put them in the Singular, making necessary changes. Compile special questions to the underlined words. 1. All organizations are involved in management. 2. These goals may vary from one enterprise to another. 3. Such conditions are conducive to maximum efforts of the people. 4. People are able to perform their task efficiently and effectively. 5. Group goals are attained through co-operation. 6. Translate these sentences into English. 1. Менеджмент — это самостоятельный вид профессиональной деятельности. 85 2. Менеджмент направлен на достижение определенных намеченных целей путем эффективного использования материальных и трудовых ресурсов. 3. Менеджмент включает изучение рынка, производство продукции с минимальными затратами и реализация ее с максимальной прибылью, управление персоналом, а также анализ информации и разработку программ для достижения поставленной цели. 4. Основная функция менеджмента – это умение достигать поставленных целей. 5. Менеджмент – это наука, позволяющая находить наилучшее решение в каждой конкретной ситуации. 6. Менеджмент – это информационный, целенаправленный процесс воздействия на коллектив людей. 7. Практически все известные зарубежные энциклопедии трактуют понятие «менеджмент» как процесс достижения целей предприятия посредством привлечения других людей. 7. Sum up the text and discuss with your partner the necessity of talent management and the difficulty to find it. Talent Management Talent management is an essential strategic HR practice aimed at improving business performance. People who perform at higher levels generate greater profits for businesses, much needed in highly competitive environments where it is increasingly challenging to gain a competitive edge. In our knowledge driven age, all businesses need to make talent management a strategic priority in order to ensure that it has the right talent producing to its potential at the right time. 86 Skilled workers are in shorter supply in many industries, older workers are retiring, employees are not feeling engaged, turnover is very expensive, managing a global workforce is challenging as well as expensive and educated workers expect more from their careers. They are harder to satisfy. Effective talent management requires an integrated series of HR systems and components including recruitment, performance management, career management, people development, succession planning, effective deployment and employee engagement. Talent management can be led and supported by the HR function but it must be owned by all senior executives and regarded as one of their strategic priorities. This means that they need to be personally better at managing and engaging people. The real problem is that they would rather focus on the more exciting kinds of work such as winning major new business, acquiring other companies or making great deals. They want HR to provide them with fully competent, motivated people so they won't have to spend too much time cultivating talent themselves. This mindset must change in order for talent management to be more than a slogan. Management as a Profession Over a large few decades, factors such as growing size of business unit, separation of ownership from management, growing competition etc. have led to an increased demand for professionally qualified managers. The task of manager has been quite specialized. As a result of these developments the management has reached a stage where everything is to be managed professionally. A profession may be defined as an occupation that requires specialized knowledge and intensive academic preparations to which entry is regulated by 87 a representative body. The essentials of a profession are: Specialized knowledge. A profession must have a systematic body of knowledge that can be used for development of professionals. Every professional must make deliberate efforts to acquire expertise in the principles and techniques. Similarly a manager must have devotion and involvement to acquire expertise in the science of management. Formal Education and Training. There are numbers of institutes and universities to impart education and training for a profession. No one can practice a profession without going through a prescribed course. Many institutes of management have been set up for imparting education and training. Social Obligations. Profession is a source of livelihood but professionals are primarily motivated by the desire to serve the society. Their actions are influenced by social norms and values. Similarly a manager is responsible not only to its owners but also to the society and therefore he is expected to provide quality goods at reasonable prices to the society. Code of Conduct . Members of a profession have to abide by a code of conduct which contains certain rules and regulations, norms of honesty, integrity and special ethics. A code of conduct is enforced by a representative association to ensure self discipline among its members. Any member violating the code of conduct can be punished and his membership can be withdrawn. The AIMA has prescribed a code of conduct for managers but it has no right to take legal action against any manager who violates it. Representative Association. For the regulation of profession, existence of a representative body is a must. For example, an institute of Charted Accountants of India establishes and administers standards of competence for the auditors but the AIMA however does not have any 88 statuary powers to regulate the activities of managers. Thus it is quite clear that management fulfills several essentials of a profession, even then it is not a full-fledged profession because: It does not restrict the entry in managerial jobs for account of one standard or other. No minimum qualifications have been prescribed for managers. No management association has the authority to grant a certificate of practice to various managers. All managers are supposed to abide by the code formulated by AIMA. Competent education and training facilities do not exist. Managers are responsible to many groups such as shareholders, employees and society. A regulatory code may curtail their freedom. Managers are known by their performance and not mere degrees. The ultimate goal of business is to maximize profit and not social welfare. That is why Haymes has rightly remarked, “The slogan for management is becoming - ’He who serves best, also profits most’.” Vocabulary ownership – собственность; владение; право собственности competition – конкуренция, конкурентная борьба demand – спрос, требование, настойчивая просьба demands – запросы, требования to be in demand – пользоваться спросом occupation – занятие; род занятий, профессия to acquire expertise – приобретать профессиональные знания; практический опыт to impart – 1)давать, наделять; 2) сообщать, передавать 89 social norms and values – социальные нормы и ценности a code of conduct – кодекс поведения to abide by – следовать (чему-л.), действовать в соответствии с (чемл.); придерживаться (чего -л.) to violate – нарушать to withdraw – 1) отзывать, отменять 2) прекращать representative body – представительный орган a must – необходимость, обязательный атрибут full-fledged profession – полноценная профессия to restrict – ограничивать to grant a certificate – вручать свидетельство (сертификат) to curtail one’s freedom – ограничивать свободу the ultimate goal – конечная цель AIMA (Alternative Investment Management Association) – Ассоциация управления альтернативными инвестициями 1. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What has led to an increased demand for professionally qualified managers over a large few decades? 2. How may a profession be defined? 3. What is meant by specialized knowledge? 4. What must a manager have to acquire expertise in the science of management? 5. What are professionals primarily motivated by? 6. What is meant by a code of conduct? 7. Why is it necessary to enforce a code of conduct? What happens if a member of an organization violates the code of conduct? 8. What is meant by representative association? 90 9. What proves that management is not a full-fledged profession? 10. What is considered to be the ultimate goal of business? 2. Explain these words and word combinations in English: Ownership, to be in demand, to acquire expertise, to abide by a code of conduct, to withdraw one’s membership, to curtail freedom, to maximize profit 3. Transform the sentences into negative and translate them. 1. There are numbers of institutes and universities to impart education and training for a profession. 2. Profession is a source of livelihood. 3. Existence of a representative body is a must. 4. It is quite clear that management fulfills several essentials of a profession. 5. Managers are responsible to many groups. 6. The ultimate goal of business is to maximize profit and not social welfare. 4. Translate these sentences. Define the tense form of the predicate. Compile special questions to the underlined words. 1. The task of manager has been quite specialized. 2. A profession requires specialized knowledge and intensive academic preparations. 3. Many institutes of management have been set up for imparting education and training. 4. Professionals are primarily motivated by the desire to serve the society. 5. The AIMA has prescribed a code of conduct for managers. 6. No management association has the authority to grant a certificate 91 of practice to various managers. 5. Finish the following sentences: 1. As a result of these developments the management… 2. A profession must have… 3. A manager is responsible not only to … 4. A code of conduct contains … 5. No management association has the authority… 6. The slogan for management is becoming… 6. Translate these sentences into English. 1. Право собственности может быть абсолютным или ограниченным. 2. У нашей фирмы серьёзные проблемы из-за конкуренции с другой компанией, и нам придётся удвоить наши усилия, чтобы преуспеть. 3. На сегодняшний день особенно ценятся руководители проектов, налоговые аналитики и инженеры. 4. В современной теории и практике под менеджментом понимается процесс руководства (управления) отдельным работником, рабочей группой и предприятием в целом. 5. Она любит свою профессию, т.к. считает, что менеджер несет ответственность не только перед своим руководителем, но и перед обществом в целом. 6. Несколько экспертов предложили разработать кодекс поведения по правам человека. 7. Стороны согласились применять условия и принципы Соглашения. 92 8. Административная группа должна быть преобразована в полноправный исполнительный орган. The Four Functions of Management Most managers carry out four different functions of management: planning, organizing and staffing, leading, and controlling. Some managers may primarily focus on one or two of them. These functions are indicated in the order in which they occur. Planning Planning must be completed first. Planning is the act or the process of creating goals and objectives as well as the strategies to meet them. Planning also involves figuring out the resources that are needed and the standards that must be met. Organizing and Staffing Then organization can take place. Organization allows managers to lead and control employees and activities to get work done. Organizing is getting the resources arranged in an orderly and functional way to accomplish goals and objectives. A manager must organize people, work processes, and equipment so that the work is well coordinated. Managers also hire and train employees – and fire them when necessary. They are responsible for making sure employees have all the tools they need to do their jobs well. Leading Good management also requires good leadership. Leading involves providing guidance to employees so that they can fulfill their responsibilities effectively. There is more to leading than just giving orders. Leading means providing direction and vision. You have to create a vision of the company to inspire your employees. You need to set standards, so that your 93 workers know their goals. Leaders also have to delegate work, enforce policies, oversee time management, and provide feedback on employees’ work. Resolving conflicts between workers is also a leadership task. Good managers lead by example. This is especially important when leading a team. Showing respect to others, honesty, loyalty, courtesy, and a strong work ethic can have a positive effect on employees. Managers who show motivation, initiative, cooperation, and punctuality demonstrate to employees the importance of each person’s contribution. Controlling Controlling involves measuring how the business performs to ensure that financial and operational goals are met. Controlling the operation means keeping the company on track and making sure goals are met. Managers keep track of the budget, the schedule, and the quality of the products or services they provide. They also monitor their employees and review their performance according to standards. Taking corrective action when goals are not met is another management task. Controlling also involves monitoring customer satisfaction. Your marketing manager can measure the success of your comic book by studying sales figures and reviews. You might find out your comic book sold well in certain parts of the country but sold poorly in others. If you comic book is more popular with adults than children, you might want to develop a new marketing plan. A challenge for many managers, especially in small businesses, is dealing with multiple objectives, each at a different functional level. For example, suppose your company’s manager discusses plans to produce a new comic book with the marketing and production teams. The manager directs the marketing team to research the national and global markets for 94 comic books. The manager also tells the production team to prepare to produce the new product. Vocabulary to create – создавать; порождать, производить to hire – нанимать to train – обучать to fire – увольнять с работы (с должности) tool – инструмент; оборудование; орудие, средство to require – требовать to fulfill – выполнять; делать, исполнять, осуществлять, совершать to inspire – воодушевлять, вдохновлять to set a standard – устанавливать критерий / норму to enforce – осуществлять, приводить в исполнение to provide feedback – обеспечивать обратную связь contribution – вклад, взнос to keep track of smth. – следить за чем-л. performance – выполнение; работа; производительность; показатель деятельности customer – клиент, потребитель team – команда, группа 1. Write the transcription of the words and train their pronunciation. create strategy equipment require guide guidance inspire enforce policy contribution ensure budget quality schedule measure discuss 95 2. Form derivatives of the following words and translate them into Russian. Memorize the words and use one from each group in a sentence of your own. Example: different (различный, разный, другой, иной) → difference (разница, отличие, различие) → to differ (отличаться, различаться) → differential (разница в оплате труда) → differently (по-другому, иначе; различно, по-разному) → differentia (отличительное свойство, отличительный признак вида или класса) → differentiate (различать, проводить различия; дифференцировать) to create, orderly, functional, to train, guidance, fulfill, to inspire, respect, to measure, to contribute. 3. Complete the table. Verb Noun to cooperate cooperation to focus training to guide to solve creature initiative to delegate inspiration to monitor to accomplish coordination 96 to discuss enforcement to research development to require motivation success to manage 4. Translate the following words and word combinations. 1) осуществлять кадровое обеспечение; 2) достигать требуемых показателей; 3) определять (вычислять) количество необходимых ресурсов; 4) принимать на работу и обучать работников; 5) финансовые и производственные показатели; 6) эффективно выполнять свои обязанности; 7) определять (устанавливать) стандарты; 8) делегировать (передавать) полномочия; 9) демонстрировать мотивацию; 10) инициатива; 11) изучать информацию о сбыте (данные о сбыте, торговую статистику); 12) совершенствовать маркетинговое планирование (план по сбыту продукции); 13) функциональный уровень; 14) изучать внутренний и внешний рынки; 15) готовить к выпуску новый продукт. 5. Fill in prepositions or particle to where necessary and translate the sentences into Russian. 1. Most managers carry … four different functions … management: planning, organizing and staffing, leading, and controlling. 2. Some managers may primarily focus … one or two … them. 3. Planning involves figuring … the resources. 97 4. Managers are responsible … making sure employees have all the tools they need … do their jobs well. 5. Good management also requires … good leadership 6. You have … create a vision … the company … inspire your employees. 7. Managers also have … delegate … work. 8. A challenge … many managers, especially … small businesses, is dealing … multiple objectives, each … a different functional level. 6. Read the text again and answer the questions on it. 1. How many functions do managers carry out? What are they? 2. What does planning involve? 3. What does a manager do while carrying out his organizing function? 4. What types of activities does leading involve? 5. What is the function of controlling? 7. The word motivation (syn.: incentive, motive) has the following equivalents in Russian: стимулирующий фактор, мотив, стимул (то, что побуждает человека к действию). а) Match the phrases from column A with their Russian equivalents in column B. A B 1. to keep up motivation а. интенсивность мотивации 2. human motivation b.мотивация кнута и пряника (использование системы поощрений и наказаний для мотивации сотрудников) 3. source of motivation c. внутренняя мотивация 98 4. secondary motivation d. внешняя мотивация 5. primary motivation e. источник мотивации 6. intrinsic (internal) motivation f. поддерживать мотивацию 7. personal motivation g. структура мотивации 8. motivation intensity h. вторичная мотивация 9. employee motivation i. человеческая мотивация 10. team motivation j. личностная мотивация, личный мотив, мотив личного характера 11. carrot and stick motivation k. первичная мотивация 12. motivation pattern l. стимулирование группы (команды, коллектива) 13. extrinsic (external) motivation m. мотивация работников (труда) б) Use seven word combinations from column A in sentences of your own. Example: People who are intrinsically motivated work on tasks because they find them enjoyable. 8. The word planning has the following equivalents in Russian: планирование, проектирование, составление плана (проекта, программы); разработка планов деятельности организации (одна из функций менеджмента). а) Match the phrases from column A with their Russian equivalents in column B. А В 1. planning of objectives a. группа планирования 2. planning authority b. планирование прибыли 3. planning process c. последовательность 99 планирования 4. planning committee d. планирование целей 5. business planning e. этап планирования 6. planning group f. планирование в изменяющихся условиях 7. planning of profit g. процесс планирования 8. planning sequence h. система планирования 9. planning stage i. область планирования 10. production planning j. специалист по планированию 11. planning analyst k. органы планирования 12. planning under uncertainty l. комитет по планированию 13. planning under dynamic m. функция планирования conditions 14. planning cycle n. плановые расчеты 15. planning area o. процесс планирования 16. planning system p. планирование в условиях неопределенности q. допущение ошибок в 17. planning estimates планировании 18. planning function r. цикл планирования 19. planning flow s.планирование производства 20. inaccurate planning t. бизнес-планирование (составление бизнес-плана) б) Use ten word combinations from column A in sentences of your own. 100 9. Fill in the table with major functions of management given in the box. to influence employees, to motivate, to evaluate performance, to coordinate resources, to set objectives, to solve problems, to set standards of work, to obtain resources, to guide people, to resolve conflicts, to make long-term plans, to monitor customer satisfaction, to cut the staffing, to show respect to others, accurate planning, carrot and stick motivation, to review performance, to delegate work, to inspire employees Planning Organizing and Staffing Leading Controlling to show respect to others 10. Make up a dialogue discussing the functions of management and their significance. UNIT 3. PUBLIC MANAGEMENT Forms of Business Organization Sole Proprietorship There are three principal forms of business organization: the sole proprietorship, the partnership, and the corporation. The simplest form of business organization is the sole proprietorship, which is owned by one person. Many small businesses start out as sole proprietorships. The owner has relatively unlimited control over the business and keeps all the profits. These firms are usually owned by one person who has day-to-day responsibility for running the business. Sole 101 proprietors own all the assets of the business and the profits generated by it. They also have complete responsibility for any of its liabilities or debts. In case of breach of contract the business property and personal assets of the owner may be taken to pay judgments for damages awarded by courts. Sole proprietorships are the most numerous form of business organization. No charter and permit are needed and there are no particular legal requirements for organizing or conducting a sole proprietorship. When started, many sole proprietorships are conducted out of the owner's home, garage, or van and inventory may be limited and may often be purchased on credit. Advantages of a sole proprietorship 1. Easiest and least expensive form of ownership to organize. 2. Sole proprietors are in complete control of business, and within the law, may make any decisions. 3. Sole proprietors receive all income from the business to keep or reinvest. 4. Profits from the business flow-through directly to the owner's personal tax return. 5. The business is easy to dissolve, if desired. Disadvantages of a sole proprietorship 1. Sole proprietors have unlimited liability and are legally responsible for all debts against the business. Their business and personal assets are at risk. 2. Sole proprietors may be at a disadvantage in raising funds and are often limited to using funds from personal savings. 3. Sole proprietors may have a hard time attracting high-caliber employees, or those that are motivated by the opportunity to own a part of the business. 102 Main Features of a Sole Proprietorship: (+) Easy to organize (+) Owner has complete control (+) Owner receives all income (-) Owner has unlimited liability (-) Benefits are not business deductions Vocabulary feature – особенность sole proprietorship – единоличное владение бизнесом owner – владелец; собственник, хозяин unlimited liability – неограниченная ответственность income – доход benefit – выгода, прибыль deductions – отчисления advantage – преимущество disadvantage – неудобство, недостаток to run a business – вести дело, управлять предприятием within the law assets – в рамках закона liabilities – средства, фонды, авуары, имущество debt [det] – долги, денежные обязательства, долг breach of contract – нарушение контракта to start out – начинать профессиональную деятельность legal requirements – законные ограничения inventory – материально-производственные запасы charter – документ, разрешающий создание компании permit – разрешение to raise funds – привлекать фонды, мобилизовать средства 103 personal tax return – личная налоговая декларация 1. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What are the three principal forms of business organization? 2. What is a sole proprietorship? 3. What are the advantages of sole proprietorship? 4. What are the disadvantages of sole proprietorship? 5. What are the main positive and negative features of a sole proprietorship? 2. Read and translate the following sentences. Make them active, adding a subject if necessary. 1. The sole proprietorship is owned by one person. 2. In case of breach of contract the business property and personal assets of the owner may be taken to pay judgments for damages awarded by courts. 3. No charter and permit are needed. 4. Sole proprietors are often limited to using funds from personal savings. 5. Employees are motivated by the opportunity to own a part of the business. 6. Many sole proprietorships are conducted out of the owner's home, garage, or van. 7. Inventory may be limited and may often be purchased on credit. 3. Read and translate. Make the following sentences passive. 1. Many small businesses start out as sole proprietorships. 2. The owner keeps all the profits of the business. 104 3. Sole proprietors own all the assets of the business and the profits generated by it. 4. Sole proprietor, and within the law, may make any decisions. 5. Sole proprietors receive all income from the business to keep or reinvest. 6. The business is easy to dissolve. 4. Fill in the appropriate words given below. Translate. Sole proprietorship, employer identification number, seizing, breach of contract, insurance, limited liability corporation, personal Social Security number, liability, business, employees, ends, the Internal Revenue Service, incorporation A … is the easiest form of … to begin by a single individual. Rules for sole proprietorships do not permit …. Because the business is unincorporated and also is not a ..., the personal assets of the sole proprietor and the business assets are one and the same for … purposes. Adequate … or other protection is important because claims against the business could result in … of a home. Another remedy for … can be "damages" or compensation of money. Sole proprietors must file various tax forms with … and pay any taxes due. The sole proprietor does not file taxes under an … like other businesses do but rather under his …. Death is an area where a sole proprietorship may be problematic. By definition, a sole proprietorship … with the proprietor's death. The business is sold to a new owner or is reorganized into another form, such as …. 5. Translate the following text into English. Индивидуальное предприятие – наиболее простая форма ведения бизнеса в США. Под данной формой, как правило, подразумева105 ется именно предприятие одного владельца. Основной недостаток этой формы предприятия – неограниченная ответственность учредителя, который отвечает за долги предприятия всем своим имуществом. Компания налогами не облагается. Налоги уплачивает учредитель согласно действующим ставкам. Все доходы индивидуального предприятия автоматически считаются доходами его владельца. В случае смерти или недееспособности владельца происходит автоматическое закрытие компании. 6. Read the text once more and write a short essay on: Sole Proprietorships, their advantages and disadvantages, using some additional information. Partnership In a partnership, two or more people share ownership of a single business. Like proprietorships, the law does not distinguish between the business and its owners. The partners should have a legal agreement that sets forth how decisions will be made, profits will be shared, disputes will be resolved, how future partners will be admitted to the partnership, how partners can be bought out, or what steps will be taken to dissolve the partnership when needed. Many partnerships split up at crisis times. They also must decide up front how much time and capital each will contribute, etc. Advantages of a partnership 1. Partnerships are relatively easy to establish; however partners should develop the partnership agreement. 106 2. With more than one owner, the ability to raise funds may be increased. 3. The profits from the business flow directly through to the partners' personal tax returns. 4. Prospective employees may be attracted to the business if given the incentive to become a partner. 5. The business usually will benefit from partners who have complementary work skills. Disadvantages of a partnership 1. Partners are jointly and individually liable for the actions of the other partners. 2. Profits must be shared with others. 3. Since decisions are shared, disagreements can occur. 4. The partnership may have a limited life; it may end upon the withdrawal or death of a partner. There exist different types of partnerships: 1. General partnership Partners divide responsibility for management and liability, as well as the shares of profit or loss according to their internal agreement. Equal shares are assumed unless there is a written agreement that states differently. 2. Limited partnership and partnership with limited liability "Limited" means that most of the partners have limited liability (to the extent of their investment) as well as limited management decisions, which generally encourages investors for short term projects, or for investing in capital assets. This form of ownership is not often used for operating retail or service businesses. Forming a limited partnership is more complex and formal than that of a general partnership. 107 3. Joint venture Joint venture acts like a general partnership, but it is formed for a limited period of time or a single project. If the partners in a joint venture repeat the activity, they will be recognized as a continuing partnership and distribute accumulated partnership assets upon dissolution of the entity. Main Features of a partnership: (+) Easy to organize, but needs agreement (+) Partners receive all income (-) Partners have unlimited liability (-) Partners may disagree (-) Life of business may be limited Vocabulary partnership – товарищество, партнерство (некорпорированная фирма, которой владеют и которой управляют два лица или более) general partnership – компания с неограниченной ответственностью limited partnership – товарищество с ограниченной ответственностью to distinguish – различать, проводить различие to set forth – излагать, формулировать legal agreement – юридическое соглашение complementary – добавочный, дополнительный capital assets – 1) основные фонды (машины, здания, сооружения, оборудование и т. п.); 2) оборотные средства retail – розничная продажа to the extent of – до размера, в пределах share – доля, часть; квота; акция withdrawal – уход joint venture – совместное предприятие 108 to dissolve the partnership – аннулировать, расторгать партнерство dissolution of the entity – ликвидация экономического объекта 1 . Answer the questions on the text: 1. What is a partnership? 2. What is the difference between the limited partnership and general partnership? 3. What are the advantages of partnership? 4. What are the disadvantages of partnership? 5. What is a joint venture? 6. What should partners have to be able to run their business? 2. Guess what is meant by the following: 1. A negotiated and typically legally binding arrangement between parties as to a course of action. 2. A business or firm owned and run by two or more partners. 3. Property owned by a person or company that is purchased for long-term use and is not likely to be converted quickly into cash, such as land, buildings, and equipment. 4. An association of persons who are all personally liable for any legal actions and debts the company may face. 5. The maximum amount a person participating in a business can lose or be charged in case of claims against the company or its bankruptcy. 6. An association of two or more individuals or companies engaged in a solitary business enterprise for profit without actual partnership or incorporation. 7. A thing that motivates or encourages one to do something. 109 8. A special type of partnership which is very common when people need funding for a business, or when they are putting together an investment in a real estate development. 9. The sale of goods to the public in relatively small quantities for use or consumption rather than for resale. 10. One of the equal parts into which a company's capital is divided, entitling the holder to a proportion of the profits. 11. The closing down or dismissal of an assembly, partnership, or official body. 3. Find in the text sentences containing the following Participles and translate them into Russian in writing. 1. … employees … if given the incentive… 2. … a written agreement… 3. …limited management decisions … 4. … a continuing partnership… 5. …accumulated partnership assets … 4. Translate the phrases into English and compose sentences with them. 1. решения, принимаемые партнерами; партнеры, принимающие решения; 2. доходы, распределяемые между собственниками; собственники, разделяющие ответственность; 3. меры, предпринимаемые партнерами; партнеры, предпринимающие меры; 4. сотрудники, привлекаемые в бизнес; бизнес, привлекающий сотрудников; 110 5. ограниченная ответственность; письменный договор, ограничивающий ответственность; 6. накопленные средства; партнеры, накапливающие средства. 5. Fill in with the appropriate words given below. Translate. Partnership, investments, business, equal responsibility, debts and liabilities, general partners, share, management, tax payments, debts, limited partners, profits and losses, income taxes, income and deductions, individual tax return A … is a type of unincorporated business organization in which multiple individuals, called …, manage the … and are equally liable for its…. Other individuals, called …, may invest but not be directly involved in … and are liable only to the extent of their …. Unlike a Limited Liability Company or a corporation, in a partnership each partner shares … for the company's …, and its …. The partnership itself does not pay …, but each partner has to report their … of business profits or losses on their …. Estimated … are also necessary for each of the partners for the year in progress. Partnerships must file a return on Form 1065 showing …. Estimated tax payments are also required if they expect their income to be greater than $1,000. 6. Translate the following text into English. Товарищество – это организационно-правовая форма, при которой бизнесом владеют два или более партнеров. При этом предприятие находится в общей долевой собственности владельцев. Доля каждого определяется исходя из размера его вклада в уставный фонд предприятия, размер которого собственники определяют самостоятельно, но не ниже минимума, установленного законом. Отличительной чертой товарищества с ограниченной ответственностью является 111 то, что в отличие от частного предприятия владельцы по долгам своего предприятия отвечают только своей долей вклада. Личное имущество остается неприкосновенным. При смешанном товариществе партнеры (учредители) делятся на действительных членов и членоввкладчиков. При этом первые несут ответственность перед предприятием всем своим имуществом, а вторые – только в пределах вклада, имея разные возможности в управлении. Важно отметить, что товарищество является оптимальной формой для многих видов бизнеса, особенно для тех, которые требуют такой начальный капитал, который одному владельцу не собрать или не занять. 7. Read the text once more and write a short essay on: Partnerships, their types, their advantages and disadvantages, using some additional information. Corporation A corporation is chartered by the state in which it has headquarters. It is considered by law to be a unique entity, separate and apart from those who own it. A corporation can be taxed; it can be sued; it can enter into contractual agreements. The owners of a corporation are its shareholders. The shareholders elect a board of directors to oversee the major policies and decisions. The corporation has a life of its own and does not dissolve when ownership changes. Advantages of a Corporation 112 1. Shareholders have limited liability for the corporation's debts or judgments against the corporations. 2. Generally, shareholders can only be held accountable for their investment in stock of the company. (Note however, that officers can be held personally liable for their actions, such as the failure to withhold and pay employment taxes.) 3. Corporations can raise additional funds through the sale of stock. Disadvantages of a Corporation 1. The process of incorporation requires more time and money than other forms of organization. 2. Corporations are monitored by federal, state and some local agencies, and as a result may have more paperwork to comply with regulations. 3. Incorporating may result in higher overall taxes. Dividends paid to shareholders are not deductible form business income, thus this income can be taxed twice. Main features a Corporation: (+) Shareholders have limited liability (+) Can raise funds through sale of stock (+) Life of business is unlimited (continuity of life) (-) To incorporate a firm takes time and money (-) May result in higher overall taxes Vocabulary incorporation – 1) объединение, корпорация; 2) регистрация корпораций entity – организация headquarters – главное правление (фирмы) to be sued – преследоваться в судебном порядке 113 shareholders – акционеры, пайщики, владельцы акций stock – акции contractual agreement – контракт, договор to oversee – наблюдать, следить to be held liable – нести ответственность to be accountable – нести ответственность employment taxes – налог на фонд заработной платы continuity of life – непрерывность существования overall taxes – суммарные налоги to incorporate a firm – оформить юридический статус фирмы как корпорации to comply with regulations – выполнять предписания (правила) 1. Answer the questions on the text: 1. What is a corporation? 2. Why is a corporation considered to be unique? 3. Who are the owners of a corporation? 4. What is necessary to form a corporation? 5. Who oversees the major policies and decisions? 6. What are the advantages of corporations? 7. What are the disadvantages of corporations? 2. Guess what is meant by the following: 1. being the only one of its kind; unlike anything else; 2. establishment of a firm, formation of a company; 3. a general term for any institution, company, corporation, partnership, government agency, university, or any other organization which is distinguished from individuals; 114 4. owners of shares in a company; 5. the capital raised by a business or corporation through the issue and subscription of shares; 6. a group of people comprising the governing body of a corporation; 7. an agreement with specific terms between two or more persons or entities in which there is a promise to do something in return for a valuable benefit; 8. the unbroken and consistent existence or operation of something over a period of time; 9. entire compulsory contribution to state revenue, levied by the government on workers' income and business profits; 3. Translate the sentences, define the tense form of the predicate and compose special questions. 1. The owners of a corporation are its shareholders. 2. The corporation has a life of its own. 3. Corporations can raise additional funds through the sale of stock. 4. Corporations are monitored by federal, state and some local agencies. 5. Shareholders can only be held accountable for their investment in stock of the company. 6. The shareholders of a corporation hold an election to choose people who have been nominated to direct or manage the corporation as a board. 4. Translate the following sentences; define the meaning of the modal verbs. Make the sentences active or passive, if possible. 1. A corporation can be taxed. 2. Officers can be held personally liable for their actions. 115 3. Corporations may have more paperwork to comply with regulations. 4. Incorporating may result in higher overall taxes. 5. A corporation's liability for damages or debts must be limited to its assets. 6. Major policy decisions must be made by resolution of the Board. 5. Write one sentence with each verb, using the phrases from the text: to be sued; to oversee; to incorporate; to comply with; to elect; to require; to monitor; to tax; to withhold; to charter. 6. Translate the following text into English: Корпорация это одна из основных форм предпринимательства, которая представляет собой объединение, союз предприятий или отдельных предпринимателей на основе частно-групповых интересов. В некоторых странах корпорации являются юридическими лицами. Они включают в себя право владения, получения ссуды, закладывания и ликвидации имущества, право управления своими собственными делами, обращения в суд. С другой стороны корпорации несут ответственность перед законом и потому на них можно подать в суд. Предприниматели, желающие образовать корпорацию, обращаются в соответствующие учреждения страны за регистрацией устава, в котором обговариваются права и обязанности корпорации, продолжительность ее жизнедеятельности (обычно около 35 лет). В США, к примеру, корпорации составляют сравнительно небольшой процент от всего количества кампаний, но они контролируют значительную часть американского бизнеса. 116 7. Read the text once more and write a short essay on: Corporations, their advantages and disadvantages, using some additional information. Board of Directors What is the Purpose of a Board of Directors? A company's board of directors helps management develop business plans, economic policy objectives, and business strategy. A board of directors often selects the chief executive of the business, supports him, reviews his performance, and may dismiss him. Through regular meetings, the board helps ensure effective organizational planning and sees that company resources are managed effectively. The board of directors also sees that the company meets regulatory requirements that apply to that business. The board of directors also must assess overall performance of the corporation. Directors monitor a company's financial performance and the success of its products, services and strategy. Directors are expected to follow developments that affect the business. They must set aside any potential conflict between their personal or individual business interests to support the well-being of the business which they serve. Board of Directors The most effective board of directors will be a group of professionals who bring a breadth of skills, experience and diversity to a company. As the company grows and changes, the governing board also will change to meet changing needs and circumstances. Major Duties of Board of Directors are the following: 1. Select and appoint a chief executive to whom responsibility for the administration of the organization is delegated, including: 117 - to review and evaluate his/her performance regularly on the basis of a specific job description, including executive relations with the board, leadership in the organization, in program planning and implementation, and in management of the organization and its personnel - to offer administrative guidance and determine whether to retain or dismiss the executive 2. Govern the organization by broad policies and objectives, formulated and agreed upon by the chief executive and employees, including to assign priorities and ensure the organization's capacity to carry out programs by continually reviewing its work. 3. Acquire sufficient resources for the organization's operations and to finance the products and services adequately 4. Account to the public for the products and services of the organization and expenditures of its funds, including: - to approve the budget, and formulate policies related to contracts from public or private resources - to accept responsibility for all conditions and policies in new, innovative, or experimental programs. Major Responsibilities of Board of Directors 1 Determine the Organization's Mission and Purpose 2. Select the Executive 3. Support the Executive and Review His or Her Performance 4. Ensure Effective Organizational Planning 5. Ensure Adequate Resources 6. Manage Resources Effectively 7. Determine and Monitor the Organization's Programs and Services 8. Enhance the Organization's Public Image 9. Assess Organization's Performance 118 Vocabulary economic policy – экономическая политика chief executive –исполнительный директор to ensure –обеспечивать to dismiss (to fire) – увольнять, освобождать от обязанностей regulatory requirement – законное требование overall performance – общий результат деятельности (фирм) или работы (предприятий), эффективность работы financial performance – финансовое состояние to set aside –прекращать, прерывать well-being – благополучие, процветание diversity – разнообразие innovative – новаторский, инновационный to meet requirements (needs) – отвечать требованиям (нуждам) to acquire – приобретать, получать to account to – отчитываться перед кем-л. expenditures – расходы to assign – определять, устанавливать to enhance – увеличивать, усиливать, улучшать 1. Answer the questions on the text. 1. What are the responsibilities of a board of directors in a corporation? Name them. 2. What are major duties of a Board of Directors? 3. What can we call an effective board of directors? 2. Translate into English. 119 1. Состав совета директоров должен обеспечивать наиболее эффективное осуществление функций, возложенных на совет директоров. 2. Совет директоров должен пользоваться доверием акционеров, в противном случае он не сможет эффективно выполнять свои функции. 3. На должность члена совета директоров рекомендуется выбирать лицо, имеющее безупречную репутацию. 4. Для того чтобы совет директоров надлежащим образом выполнял свои обязанности и вносил реальный вклад в управление обществом, члены совета директоров должны обладать знаниями, навыками и опытом, необходимыми для принятия решений. 5. В состав совета директоров рекомендуется включать независимых директоров. 6. Независимые директора призваны внести значительный вклад в обсуждение и принятие решений по таким вопросам, как выработка стратегии развития общества, оценка соответствия деятельности исполнительных органов избранной стратегии, разрешение корпоративных конфликтов с участием акционеров, а также по иным важным вопросам, решение которых может затронуть интересы акционеров. 3. Sum up the text and discuss with your partner the main differences between general partnership and the LLC, the most popular type of a company in the USA. Limited Liability Company (LLC) The LLC is a relatively new type of hybrid business structure that is now permissible in US. It is designed to provide the limited liability features of a corporation and the tax efficiency and operational flexibility of a 120 partnership. Formation of LLC is more complex and formal than that of a general partnership. The owners are members, and the duration of the LLC is usually determined when the organization papers are filed. The time limit can be continued if desired by a vote of the members at expiry date (the time of expiration). LLC's must not have more than two of the four characteristics that define corporations: 1. Limited liability to the extent of assets; 2. Continuity of life; 3. Centralization of management; and 4. Free transferability of ownership interests. Helpful Vocabulary permissible – дозволенный tax efficiency – налоговая эффективность operational flexibility – гибкость операций duration – срок действия to file papers – подавать документы на регистрацию vote – голосование expiry date – дата окончания transferability – передача (имущества, права и т. п.) 4. Write a short essay on: 1. The purpose of a Board of Directors in a Corporation. 2. Major duties of a Board of Directors in a Corporation. Directors and Managers 121 As a rule a private company has only one director. A public company must have at least two directors. Usually there is no upper limit on the number of directors a public company may have. The company's notepaper must list either all or none of the names of its directors. A limited liability company or a corporation is headed by the board of directors elected by shareholders. The directors appoint one of their number to the position of managing director to be in charge of the day-day running of the company. In large organizations the managing director is often assisted by a general manager. Some companies also have assistant general managers. Many directors have deputies who are named deputy directors. Directors need not be shareholders. They are responsible for the management of a company's affairs. They are not subject to any residence or nationality restrictions. Big companies have many managers heading departments. They are all responsible to the managing director. Among various departmental managers (directors) the following can be mentioned: sales manager personnel manager chief manager district manager sales and marketing manager industrial engineering manager etc. Vocabulary upper limit – верхний предел to head – возглавлять to appoint – назначать to be in charge of smth – заведовать чем-либо, отвечать за что- либо 122 to run the company – управлять компанией to assist – помогать deputy – заместитель deputy director – заместитель директора deputy minister – заместитель министра affair – дело to be subject to smth – подпадать под действие чего-либо restriction – ограничение to be responsible to smb for smth – быть ответственным перед кем-л. за что-л. buyer – покупатель business card syn. card / visiting card – визитная карточка drive – проезд, дорога managing director – директор-распорядитель finance – финансы financier – финансист representative – представитель 1. Find the answers to the following questions in the text: 1. How many directors can a private company have? And what about a public company? 2. Who heads a limited liability company? 3. How is a managing director appointed? What are his duties? 4. Who is a general manager? 5. What is the status of a director? 6. What managers do many companies have? 7. Whose business cards were quoted? What information did they give? 2. Translate into English. 123 1. В этом районе работает торговый представитель фирмы. Где он сейчас? 2. Здесь же показаны пять вариантов визитных карточек. 3. В этом упражнении пять предложений на перевод. 4. Бизнес-план фирмы содержит пять разделов. 3. Translate the following word combinations into Russian; use them in the sentences of your own: 1. company's note-paper; 2. limited liability company; 3. residence restrictions; 4. nationality restrictions; 5. sales manager; 6. personnel manager; 7. deputy director; 8. assistant general manager. Ex. 4. Underline the modal verbs, read and translate the sentences into Russian: 1. A public company may have as many directors as it finds necessary, but not less than two. 2. The directors are to appoint one of them to the position of managing director. 3. In large companies the managing director can be assisted by a general manager. 4. The managing director is to take care of day-to-day running of the company. 5. Companies can also have assistant general managers. 6. I'm afraid I can't remember all this information. 7. You needn't remember it all. 8. You should simply remember that the titles of the heads of the companies can be different. 5. Choose the right form and translate the sentences: 124 1. (Is/Are) there usually an upper limit on the number of manag- ers in a company? 2. As far as I know there (is/are) no limit. 3. There (was/were) three managers in the company. 4. There (wasn't/weren't) many managers in the corporation. 5. Do you know if there (is/are) any sales managers in this de- partment? 6. If I am not mistaken there (is/are) not a single sales representa- tive in this area. 7. There (is/are) a representative in the northern part of the country. 6. Have a look at the chart showing some qualities making a good manager. Say which of these qualities seem most important to you; which of these qualities can be taught; where they can be taught. Being decisive: able to make quick decisions Being efficient: doing things quickly, not leaving tasks unfinished Being friendly and sociable Being logical, rational and analytical Being able to communicate with people Being able to motivate, inspire and lead people Being authoritative: able to give orders Being competent: knowing his job perfectly as well as the work of his subordinates Being persuasive: able to convince people to do things Having good ideas 7. Complete the sentences with the following words: shareholders, directors (director), management, nationality restrictions, board, assistant, public company, managing director, junior executive, col- 125 league, supervisor; staff, senior executive, superior, employee, middle manager, subordinate, work-force 1. The company's note-paper must list either all or none of the names of its ... . 2. Directors need not be ... . 3. They are responsible for the ... of a company's affairs. 4. They are not subject to any residence or... . 5. A ... must have at least two directors. 6. The shareholders are to elect... of directors. 7. Some companies also have ... general managers. 8. The group of executives working below the top managers are generally called … . 9. Valerie is an important person in our company. She is a member of the Board of … . 10. Peter, a recent university graduate, has been with the firm for a year. He is at present a .... and is being trained for a managerial position. 11. Their .... is expanding rapidly. They now have over 5.000 employees. 12. At least 50% of our .... have been with the company over ten years. 13. .... in an organization generally have more fringe benefits than lowerlevel managers. 14. We are a small group in the Research and Development Department. Fortunately, I get on well with all my … . 15. Our telephone operators work under the direction of a … . 16. I work under Mr. Brown. He's my … . 17. Shelia and Tom work under my authority. I am their boss and they are my … . 18. I am responsible for .... training and development. 19. A .... is a person of high rank in an organization, usually next in importance to the Chairman. 8. Sum up what the text says about: a) directors of private companies; b) directors of public companies; c) directors of limited liability companies, their assistants and deputies; d) managers. 126 9. Sum up the text and discuss with your partner the roles of managers in an organization. Ten Roles That Managers Perform in Organizations Successful organizations are led by experienced and knowledgeable managers. These leaders develop, implement and maintain the organization's goals and objectives, and they lead their employees and motivate them to meet these goals. Although good managers may make the effort look easy, their responsibilities are mounting and endless. Business Development Business development is an essential responsibility in every organization. In most situations, high-level managers such as CEOs, CFOs and other executives are responsible for mapping out the activities of the business. However, managers of all levels are responsible for enforcing those decisions. Staffing Manager Staffing requirements are often the manager's responsibility. The manager has hands-on knowledge of the skills and experience that is required to fill the positions and screens and staffs his team for excellence. Trainer In addition to the hiring responsibilities, managers often train their staff to ensure that the required skills are developed in the intended manner. Knowledgeable managers are usually capable of addressing training questions and material and can provide hands-on answers and examples for clarification. Project Manager Managers are expected to develop, implement and lead projects as 127 necessary. Managers must have the foresight and experience to bring forward the best in the people, redirect their staff's energy when necessary and motivate them toward the goal's completion. Communicator A manager must have strong communication skills. The manager should be able to clearly communicate even the most complicated information in spoken and written form, to people of all levels. Counselor Many times, managers must become counselors. Managers are the ones that staff members seek out when difficulties arise and a solution is needed. Regardless of whether the problems are business or personal issues, managers must know how to empathize and direct their staff to keep them focused on meeting company goals. Influencer Managers must be influential. They must be able to sway customers that their organization meets their requirements and provide authority over their staff. Managers should be strong-minded leaders who lead by example. Evaluator Leaders must be able to analyze situations, criteria and work habits to ensure the organization's quality standards are being met. In this, the manager must evaluate the information before them and determine if the information meets company standards. Scheduler The ability to schedule and meet deadlines is a driving force in a successful manager. The manager must be able to create schedules for the staff, suppliers and inventory while ensuring that the slots overlap effectively and efficiently. 128 Innovator The most successful managers are innovators. They find new, more efficient ways for their departments and teams to complete their tasks. They also save their companies money on overhead and supplies, keeping their organization's finances healthy. 10. See the list of most popular jobs for business management majors. Work in pairs to make up a dialogue. Methodology Jobs ranked by popularity among graduates. Annual pay for Bachelors graduates without higher degrees from all colleges. (From http://www.payscale.com) Looking for a Job When a company needs to recruit or employ new people, it may decide to advertise the job or position in the "NEED HELP" section of a 129 newspaper. People who are interested can apply for the job by sending in a letter of application or covering letter (in the USA — cover letter) and a curriculum vitae or CV (in the USA — resume) containing details of their education and experience. A company may also ask candidates to complete a standard application form. The company's Human Resources department will then select the most suitable applications and prepare a shortlist of candidates or applicants, who are invited to attend an interview. Another way for a company to hire is by using the services of a recruitment agency, which provides a list of suitable candidates. The CV (curriculum vitae) is presenting your education, skills and experience to the employer. CV demonstrates the suitability of an applicant for the job. As well as providing an insight into previous qualifications and experience, it should show the employer the skills and qualities the applicant has, that will match the position being applied for. In compiling CV the applicant has one objective only — to get an interview in order to get the job. A CV must be accurate, interesting and up-to-date. It must be presentable so that it makes the best impression possible and gets noticed. It should be relevant — targeted to the needs of each particular position. In your CV you need to bring together details of your qualifications, details of the job itself, details of the qualifications and skills required, evidence from your personal profile that matches the employers" criteria. This information will help you to prioritize the detail that should be included in your CV. The CV must be accurate, brief and clear. Describe your skills and achievements as positively as possible. Applicants" skills and qualities that are most often sought by employers are listed below. 130 Communication is an ability to communicate orally, in writing or via computer communication system. Team work means working well with others in order to achieve a common objective. Leadership is a skill and quality of being able to motivate and encourage others, being a leader. Initiative is an ability to see opportunities and to set and achieve goals. Problem solving is thinking things through in a logical way in order to determine key issues. Creative thinking is useful. Flexibility and adaptability are abilities to handle changes and adapt to new situations. Commitment means having energy and enthusiasm in pursuing projects. Interpersonal skills are abilities to relate well to others and to establish good working relationships. Numeracy is competence and understanding of numerical data, statistics and graphs. Additionally, employers like to see that applicants have some business awareness — having an insight into what is happening in industry or commerce and the impact this could have on the organization. Vocabulary to recruit – нанимать, брать на работу to advertise – давать объявление section of a newspaper – рубрика газеты apply for a job – подавать заявление на должность letter of application (covering letter) – сопроводительное письмо 131 curriculum vitae (CV) or resume – резюме to complete an application form – заполнить анкету Human Resources department – отдел по работе с кадрами shortlist of candidates – окончательный список кандидатов to attend an interview – посещать интервью recruitment agency – кадровое агентство insight – взгляд up-to-date – новейший impression – впечатление to get noticed – зд. быть замеченным, привлечь внимание relevant – релевантный, уместный targeted to the needs – нацеленный на потребности particular position – конкретная должность clear – ясный, четкий achievements – достижения orally – устно flexibility – гибкость adaptability – адаптивность commitment – приверженность; убеждения numeracy – способность к количественному мышлению data – информация awareness – осведомленность 1. Scan the text to find the answers to the following questions: 1. Where does the company usually publish the advertisement? 2. What candidates do usually send to the company? 3. What is the role of Human Resources department? 4. What is the role of CV in the process of recruitment? 132 5. What should CV look like? 6. What skills and qualities are most often sought by employers? 7. What is "problem solving"? 8. What is "numeracy"? 9. What is "business awareness"? 2. Translate the following sentences into Russian. 1. A company may decide to advertise a position in the "NEED HELP" section of a newspaper. 2. Candidates are expected to send their CVs and covering letters to the potential employer. 3. Some companies require candidates to complete a standard application form. 4. Human Resources department or a recruitment agency prepares a shortlist of candidates to interview. 5. Recruitment agencies are called "search firms" in the United States. 6. The CV presents your qualifications, skills and personal qualities. 7. When the applicant compiles the CV he or she has only one objective — to get a job interview. 8. A CV must make the best impression possible and be targeted to the needs of each position. 9. The CV must be brief, accurate and clear. 3. Finish the following sentences. 1. Job positions are advertised in ... . 2. A company may ask candidates to ... . 3. The company's Human Resources department... . 4. The company may also use ... . 5. CV must be ... . 6. Communication is... . 7. Team work means ... . 8. Initiative is... 4. Translate the following sentences into English. 1. Коммуникативность — это способность общаться устно, письменно или через компьютер. 2. Гибкость и адаптивность являются важными качествами для бизнесмена. 3. Способность работать в 133 команде означает умение работать с другими для достижения общей цели. 4. Способность к количественному мышлению является важным навыком для работы с цифровыми данными, статистическими данными и графиками. 5. Наймодатели хотят видеть в кандидате работника, осведомленного в сфере, в которой он собирается работать. 6. Компания может также попросить кандидата заполнить стандартное заявление (форму). 7. Отдел кадров компании подбирает наиболее подходящие кандидатуры и подготавливает окончательный список кандидатов, которые будут приглашены на интервью. 8. Резюме представляет информацию о вашем образовании, умении и опыте работы. 9. Компания также может нанимать сотрудников через фирму, занимающуюся подбором персонала (рекрутинговую компанию). Text A: Employment Agencies In Britain there is a special service for school leavers, the Careers Advisory Service, which helps young people who are looking for their first job. Careers Officers give practical advice on interview techniques, application forms, letters, pay, National Insurance and Trade Unions. One business organization that you may use when you are jobhunting(1) is an employment agency. There are the state employment services and nonprofit agencies that do not receive fees for finding jobs for people. There exist also some private employment agencies which receive a fee. Some employment agencies see applicants without an appointment. These include the state employment services and nonprofit agencies. Counselors there may spend a few minutes with each applicant. But an agency that deals with technical and higher-salaried jobs, spends much more time with each applicant. Appointments are necessary in 134 this type of agency, where a counselor may be able to see only a few applicants a day. An interview for any kind of job, whether the interview is obtained through a friend, classified advertisement, or an agency, generally requires an appointment. It is important to be on time for your appointment. If you have made an appointment and cannot keep it, or if you will be more than ten minutes late, you should always call the interviewer. If you do not cancel the appointment or notify the interviewer that you will be late, you will create a negative impression on your possible employer. To make efficient use of time, American business people schedule their days hour by hour. In most American business situations, appointments are a necessary courtesy. Note: job-hunting - looking for work Text В: "....They Live by the Appointment Book." Victor had recently arrived in the United States, and he did not completely understand the need for appointments. He thought his friend was exaggerating. One day he went to an employment agency. This agency specialized in placing people according to their qualifications. Victor wanted to start working as soon as possible so that he could afford his own apartment. When he arrived at the agency at 10 a.m. the receptionist said to him, "Do you have an appointment?" Victor looked around the office and said, "No, I don't, but I see that there are very few people waiting here. I'm sure the counselor can see me. "The receptionist answered, "I'm sorry. This agency works by appointment only." She told him to leave his resume, fill 135 out an application, and make an appointment. Victor did not have a resume, but he was able to get an appointment in two days. Before dinner that evening, Victor dropped in on his friend Andre. He told Victor again why sometimes in America you cannot just drop in. Victor then turned to his friend and said, "Andre, you are right. In America you don't live from day to day — you live from appointment to appointment!" (adapted from "Working World" by Baskin M.) 1. Find in texts A and В equivalents for the following words and phrases: 1) быть готовым к переменам (изменениям); 2) создать положительное/ отрицательное впечатление; 3) заполнить анкету для поступления на работу; 4) решить, принять решение; 5) приобрести знания/опыт работы; 6) дать детальную информацию; 7) час за часом; 8) эффективно использовать; 9) предлагать что-либо (советовать); 10) подбирать работу согласно квалификации; 11) специализироваться в области; 12) самооценка; 13) обратиться к кому-либо; 14) изучать чтолибо (пойти на курсы). 2. Match the idioms in column A with definitions in column B. A 1. self appraisal 2. self concept 3. self evaluation 4. resume 5. give notice 6. give me a call 7. create a good impression 8. classified ad 9. drop in B a. to consider smth after delaying it b. to visit without an appointment c. to get an appointment d. newspaper listing of job e. your own view of yourself f. to give someone a good opinion of you g. summary of one's employment record h. a form to be filled in when applying for smth i. determine your own value or worth 136 10. get around to smth 11. make an appointment 12. application form 1 2 3 4 j. estimate your own qualities, abilities k. telephone me l. inform your employer in advance that you are leaving the job 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 3. Replace the italicized parts of the sentences by words and word combinations from the vocabulary. 1. In American business practice making appointments is a rule of polite behavior. 2. He went to an employment agency to meet a person who gives advice, but first he had to talk to the employee who receives callers and answers the phone. 3. He went to the manager in order to formally ask for a job. 4. He doesn't work at the moment, he is out of work. 5. The company gives provisions against sickness, death, damage and loss. 6. His parents couldn't make him leave the job, they could only give advice. 7. His program was very busy, every hour was occupied. 8. These agencies deal only with people having no trade. 4. Complete the sentences given below, choose the right word. a) job— position— occupation "job" - anything that one has to do, task, duty; "position" - a person's relative place, as in society; rank, status; "occupation" - that which chiefly engages one's time; one's trade. 1. He was unemployed doing only odd … . 2. Knitting is a useful … for long winter evenings. 137 12 3. This aid is for those who have a very low .... in society. 4. My sister occupies an important … in the Department of Health. 5. The police called the company to find out his … at the moment. 6. He had a hard … painting the car. b) force— make "force" - do smth by force or as if by force; compel; "make" - to cause or force (followed by an infinitive without "to"). 1. They … the confession from him. 2. The robbers … the cashier lie on the floor and took the money. 3. They … me repeat the story again. 4. He would have never done it, but he was … to do it. c) leave— graduate "leave" - graduate (school); "graduate (from)" - to get a degree or diploma, to complete a course of study at a college/university. 1. He ... from Columbia University last summer. 2. She ... school 2 months ago and couldn't find a job. 3. What University did you ... from? 5. Fill in prepositions where necessary. 1) After leaving school a young person faces....a very difficult problem – choosing an occupation. 2) The majority of young people do not get around....making a decision until they leave school. 3) Boys and girls seldom talk about this problem ... with the family. 4) One has to take special courses to qualify ... the job. 5) There is a special advisory service which counsels.... people who are looking.... work. 6) There are nonprofit agencies that deal.... nonskilled positions. 7) This agency specializes.... placing people ... their qualifications. 8) The agency helped me find .... the infor138 mation I needed. 9) You can turn.... your teacher... advice and help. 10) Counselors give practical advice.... interview techniques, application forms, etc. 11) He made an appointment with the career officer 11 o'clock. 12) A counselor can see only a few applicants.... a day. 13) An interview.... any kind of job generally requires an appointment. 14) He was.... 20 minutes late and created a negative impression.... the employer. 15) American business people schedule their day hour.... hour. 16) On the wall he saw a notice "The agency works .... appointment only". 17) He didn't know how to fill.... the application form. 18) It turned out that he travelled to the agency.... nothing as he didn't make an appointment.... advance. 19) Appointment is a necessary courtesy, you can't just drop … . Ex.6. Translate the following sentences 1) Когда я вошла в офис агентства, секретарь, встречающий посетителей, спросил меня, назначена ли у меня встреча. 2) У меня назначена встреча с Мисс Харрис на 10:15. 3) Я проходил мимо вашего агентства и решил зайти и поговорить с одним из ваших сотрудников. 4) Он не пришел в назначенное время на встречу с Мистером Брауном, это, конечно, произвело крайне отрицательное впечатление. 5) Анкета для поступления на работу заполняется печатными буквами. 6) Вам придется начать работу с самой маленькой должности, чтобы приобрести необходимый опыт. 7) Вы должны пойти на курсы, чтобы приобрести знания, необходимые для этой работы. 8) Агентство поможет вам подобрать работу согласно вашей квалификации. 9) Агентство "Manpower" специализируется именно в этой области. 10) Ему предложили две разные должности, но он не мог решить, какую выбрать. 7. Which statement is a good example of the meaning of the italicized word? 139 1. He thought that his friend was exaggerating. a. He was shouting to make his point understood. b. He made it seem much more important than it really was. 2. One day he went to an employment office. a. office where he worked b. organization that helps people to find an occupation. 3. The employment office places people according to their qualifications. a. the office which helps people to find a place to live. b. the office which advises people on the job and interview technique. 4. He thought he was imposing on his brother and sister-in-law. a. He made things very difficult for his brother. b. He made his brother work hard. 5. He couldn't afford his own apartment. a. he couldn't live alone. b. he didn't have enough money to pay the rent 6. One should have definite qualifications for the job. a. education and work experience b. definite personal features 8. Translate the following sentences. 1) Сейчас во многих странах много безработных. 2) Особенно много безработных среди молодых людей только что закончивших школу. 3) У них нет необходимого образования и опыта работы. 4) Часто, чтобы получить необходимую для работы квалификацию (образование и опыт работы), надо закончить специальные курсы. 5) Молодые люди в течение года получают пособие по безработице. 9. Fill in the right word from the word-column. 140 Out of Work In Britain a lot of people are ... . Tracey Chapman is 18, and she ... a year ago. She lives in the North East, an area of high ... . She hasn't been able ... yet. "My dad just doesn't under- 1. left school 2. to find a job 3. given up 4. looking through stand. He started working in a steel mill when he 5. receptionist was 15. Things are different now, but he thinks I 6. move to should start bringing home some money. Oh, I 7. living on my own get my ... but that isn't much and I'm fed up with 8. out of work ... for it every Thursday. I hate having to ask my 9. queuing mum and dad for money. Oh, my mum gives me 10.local paper a couple of pounds for tights now and then, but 11.applicants she can't stand seeing me at home all day. I've 12.take any job almost ... looking for a job. I buy the... every day but I'm really tired of...the "Situations Vacant" column. There are 50 ... for every job. I was interested in being a dentist's ... because I like 13.unemployment benefit 14.youth unemploy- ment meeting people, but now I'd ... at all. People ask me why I don't... London, but I don't want to leave my family and friends. Anyway, I'm scared of ... in a big city." 10. Translate the following sentences. 1) Они ищут работу, обращаются в специальные агентства и просматривают объявления в газете в рубрике "Требуются". 2) Мэри хотела получить место секретаря в приемной, но на это место было 40 кандидатов. 3) Она не получила его, теперь она согласна на любую работу, т.к. ей надоело стоять в очереди за пособием каждую неделю. 141 4) Роджеру за 50. Он проработал в одной компании более 30 лет. 5) Из-за экономических трудностей в отрасли он попал под сокращение штатов. 6) Он опять начал искать работу, но т.к. ему уже за 50, он получил много отказов. 7) Все кандидаты были моложе его, хотя у них было меньше опыта. 8) Ему необходимо получить новую профессию, но никто не хочет обучать человека, который скоро должен уйти на пенсию. 11. You came to an employment agency and have to answer their questionnaire. “PERSONNE l CORPS "” Professional Recruitment & Selection Tel. 275-35-02 Fax 275-36-96 Questionnaire 1. Are you seeking a) full-time employment? b) part-time employment? 2. Which of these is most important for you? (Please number 1-5 in order of importance) money □ people □ security job satisfaction an interesting job □ □ □ □ □ yes no Do you like meeting people □ □ working alone □ □ working with other people □ □ working with your d) hands □ □ e) travelling □ □ 4. What do you like doing in your free time? 3. a) b) c) 12. What should you do to find a job? Find the logical sequence of the steps you should take. — get an invitation for an interview — make an appointment with an employment agency counselor — read the classified ads — think what kind of job you want — analyze your skills, personality traits and accomplishments 142 — get ready for the interview — find out what employment agency you can use — find out as much as you can about the company 13. Read and translate the dialogue. Learn it by heart. Looking for a job Here is a talk between two acquaintances: A: So, Bruce, when you lost your job, how long did you take to find another job? B: Well, not too long compared with some people. Just six months. I remember that I sent 700 resumes. A: Seven hundred job applications in six months. That's incredible! B: Well, it's only about four a day. A: Maybe, but that's a lot of paperwork... S: Well, I guess so. A: And what was your job before that? B: Well, you see, I worked as a policeman in the early 1990. Then I worked as National Sales Manager with Excel. But the company closed because of heavy competition and I lost the job. A: And where are you working now? В: I’ve got a job in Rochester Telephone. I'm in the Marketing Department. I develop new markets for phone services. A: How long have you been working there now? B: Just two months. It's great to be employed again! A: Bruce, and what advice would you give to someone who is looking for a job? B: Well, firstly — attack the problem immediately. Don't go on a long holiday — it won't help you to find a job. A: It's just wasting time. 143 B: That's right. Secondly, work, work, work on looking for a job. Before you lost your job, you did a 40-hour week, so why not now? A: So work full-time on your job applications. B: Yes, but at the same time — relax occasionally. Go to the beach, have lunch with friends, go to the gym — you need a break from time to time, even when you are unemployed. A: Useful advice. Any more? B: Yes. It's nice to meet people who are in the same situation as you – other unemployed people. You realize you are not the only unemployed person in town, and you can give each other some good ideas. A: So you should meet people in the same position. Anything else? B: Yes. Don't apply for a job if you don't want it — be selective. If you go for an interview for a job you don't want — you are stupid. You won't get it. A: Very true. What about friends and colleagues? B: Yes, they can be very useful. Talk to them as often as possible. That's how I got my present job, I learned about it from my friend. Vocabulary incredible – невероятный break – перерыв heavy competition – острая конкуренция to have a break – быть to waste – терять на перерыве, отдыхать to relax – расслабляться to need a break – нуж - occasionally – иногда, от случая к случаю даться в отдыхе to be unemployed – не иметь работы a tea (lunch) break – пер stupid – глупый рыв на чай (ланч, обед) Библиографический список 1. Агабекян И.П. Английский для менеджеров: учеб. пособие / 144 И.П. Агабекян. – 7-е изд. – Ростов н/Д: Феникс, 2006. – 416 с. 2. Агабекян И.П. Английский язык для экономистов: учеб. пособие / И.П. Агабекян, П.И. Коваленко, Ю.А.Кудряшова. – М.: ТК Велби, Проспект, 2006. – 368 с. 3. Алонцева Н.В. Английский язык для направления «Менеджмент»: учебник для студентов учреждений высш. проф. образования / Н.В. Алонцева, Ю.А. Ермошин. – М.: Академия, 2011. – 272 с. 4. Любимцева С.Н. Английский язык для студентов финансовоэкономических специальностей вузов. Начальный курс: учебник / С.Н. Любимцева. – М.: Высш. шк., 2004. – 296 с. 5. Шевелева С.А. Основы экономики и бизнеса: учеб. пособие для учащихся сред. проф. учеб. заведений / С.А. Шевелева. – М.: ЮНИТИ-ДАНА, 2008. – 496 с. 6. Everyday English: учеб. пособие для студентов гуманитар. ВУЗов и старшеклассников школ и гимназий с углубленным изучением англ. яз. / под ред. Т.Ю. Дроздовой. – СПб.: Химера, 2011. – 592 с. 7. Brown Betty J. Introduction to Business / Betty J. Brown, John E. Clow. – Glencoe / McGraw Hill, 2008. – 268 p. 8. How do I get a graduate job in management? [Электронный ресурс]. – Электрон. статья. – Режим доступа: http://targetjobs.co.uk/career-sectors/management/special-features/how-doi-get-a-graduate-job-in-management. – Загл. с экрана. 9. Management as a Profession [Электронный ресурс]. – Электрон. статья. – Режим доступа: http://www.managementstudyguide. com/management_profession.htm. – Загл. с экрана. 145 10. McCrimmon M. Talent Management [Электронный ресурс] / М. McCrimmon. – Электрон. статья. – Режим доступа: http://www.leadersdirect.com/talent-management. – Загл. с экрана. Оглавление Предисловие …………………………………………………………… 3 146 UNIT 1. FINANCE ……………………………………………………. 4 What is Finance? ………………………………………………… 4 Personal Finances ……………………………………………….. 8 Personal Expenditure ……………………………………..…….. 15 Eight Steps to Getting Your Finances in Order …………..…….. 23 Overview of Techniques and Sectors of the Financial Industry …………………………………………………………. 30 Corporate Finance ……………………………………………… 38 Public Finance …………………………………………….……. 43 UNIT 2. MANAGEMENT …………………………………………… 67 Interpretations of Management ………………………………… 67 What is a Manager? ……………………………………………. 71 The Concept of Management and the Mission of a Manager ….. 76 What is Management? …………………………………………. 82 Talent Management ……………………………………………. 86 The Four Functions of Management …………………………… 92 UNIT 3. PUBLIC MANAGEMENT ……………………………..…. 101 Forms of Business Organization ……………………………… 101 Partnership ……………………………………………………. 106 Corporation …………………………………………………… 112 147 Board of Directors ……………………………………………. 116 Directors and Managers ……………………………………… 121 Looking for a Job …………………………………………….. 129 Employment Agencies ……………………………………….. 133 Библиографический список ……………………………………….. 144 Учебное издание 148 Липка-Ким Юлия Александровна Соловьева Ирина Николаевна Эмирзиади Елена Сергеевна Английский язык в профессиональной сфере Учебное пособие Лицензия ЛР № 020525 от 02.06.97 Редактор Н.П. Романова Сдано в производство Форм. бум 60 х 84 1/16 Бум. тип. №2 Печать офсетная Гарнитура Times New Roman Уч.-изд. л. 6,4 усл. печ. л. 6 Тираж 100 экз. Заказ № Забайкальский государственный университет 672039, Чита, ул. Александро-Заводская, 30 РИК ЗабГУ 672039, Чита, ул. Александрово-Заводская, 30 www. rik-romanova-chita@mail.ru 149