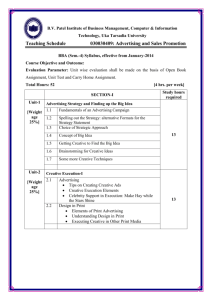
18 Terms - Advertising Institute of Australasia
advertisement

ADVERTISING TERMS ABOVE THE LINE - advertising conducted in recognised media. ACCOUNT SERVICE (often called 'Client Service'). The members of an Advertising Agency who are responsible for the supervision of planning and preparation of advertising for one or more Advertisers (‘clients’ or 'accounts') and for the primary liaison between Agency and Advertiser. AD PAGE EXPOSURE (APX) - a term used to describe how frequently readers look at an average advertising page in a particular issue of a magazine. It relates to how many times an issue is picked up and read by each reader, and how many pages they are exposed to each time. ADSTOCK – a concept which relates to the memory retention level in prospects, particularly during periods of advertising inactivity. When advertising occurs, awareness levels are supplemented; when advertising ceases, awareness levels will progressively reduce. At any given time, the current remembrance level is called the brand’s ‘Adstock’. ADVERTISING FEDERATION OF AUSTRALIA (AFA) – the association which represents advertising agencies. ADVERTORIAL – paid advertising in an editorial format. Often required to be labelled “advertisement” in print or made clear as a paid segment in electronic media to ensure reader understands that it is an advertisement. AIDED RECALL - when a respondent to research is asked to remember an event with the aid of a visual or oral stimuli (e.g. being shown a magazine when asked if they have read a particular issue). AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) – radio broadcasting method mainly used by talk stations. ANALOGUE – continuous signal for conveying data electronically. Currently used by television stations, but being replaced by digital method as consumers convert equipment. APPROACH - the distance from an outdoor sign to the point where it is first visible. ARTWORK - the elements of a print advertisement in their final configuration ready for use. Also refers to material prepared for use as television supers, etc., and drawings produced by an illustrator. AUDIENCE - the potential or expected number of people who have an opportunity to be exposed to an advertising message, or a media vehicle. AUDIENCE FLOW – the ebb and flow of audiences in television and radio. AUDIENCE PROFILE - or AUDIENCE COMPOSITION - the size and type of the groups of people who make up the audience for any particular medium. 1 AUDIENCE SKEW - the way the audience for a particular medium or program differs from the average. (e.g. a radio station which attracts a large proportion of teenage listeners is 'skewed' towards this group.) AUDIENCE TURNOVER - the frequency with which an audience changes over a period of time. (e.g. the people listening to a radio station at midday may be totally different to those listening to the same station at 6.30 am.). AUDIT – independent checking. Often related to independent verification of media buying. AUDIT BUREAU OF CIRCULATIONS (ABC) - the organisation responsible for administering and publishing audited circulation data for those newspapers and magazines which charge a cover price for their publication. Also involved in internet auditing. AUSTRALIAN ADVERTISING RATE AND DATA SERVICE (AARDS) – media and production guide for print media in Australia. AUSTRALIAN BROADCASTING AUTHORITY (ABA) – government body responsible for administering commercial television and radio. AVAILABILITY - a particular time which remains available to place a television commercial. Can also be used to describe advertising opportunities in other media. AVERAGE AUDIENCE - the estimated audience of a medium at any one time, averaged over a nominated period of time (e.g. a radio station may have an average audience of 50,000 people listening during their breakfast session. However, its audience at 6am may only be 5,000, whilst at 7.30am it may be 95,000. The larger the element being averaged, the less useful/accurate the average figure is likely to be.) AVERAGE FREQUENCY - (see Frequency). AVERAGE ISSUE READERSHIP - an average issue reader of a publication is one who conforms to a stated readership criteria (e.g. a reader who 'looks into' any issue of a weekly magazine in the previous 7 days). Since various readership surveys may use different criteria, the basis of this definition should be remembered when interpreting readership data. BAIT ADVERTISING - illegal advertising of exceptional prices or terms for a product in order to attract prospects to a store where they find it difficult or impossible to buy the product as advertised. BANNER – a sign used for outdoor promotion, or a web site advertisement. BASE - the total from which percentages are derived in a survey report. BASE RATE - the basic unit cost associated with advertising in each medium, before the application of loadings for specific requirements, or discounts for volume usage, etc. BELOW THE LINE - promotional activities , store promotions and displays, and other methods of reaching consumers which are not 2 advertising in recognised media. Can also include other activities including co-operative advertising, trade discounts, etc. BILLBOARDS - announcements of up to ten seconds at the opening and closing of a television program to identify the program sponsor. Also used to describe outdoor advertising posters. BILLINGS - the total financial turnover of an Advertising Agency. The sum total of the agency clients' budgets. BLACK AND WHITE (B&W) - black images only on the paper (usually white) in print media. Images without colour on television. Also called 'monotone' (one colour). BLEED PAGE - where the print area of a magazine advertisement extends to the trimmed edge of the page on one or more sides. Within the bleed size is a 'safe area' or 'type area' which must contain the advertising message. BOOKING - the act of purchasing media space and time. BRAND DEVELOPMENT INDEX – Index of relative strength of a brand in different markets (geographic or demographic). BROADSHEET - a particular newspaper size, approximately 56 centimetres deep x 10 or 11 columns wide. Broadsheet newspapers around the world are designed to appeal to a more up-market reader, and generally have a lower circulation base than the mass appeal Tabloids. In Melbourne, ‘The Age’ is a broadsheet paper. BROADSIDE - a very large direct mail folder, often used in Trade promotion. BROWSER – internet viewing software. BUDGET - funds set aside for a particular purpose. BURST – heavy advertising (especially television) advertising in a short time period. BUSINESS PRESS - publications directed to a particular industry, trade or profession. CALL SIGNS - Television and radio stations are known by call signs. The final letter in a television station call sign signifies its state location (e.g. GTV 9 - Victoria, SAS 10 - South Australia, TVT 6 Tasmania). The numerical identification refers to the channel. Radio station call signs have historically been prefixed with a number identifying their home state (e.g. 2 - New South Wales and Australian Capital Territory, 3 - Victoria, 4 - Queensland, 5 - South Australia, 6 Western Australia, 7 - Tasmania, 8 - Northern Territory), but with new stations and call sign changes most stations don’t include this prefix in promotion and the name is often based on the local broadcast frequency of the station (e.g. Gold 104) or promotable letters (e.g. FOX-FM). CAMPAIGN - an advertising effort for a product or service, extending for a specified period of time. CANCELLATION DEADLINE - the last date for cancelling an advertisement which has been booked without incurring a penalty. The cancellation deadline varies between media (e.g. for general 3 bookings - Television 70 days prior, Radio 42 days prior, Newspapers 3 days prior). Special preference bookings (e.g. Television sponsorships, Newspaper special preferred positions, etc.) are often either non-cancellable or have longer deadlines imposed. CARD RATE - the cost of advertising quoted by a media vehicle on a rate card. Special low rates are often called 'off the card'. CATEGORY DEVELOPMENT INDEX - Index of relative strength of a product category in different markets (geographic or demographic). CENTRE SPREAD - an advertisement appearing on the two facing centre pages of a publication. CHECKING - verifying the appearance of advertising booked in newspapers and magazines to ensure it has appeared in accordance with instructions. In electronic media the act of checking is called 'monitoring'. CIRCULATION - the total number of copies of a particular publication which are distributed, based on an average of a number of issues. Most publications have their circulations independently audited - by the Audit Bureau of Circulations, or the Circulations Audit Board. CIRCULATIONS AUDIT BOARD (CAB) - an organisation responsible for administering and publishing audited circulation data for publications (including specialist consumer or trade magazines) where more than half the number of copies are distributed free. CLASSIFICATION DATA - the information which survey respondents provide to enable them to be classified into demographic or psychographic groupings. CLASSIFIED ADVERTISING - newspaper advertising in a special section of the paper which is set aside for companies and individuals to promote their goods and services under special headings, e.g. houses for sale, positions vacant, motor vehicles for sale, etc. Much classified advertising is purchased line by line, although display formats are used by some advertisers. CLICK THROUGHS – a measure of the number of times an internet advertisement is clicked-on (opened) by viewers. CLIENT - normally the advertiser company, who is a client of the Advertising Agency. Also referred to as an 'Account' - hence 'Account Service'. CLUTTER - a media environment where there is considerable competition from other elements (especially other advertisements) which may detract from the impact of an individual message. Especially relates to the number of television commercials in a break, or the page environment in a newspaper. COLLECTOR'S DISTRICTS (CD's) - the smallest geographic districts for which Census information is available from the Australian Bureau of Statistics. COLOUR SEPARATIONS - the material required as part of the process of reproducing full colour in print. The original full colour artwork and/or photography is separated into the four colours 4 required for the printing process. Material is mainly processed direct from computer to printing plate or printed image. COLUMN CENTIMETRE (col cm) or Single Column Centimetre (scc) - the unit of charging for newspaper advertising space. Each newspaper page is divided into a number of columns, and the columns are a fixed centimetre length. e.g. a newspaper with a depth of 38 centimetres, and with 7 columns has 266 column centimetres to a page. If the advertising cost was $50 per c.c. then the cost of a full page advertisement would be 266 x $50 = $13,300. COLUMN WIDTH - the width of type columns on a printed page. Can vary considerably from one publisher to another. COMBINATION CUMES - used in radio to show the cumulative audience which can be reached through various combinations of multiple stations. COMMERCIAL BREAK - an interruption to television and radio programs to broadcast a commercial or group of commercials. COMMISSION - a commission (usually 10%) given by the media to their customers. It is based on the total amount spent each month in each medium, and is granted on condition that the purchaser fulfils a number of conditions including payment of each media account within an agreed time. Until 3 February 1997, media commissions were restricted to approved (accredited) Advertising Agencies, but may now be offered to all buyers at the discretion of individual media. CONFIDENCE LIMIT - the range (+ or -) within which a certain figure in a survey report can be generally relied upon. Confidence levels are expressed in terms of 'standard errors', and are affected by a variety of factors including the number of people in the survey sample. See 'Sample Error'. CONSUMER PRICE INDEX (CPI) – on-going measure of the inflation rate. CONTINUITY - the way the media elements of a campaign form a total unit. Some media add a high degree of continuity to a campaign (e.g. outdoor advertising which can be seen 24 hours a day 7 days a week over extended periods of time). Others often achieve a form of continuity which is more regular than continuous (e.g. newspaper advertisements on a fixed day each week). Continuity allows target audiences an opportunity to see elements of a campaign at regular intervals. COOKIE – piece of information inserted in user’s web browser from web server, usually for the purpose of identifying user for future transactions. 5 CO-OPERATIVE ADVERTISING - retail advertising subsidised by a National Advertiser so that Retailer and National Advertiser share the cost. It ensures the National Advertiser has retail support for the product, and reduces the cost (or increases the volume) of advertising for the Retailer. COPY DEADLINE - the final deadline for the supply of the advertising material to a newspaper or magazine. CORPORATE IMAGE - the mental picture held by members of the public of a company's character or personality. CO-SPONSOR - two or more sponsors of a television or radio program, each sharing the advertising time cost. COST EFFICIENCY - a comparison of the cost of reaching an audience through various elements of the media. It involves determining the cost on the basis of a common denominator for the particular medium (e.g. cost per thousand readers or viewers) and comparing alternative newspapers or magazines or radio stations or television programs. Comparing alternative media (e.g. television with newspapers) on this basis is not valid since there are so many other variables which must also be considered. COST PER TARP - a measurement which allows comparison of the relative cost of reaching a target audience through alternative television programs. Cannot be used to compare relative costs in different sized markets. COST PER THOUSAND (CPM) - reducing the cost of a particular media vehicle to a CPM allows comparison with another vehicle in the same medium to establish cost efficiencies. It is determined by dividing the equivalent rate by the number of thousands of people in the target audience. COVER - the outside leaf of a magazine, comprising front cover, inside front cover, inside back cover, and outside back cover. These positions are considered prime, and attract a premium price for advertisers. Major consumer magazines (and many other magazines) do not accept advertisements on the front cover. COVER DATE – date printed on front cover of magazine (‘Issue Date’). Not necessarily the same as the on-sale date. COVERAGE - normally used to describe the prime geographical area reached by a medium. Can also be used to show the degree to which a medium or an advertising schedule will reach a particular type of audience. COVERAGE AREA – geographic area covered by the medium. In electronic media it is affected by signal frequency and strength. CUMULATIVE AUDIENCE (CUME) - actually means 'accumulated audience' or the total number of different individuals (or households) which a medium or a defined section of a medium will reach over a given period of time. DATACASTING – transmission of internet-type data (including interactive technology) for reception by a television set. 6 DATA FUSION – fusing (merging) data from more than one type of survey (e.g. product purchase behaviour with media audiences). DAY PART - sections of the day, used to reflect changing audience habits in electronic media from morning to afternoon to evening. DECODER - A device which decodes encrypted signals. DELETE AND CHARGE – television stations may allow airtime to be paid for, but used later, if airtime must be cancelled after deadline due to unavoidable circumstances. DEMOGRAPHICS - physical characteristics of a media audience, including age, sex, income, education level, geographic location, etc. DIARY METHOD -(or Diary Personal Interview Method) the collection of media data through individual or household diaries, supplemented by personal interview. Radio surveys in Australia currently use the Diary Method. DIE CUT - a hole which has been deliberately cut into the paper in a leaflet or booklet. Often used as a design element to reveal part of the following page. DIGITAL RADIO RAPID TRANSFER (DART) – delivery of radio commercials to stations by internet broadband. DIGITAL COMPRESSION - Reduces information transmitted to a compressed state. DIGITAL SIGNALS - greatly enhances picture and sound quality over conventional (analogue) signal. Television is being converted to digital as consumers purchase new digital receiving equipment. Will also be available for radio use. DIGITISATION - converts analogue signals to digital. DIRECT BROADCAST BY SATELLITE (DBS) - programs beamed directly by satellite to antennas located at pay TV subscribers homes. Also called DTH or ‘Direct to Home’. DIRECT MAIL ADVERTISING - advertising material sent through the mail, addressed to prospective purchasers. DIRECT MARKETING - selling direct to the consumer, without using Wholesalers or Retailers. DIRECT RESPONSE ADVERTISING - advertising designed to gain a response directly to the Advertiser, outside the normal retail store structure. DISCOUNT - a reduced rate which has been negotiated, often in conjunction with agreement to purchase a particular volume of advertising time or space. Production suppliers sometimes offer discounts for quicker than normal settlement of their accounts. DISPLAY - showing physical merchandise to attract customers. Usually in store windows or on the sales floor. DISPLAY ADVERTISING - newspaper advertising which is bought by the column centimetre, as opposed to that purchased on a line by line basis. Display advertising appears throughout the newspaper. DISTRESS SPACE – advertising space made available (at discount rates) at the last moment due to unforeseen cancellation. Some media 7 use it as a ploy to sell additional advertising where there has been no cancellation. DISTRIBUTION - the spread of influence of a medium either in terms of the area covered or the make-up of the audience. Also the method by which a product is made available to consumers. DOMINANCE - advertisements or campaigns which stand out by virtue of their larger size or increased frequency. The market leader in a particular industry often holds a position of dominance in the preferred medium for companies in that industry. DOUBLE SPOTTING – placing more than one commercial in a television (or radio) program. DOWN-MARKET - a colloquial term for a market segment at the lower end of the socio-economic scale. DRIP – low levels of television weight over a prolonged period. DUBB – the copy of the commercial sent to a television or radio station. Can be delivered by satellite using digital compression technology. DUPLICATED AUDIENCE - people or households who are exposed to a number of vehicles in a media plan. Commonly used in print media. EARLY GENERAL NEWS (EGN) – the front or news section of a newspaper. EBB AND FLOW - the movement of audience in electronic media from station to station at any given point in time. At any given point, individuals may stay with the same station into the next period, change to another station, or switch off. New individuals may join the audience for particular stations. Tracking an advertiser's target market as they move around the media so that advertising may continue to be directed to them (often called 'gardening') is an important function of effective media planning. EFFECTIVE FREQUENCY – the number of times a consumer must see an advertisement for it to be effective. EFFECTIVE REACH - the number of people or percentage of the potential who have had at least the number of opportunities to see the advertising which is considered the minimum necessary for it to be effective. The number will vary according to the campaign objectives and duration. ELECTRONIC MEDIA - television and radio. ETHNIC MEDIA - a broad term for media aimed specifically at ethnic groups, usually in their own language. EXCLUSIVE AUDIENCE - the number or proportion of a given target audience that is reached by a particular media vehicle and not by competitive vehicles. EXCLUSIVITY – guarantee that no competitive advertising will appear in television program, etc. EXPOSURE - any person who reads an issue of a newspaper or magazine, or views television or listens to radio during a particular program or time period. 8 FIBRE OPTIC - thin light-transmitting glass fibres used to carry information. FIELD WORK - the time period during which research interview information is obtained, and therefore the time period to which the results will relate. FILM – Material used in photography and printing (largely outdated by digital technology) and in motion picture industry (soon to be similarly superceded). FIXED DAY/NIGHT - booking television advertising for a nominated day of the week, rather than in a specific program (which is likely to be more expensive) or on a week commencing basis (which is likely to be cheaper). FIXED PROGRAM - booking television advertising in a nominated program. Most television time is booked in this way since it allows advertisers to more precisely target the audience with whom they wish to communicate. FLIGHT - a period of campaign activity in the media. It may be followed by a period of inactivity for the product, and then resume with another flight. FORMAT - the size, shape, style and overall appearance of a publication or advertisement. The organisation of each element in a radio or television broadcast. FORME CUT - a printed page which has been specially shaped as part of a design or to contour a significant element on the page. Point of Sale display material often involves forme cutting. FOUR COLOUR PRINTING - the process used to reproduce full natural colour in newspapers or magazines. Yellow, Blue (Cyan), Red (Magenta) and Black are printed from individual colour separated printing plates to provide the final printed colour image. FRAGMENTATION - the division of the available audience in a market amongst the various vehicles in a medium, e.g. television stations, newspapers, etc. For instance, the television audience continues to be fragmented as more homes subscribe to Pay TV channels. FREE-TO-AIR TELEVISION (FTA) – the free (usually referring to the ‘commercial’ and ‘government’) television networks, as opposed to pay television channels. FREQUENCY - the number of times a potential customer is exposed to the message in a given time. Usually expressed as an average figure, which means that perhaps half the market have seen the advertising more times, and half have seen it less times. Frequency or repetition of message is the most important factor in advertising effectiveness. For television, the average frequency can be determined if the number of TARPS and the percentage reach are known (e.g. 150 TARPS divided by a 50% Reach equals an average frequency of 3). FREQUENCY DISCOUNT - a discount based on the number of advertisements placed in a specified time, usually a year. Relates specifically to particular magazines. 9 FREQUENCY MODULATION (FM) – broadcasting signal of superior quality to Amplitude Modulation (AM), used by most music radio stations and for television sound. FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION - a method of showing how many advertisements each of the target audience was exposed to. e.g. Exposure 1 x times 2 x times 3 x times 4 x times 5 x times Total Schedule Target Reached 20 % 10 % 10 % 5% 2% 47 % Frequency 1 2 3 4 5 2.1 Average T.A.R.P.S. 20 20 30 20 10 100 FRINGE TIME – television time periods on both sides of peak time. GATEFOLD - a magazine page which is much larger in width than a normal page and is folded over and back into the magazine. GRAPHIC INTERCHANGE FORMAT (GIF) – computer format for simple image files. GROSS AUDIENCE - the total audience the medium reaches in a given period. GROSS IMPACTS - each time a person is potentially able to receive an advertising message they are counted as an 'impact'. Gross impacts are the total number of people who have received a message multiplied by the number of times they have seen or heard. GROSS RATING POINTS (GRP’S) – the total number of TARP’S accumulated in a designed time period. Also often known as “Total TARP’S”. GUTTER - the margin between pages in a newspaper or magazine. Most magazines have technical restrictions relating to what material (if any) can be placed near the gutter as the binding often renders some of the area unavailable to view when the publication is complete. In newspapers, many Advertisers prefer the outside of the page rather than the 'gutter edge' which is often considered less prominent. HARD CORE AUDIENCE - those members of the audience who will be exposed to most of the advertising for a product. HEAVY USER - the users who will buy and use more of a specified product than other users. For most products a small group purchase a disproportionately high volume. HIATUS – non-activity period in advertising schedule. HIGH DEFINITION TV (HDTV) - uses more than 1000 lines of information to make up a TV picture (compared to 625 for PAL) for greatly improved picture quality. Comes in a wide-screen format. HITS – the sum total of all elements downloaded from a web site. If a page has 10 elements, this means 10 hits are registered to view the page. In normal use referred to (wrongly) as meaning the number of visits to a web site. 10 HOME PAGE – the ‘front page’ of a web site. HOMES USING TELEVISION (HUT) - Overall program ratings are expressed as a percentage of the total number of homes with television. Therefore if a program has a HUT rating of 25, it means that 25% of all homes with television were tuned to the program. Since there is never 100% of sets in use, the combination of HUT ratings from all stations in a market will never total 100. Even in the period 7-10 pm the average is normally below 70%. HORIZONTAL PUBLICATIONS - business publications addressed to an audience representing the same interest regardless of industry. e.g. accountants. HYPERTEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE (HTML) – language program for hypertext documents on web sites. HYPERTEXT TRANSFER PROTOCOL (HTTP) – movement protocol for internet hypertext files. IMPACT - the degree to which an advertisement affects its audience. IMPACTS - the sum total of all the people who may be exposed to advertising, multiplied by the number of times each person will see an advertisement. IMPRESSIONS – (see ‘Impacts’) INCENTIVES - inducements (often financial) offered to company or retail sales staff to help gain support and additional sales of a product. Can also be used to describe special offers made to encourage customers to purchase. INDUSTRIAL ADVERTISING - advertising directed to industrial companies who may use the goods or services which are advertised in their manufacturing processes. INSERT - a separate printed item (leaflet, catalogue, etc) inserted into a magazine or newspaper. INSERTION - an advertisement in a print medium. INSERTION ORDER - an authorisation from an Advertiser (or Advertising Agency) to publish an advertisement in print media. INSTITUTIONAL (CORPORATE) ADVERTISING - advertising which promotes the company, as opposed to the company's products. Often designed to improve public relations by showing the company as responsible and caring for the community. INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK (ISDN) – method of moving internet data over telephone lines. INTERNET – the network enabling information to be transmitted between individual computer users. INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDER (ISP) – internet access providers and web site hosts. INTERSTITIALS – Full page advertisements on the internet. Generally shown while waiting for other information to be downloaded. JOINT PHOTOGRAPHIC EXPERTS GROUP (JPEG) – common format for computer image files 11 JUNIOR PAGE - a magazine advertisement of the same shape and proportions as a full page, but covering about half the page area with editorial filling the space above and beside on the page. KEY NUMBER - the numbers and/or letters placed at the base of a print advertisement to identify the material. Also included on television (visually) and radio (aurally) tapes prior to the commercial starting point. KEY WORDS – can be registered with internet search engines to ensure particular website appears in keyword searches. LEAD TIME - the time required to produce advertising material in time to meet media or campaign deadlines. (e.g. The magazine itself may require the material six weeks before publication, and it may take another three weeks for the Agency to prepare the magazine advertisement.) LIFE STYLE - qualitative audience characteristics relating to style of living (e.g. leisure time activities, shopping habits, product ownership, etc.) LIVE COMMERCIAL - a commercial read directly on air by a radio announcer, or produced live in the studio during a television program. Few television commercials are done 'live' since there are few live television programs, and even radio commercials which utilise the announcer on duty at the time have often been recorded earlier to ensure there are no errors and that the program format is not hindered in any way. Live commercials allow more spontaneity and a greater sense of personal involvement by the listener or viewer. LOADING - an additional cost for a preferred time or position. Can also be applied for the use of any extra facility (e.g. newspaper spot colour). LOCAL ADVERTISING - the use of media by local Retailers, Tradespeople, etc. MAIL ORDER ADVERTISING - advertising which requires prospects to purchase products and services advertised via a mailed response. MAKEGOOD - a replacement no-charge advertisement to compensate for one which has been run incorrectly by the media. MARKET - the people who constitute the buyers or potential buyers of a product or service. Can also used to describe a geographical area. MARKET POTENTIAL - the portion of the market which an Advertiser expects to capture. Can also refer to the total number of people in the target group. MARKET PROFILE - a demographic description of the people or households which form a market. MARKET SEGMENTATION - dividing the market for a product or service into groups by demographic or psychographic profiles. MARKET SHARE - the share of total industry sales volume held by a company or brand. MARKET WEIGHTS - see 'Weighted'. 12 MARK-UP - the difference between the cost and selling prices of goods and services. MATERIAL DEADLINE - the final time that advertising material will be accepted by a medium. MASS MEDIA - media directed to the community at large, rather than specific groups of people. MEAN - a statistical synonym for 'average'. MEDIA (MEDIUM) - the vehicle used by advertisers to carry their message to a defined audience. MEDIA CONSUMPTION PATTERNS - the way various segments of the population are exposed to individual media (e.g. light television viewers, heavy magazine readers, etc.). MEDIA FEDERATION OF AUSTRALIA (MFA) – association representing media planning/buying companies. MEDIA MIX - the combination of all the elements of media used in a schedule or total campaign. MEDIA STRATEGY - a plan to best achieve media and communication objectives within a budget. MEDIA VEHICLE - individual stations, publications, etc. within a medium. MEDIA WEIGHTS - the application of weights to media audience figures to express relative preferences. Also used to express relative volumes in different media during a campaign. MERCHANDISING - the elements involved in retail selling. The term 'merchandising the advertising' is often used to describe the process of 'selling' the advertising campaign to Retailers to gain their active participation and support. MICROWAVE - high frequency radio waves used for signal transmission. MONEY VALUE DISCOUNT - the levels of expenditure which will attract rate discounts with various media. Most media offer a sliding scale of discounts according to volume of money to be spent in a twelve month period. MONITORING - checking that advertising which has been booked for television and radio has been transmitted according to the purchase agreement. Stations will provide a statement of appearances, which can be verified by independent monitoring services. Many television Advertisers use monitoring services for the valuable post analysis information they provide, and since their cost can often be more than compensated by detecting transmission errors and arranging compensatory 'make-goods' in costly commercial time. MONO - a press or magazine advertisement printed in a single (monotone) colour (usually in black ink). MULTIPOINT DISTRIBUTION SERVICE (MDS) - Low powered UHF broadcasting system which allows good reception within line-of-sight to the transmitter. MULTI-SET HOMES - those homes with more than one television set. 13 NARRATION - voice commentary which ties elements of a radio, television or cinema advertisement or series of advertisements into a unit. NARROWCASTING - programming with appeal to a limited audience. NATIONAL ADVERTISING - promotion of brand name products or services - usually covering either major markets or on a fully national (Australia-wide) scale. NATIONAL PLAN - a media plan covering the whole of the country. NATIONAL TELEVISION SYSTEM COMMITTEE (NTSC) - television system used in US which operates with 525 lines per picture frame. NETT AUDIENCE - see 'Reach'. NETWORKS - a group of television, radio stations, newspapers or magazines with common ownership or which link together for promotional purposes. Some offer discounts for the use of multiple vehicles in the network. OFF PEAK TIME - periods outside peak time when television audiences are not at their maximum. Sometimes used particularly to describe the times immediately adjacent to peak times - some stations refer to these particular areas as 'shoulder times'. ON SALE DATE – date publication is available at newstands. Often different to ‘Cover Date’. OUTDOOR ADVERTISING - billboards, posters, spectaculars, etc. placed along main roads, or on the walls or roofs of buildings. OPPORTUNITIES TO SEE (OTS) - a person who is exposed to a medium for a predetermined period is classified as having an 'opportunity to see' the advertising carried by the medium. OPTIMISATION - determining the most cost efficient alternative based on nominated criteria when planning a media schedule. OUT OF ZONE – commercials broadcast in a different time zone to that booked. PACKAGES - a group of advertisements purchased as a package. Most frequently associated with radio advertising where a variety of packages can be purchased to cover selected days and time zones. Packages can sometimes be bought for off-peak television spots. PAGE IMPRESSIONS – the number of times a web page is downloaded by consumers. PASS ON – see ‘Secondary Readers’. PAY TV - a subscription television service. PAL ( PHASE ALTERNATE LINE) - television system of 625 lines per picture frame which is used in Australia, Asia, UK and most of Western Europe. PARTICIPATIONS - television commercials which appear within a program, as opposed to those shown between programs. PASS ON READERSHIP - see 'Secondary Readers'. PEAK TIME - see Prime Time. PENETRATION - the percentage of homes or people who can be reached by a particular advertising medium. 14 PEOPLE METERS - an electronic device attached to the television set in specific homes used to measure television audiences. PEOPLE USING TELEVISION (PUT) – the total number of people viewing television in a given time. PERSONAL INTERVIEW - research undertaken in a face-to-face situation. PERSONAL SELLING - selling in person, face-to-face with the prospect. POINT OF SALE ADVERTISING - advertising display material which is set up in the retail outlet. Can also be called 'Point of Purchase', which is simply the perspective from the other side of the counter, or as ‘In Store’ advertising. PORTAL – an entry point website to a collection of other sites and web services, including email and search facilities. Often intended to encourage the consumer to use the site as their ‘home page’. POSITION - the place an advertisement occupies within an advertising vehicle. POST ANALYSIS - analysing research information after the event. POTENTIAL - the total number of persons in a particular area, or demographic group. Actual reach is measured as a percentage of this total potential. PREFERRED POSITION - a specially nominated position which is desired by an advertiser, which will attract an additional cost or 'loading' when purchased. PREMIUM - something given or offered to a product purchaser as an extra inducement to purchase. PREPRINT - an advertisement, leaflet or brochure which is printed in advance and inserted into a newspaper or magazine. PRIMARY READERS - the person who made the original purchase of a publication for the purpose of reading it. PRIME TIME - the time period when television attracts the largest audience - most stations have historically considered prime time to cover 6 pm to 10.30 pm, although for the purposes of regulating advertising content the television code places it from 6 pm to midnight. Can also be used to describe breakfast sessions on radio which are that medium's maximum audience period. PRIME PROSPECT PROFILE - a profile of product and brand users by demographics and media consumption. PRODUCTION COSTS - the cost of producing the advertising material which will appear in the media. PROFESSIONAL ADVERTISING - advertising which is directed at professional people who are likely to recommend the use of an advertised product. e.g. Doctors, Architects, etc. PROFILE - the composition of the audience of a particular media vehicle. PROMO –television station announcements promoting their own programming. 15 PSYCHOGRAPHICS (PSYCHOMETRICS) - lifestyle attitudes or psychological characteristics of a media audience. PUBLIC RELATIONS - any communication created primarily to build prestige and goodwill for a company or product. In a broader sense, any article or item which the media can be encouraged to print or broadcast. PUBLISHER’S CLAIM – the publisher’s version (non-audited) of circulation numbers. PULL-THROUGH - a moving message superimposed over television program material, usually moving from right to left at the bottom of the screen. Also called a 'running super'. PULSING – bursts of heavy television advertising. QUALITATIVE - research data concerned with understanding behavioural patterns. Relates to 'why?' rather than 'how many?' QUANTIFICATION - extrapolation of survey figures so that they relate to the total population rather than the small numbers in the sample. QUANTITATIVE - research data based on volume. (e.g. numbers or percentages of people, classified by viewing, reading or listening habits). QUINTILE – dividing target into five equal groups (e.g. heaviest to lightest television users/product purchasers, etc.) and comparing research data across those groups. RANKING - the listing of data in ascending or descending order. RATE CARD - a document published by a media vehicle which contains advertising costs, mechanical requirements, deadlines, and other information of interest to Advertisers. RATE PROTECTION - an advertising rate agreed with a medium which will not be subject to any increases in the nominated period. RATINGS - the common-usage term for television and radio audience surveys. RATING POINTS - used to describe the percentage of households (HUT), or the percentage of people in a particular demographic group (TARPS) reached by a television program. REACH - the number of different people (usually related to the target market) who are exposed to the advertising message. It is the unduplicated total audience often expressed as a percentage of the potential. REACH AND FREQUENCY - an analysis of the percentage reach and the average frequency of an advertising schedule against a specified target audience. READERSHIP - the average number of readers of a particular publication. Since on average more than one person will read each copy of a publication, the number of readers will always be in excess of the circulation. READERS PER COPY - the average number of readers per copy of a newspaper or magazine. The first reader in each case is classified as 16 the primary reader; all readership in excess of one is 'pass-on' or secondary readership. REBATE - a refund adjustment which may be paid to an Advertiser whose volume of advertising over a twelve month period in a particular medium has exceeded that required to meet a previously negotiated rate level and who now qualifies for a higher discount. Particularly applies in print media. RECALL - the ability of a research respondent to remember a particular event or experience. Recall can be aided (prompted) or unaided. RECORDED COMMERCIALS - most radio commercials are prerecorded and edited at the station or at an outside recording studio. REPETITION - the process of repeating advertising to ensure that it is seen and remembered by the target audience. REPRESENTATIVE (REP.) - a person who represents a media vehicle or production house and looks after the advertising requirements of Advertisers and Advertising Agencies. RETAIL ADVERTISING - advertising by a Retailer designed to get customers to purchase from a retail outlet. Most retail advertising is price or offer orientated and designed to produce immediate results. ROAD BLOCKING – placing commercials on all free-to-air channels at the same time to reach all viewers. ROLL-OUT – product distribution and/or advertising is progressively expanded to more areas. ROTATION - a number of different advertisements which are to be rotated (each used in rotating order) during a campaign. Can also apply to commercials on radio which are rotated through different sessions, and different times within each session exposing the message to a high proportion of listeners to the station. RUN OF PAPER (ROP) - advertisements in the print media placed at the discretion of the Publisher, and which do not attract an additional cost loading. RUN OF SCHEDULE - scheduling a series of advertisements to attain the maximum potential reach of the media vehicle used (e.g. reaching various listeners, viewers or readers at a variety of different times or days). In radio terms is synonymous with 'run of station'. RUN OF STATION (ROS) - a package of radio advertisements rotated to appear on an even spread over all time zones during a week at the station's discretion to reach as many of the listeners to that station as possible. SALES PROMOTION - activities which supplement advertising and personal selling. e.g. competitions, premiums, displays, samplings, trade shows, incentives, etc. SAMPLE - a small group of people chosen to represent the total population (or 'universe') for research purposes. The sample needs to 17 be fully representative of the universe for valid conclusions to be drawn from their responses. SAMPLE ERROR - the size of 'statistical error' which is possible due to the size of the sample and the effect of chance on the results (e.g. it may be in a particular case that the likely answer to a question may be within + or - 6% of the sample response. To reduce the sample error by half (that is, to + or - 3%) normally requires the sample number to be increased fourfold). The extent of the error can readily be calculated mathematically according to the size of sample, method of sampling, and the degree of consensus in the answers. SATURATION - a high concentration of advertising in a short time. Is particularly applied to radio when a large number of commercials are purchased on a station, or on multiple stations. SET TOP BOX - a decoder unit which converts a signal from a delivery provider into a form than can be shown on a normal television set. SCHEDULE - a detailed document which shows in chart form the overall media plan for an Advertiser. It contains the individual media to be used, the total number and size of advertisements, the dates of appearance, and costs. SCHEDULE OPTIMISATION - see 'Optimisation'. SCHEDULING - each medium 'schedules' how advertising which has been booked fits into the total program for each day or each issue. SCREENS - the method of reproducing continuous tone material (e.g. photographs) in printed media by reducing them to a matrix of dots through the appropriate 'screen'. A fine screen (many more dots for more detail) can be used when printing on good quality paper, a coarse screen (fewer dots and less detail) when printing on poorer paper. SEARCH ENGINE – a method of searching for information on the internet from a central database. SECONDARY READERS - a person who reads a publication, but did not make the original purchase. Also called a 'pass-on' reader. SERVICE FEE - the fee charged to an Advertiser by an Advertising Agency to cover the cost of providing advertising services. SETS-IN-USE - the proportion of television sets in any given market which are turned on at any one time. SHARE OF AUDIENCE - the percentage of television and radio audiences tuned to particular stations. Can be expressed in many ways, including by the week, the session or program, or at any given time - by total audience, or by particular demographics. SHARE OF VOICE - the proportion of total advertising volume in an industry spent by each individual company or brand. 18 SHOT - each single section of a television or cinema commercial. SIMULCAST – a program broadcast over more than one media at the same time (e.g. television and radio). SINGLE SOURCE DATA – collecting a variety of information from a single respondent (e.g. media exposure and product purchasing). SKEW - a bias from the average or normal in a particular direction. A radio station audience can be 'skewed' towards the 18-24 age group, a TV sporting program towards males, or a magazine towards higher socio-economic groups. SLICK COVER - the printed cover on a video cassette box. SLIDE - a still picture used as a commercial announcement in cinema. Usually run a part of a group of other advertisers tied together with a recorded sound-track. SOLUS MARKET – a geographic area with only one commercial television or radio station. SOLUS POSITION - an advertisement separated from other advertisements by editorial or program material. SOUND TRACK - the recorded sound for a television or cinema commercial. SPAM – unrequested advertising material sent to internet users. SPECIAL - an elaborate one-off television or radio program. SPECIFIC ISSUE READER - a person who claims to have read a particular issue of a newspaper or magazine. SPECTACULAR - a very large outdoor sign built to order. May include cut-outs, three dimensional items, special lighting, and/or animation. SPLIT RUN - different versions of an advertisement run in alternate copies of a newspaper or magazine, or in a national magazine's different geographic areas. SPONSORED PROGRAM - a television or radio program with one or more sponsors who will each place multiple commercials during the program. Television sponsors receive 10 second opening and closing 'billboards' which announce their sponsorship. Sponsoring a program can deny access to that program for competitive products. SPOT - a radio or television time period where an advertisement is placed (e.g. a radio schedule may consist of 20 x 30 second spots). Can also be called commercials or announcements. SPOT COLOUR - a press or magazine advertisement which utilises a second (or spot colour) in addition to the black used for mono advertising. The spot colour is normally used to highlight an important point, or to make the advertisement more noticeable. STARCH SCORES - a method of measuring the readership of print advertisements through aided recall. Measures three levels of exposure - 'noted' (remembered seeing the advertisement), 'seen associated' (accurately recalled the product or brand), and 'read most' (read more than half the copy). STATION BREAK - the television time period between programs. 19 STATISTICAL DIVISION - geographical areas defined by the Australian Bureau of Statistics for which Census information is available. STATISTICAL ERROR - see 'Sampling Error'. SUPERS - normally, an element which includes wording which is added or 'supered' over a television picture - e.g. price. SURCHARGE - an additional charge which may be payable to individual advertising media if an Advertiser has not used an agreed volume of advertising space or time over a twelve month period. Particularly applies in print media. SURVEYS - research undertaken to determine the size and composition of media audiences. Most forms of consumer research are usually based on 'surveys' of one sort or another. SYNDICATED RESEARCH - surveys carried out by an independent researcher who will sell the results to any interested party. TABLOID - a particular newspaper size. The physical dimensions are usually described as being approximately 38 centimetres deep x 7 or 8 columns wide. The ‘Melbourne Herald-Sun’ is a tabloid paper. The ‘tabloid press’ is a somewhat derogatory term for this mass media vehicle. TAG – a message added to the end of a commercial. (e.g. retail availability, promotion, etc) TARGET AUDIENCE - the audience that an individual advertiser wishes to reach. TARGET AUDIENCE RATING POINTS (TARPS) - a measurement of the size of the television viewing audience of particular programs by nominated demographic groups (e.g. an Advertisers target audience is Men 18-24. If a particular program in which the Advertiser places a commercial is watched by 25% of Men 18-24 then that program is said to have a rating of 25 against that particular target audience, and has achieved 25 TARPS.) The number of TARPS for each commercial during the week for that advertiser will be totalled to provide a weekly TARPS figure. This figure will also be the result of multiplying reach by average frequency, but by itself gives no indication of the size of these important ingredients (e.g. 250 TARPS could be the result of 75% reach and an average frequency of 3.3, or 25% reach and an average frequency of 10). TARGET MARKETING - identifying and communicating with particular segments of the market. 20 TEAR SHEETS - the page from a newspaper or magazine containing an advertisement and used as proof of appearance. TELECAST - a television broadcast. TELEMARKETING - professional salespeople using the telephone to create sales, normally using prepared sales scripts. TELETEXT – sending text and graphics by television transmission. TEST MARKET - a geographical market area in which all media types are available, which is used to test an advertising and marketing program prior to launching on a national scale. THEME - the central idea in an advertisement or campaign. Also the musical identification of a program or commercial. THROUGH-THE-BOOK – estimates readership of print media by allowing respondent to view all or part of the issue in question. TIME ZONES - time periods which are grouped together for the purpose of defining radio and television sessions. Radio is divided into breakfast, morning, afternoon, drive, evening and all-night zones; television into morning, daytime, children's afternoon, peak, late night, and midnight to dawn. TOP AND TAIL – placing commercials at the start and at the end of an advertising break. TOTAL AUDIENCE - the total number of people which the medium, or the particular part of the medium in question is able to reach. TOTAL AUDIENCE PLAN - see 'Run of Station' Package. TOTAL IMPACTS (GROSS IMPACTS) - the total weight of advertising without regard to duplication. e.g. 20 million people may pass an outdoor sign in a 13 week campaign (total impacts), but only 300,000 different people (cumulative audience or reach). TRADE ADVERTISING - advertising directed to the Wholesalers and Retailers in the distribution channel, and used to inform the trade of consumer advertising and promotional activity which is to take place. TRANSPONDER - a satellite device combining receiver, frequency converter and signal amplifier. TRIM - the finished 'trimmed' size of a magazine. A bleed page is printed to cover an area larger than the trim size, and the edges are trimmed off in the binding process. TYPE AREA - the area which must contain all type and important features in a magazine advertisement. This is to ensure that nothing of importance is lost if the trimming of the finished article is not exactly correct. TYPE SIZE - the various sizes of the type used in printing which is measured vertically in 'points'. There are approximately 29 points to the centimetre. The editorial copy in most newspapers and magazines is between 6 and 10 points in size. ULTRA HIGH FREQUENCY (UHF) – television channels 12 and up. UNDUPLICATED AUDIENCE - the proportion of an audience which is unique to one media vehicle used in a campaign. 21 UNIFORM RESOURCE LOCATOR (URL) – the address of web content. UNIQUE SELLING PROPOSITION - a benefit which the opposition cannot or does not offer. UNIVERSE - the group of people who are being investigated in a survey. A small sample will be randomly selected to represent this universe since it is usually uneconomic to interview the total 'universe'. e.g. Some 600 homes are interviewed in Melbourne to reflect the TV viewing habits of all residents. UP-MARKET - a colloquial term for a market segment at the top end of the socio-economic scale. VEHICLE - the individual media publication, television or radio station. VERTICAL PUBLICATIONS - business publications directed to specific industries. e.g. mining. VERY HIGH FREQUENCY (VHF) – television channels up to 11. VIDEOTAPE - recording tape which stores picture and sound electronically. Now largely superceded by DVD technology. VIEWER – broadly, a person who spends at least 8 minutes in any quarter hour watching a particular television station or program. VIEWERS PER SET - the average number of people watching each television set which is tuned to a particular station or program. VOICE OVER - when the person delivering the message in a television commercial or announcement is unseen. It could be an announcer talking about products being shown on screen, or providing details of the following program during the final credits of the current program. VOUCHER COPIES - copies of a printed publication supplied to an Agency or Advertiser to confirm the appearance of an advertisement. VOLUME DISCOUNTS - discounts offered by individual or network media based on the annual volume of a Client's advertising expenditure in that media. WASTE CIRCULATION - the part of the audience which is not in the Advertiser's target market. Also, that part of the media which reaches areas where the product or service is not available. WEEKLY CUMULATIVE - the number of different people or households who are reached at least once by a advertising campaign over the period of one week. WEIGHTED - average figures which are altered to reflect the size or importance of relative parts.(e.g. to average results for each state in Australia may not reflect the different sizes of each market. Weighting them will give more relative importance to the result from New South Wales, and less relative importance to, say, Tasmania). WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW) – internet content accessible using HyperText Transfer Protocol (http). ZONE - a period of time in a radio or television day. 22 ZONE AVERAGE AUDIENCE - the average number of people who are viewing or listening over the time period covered by a zone. Most commonly used in radio. ZONE CUMULATIVE AUDIENCE - the total number of different people who can be reached over the time period covered by a zone. Most commonly used in radio. 23