Control Systems Test
advertisement
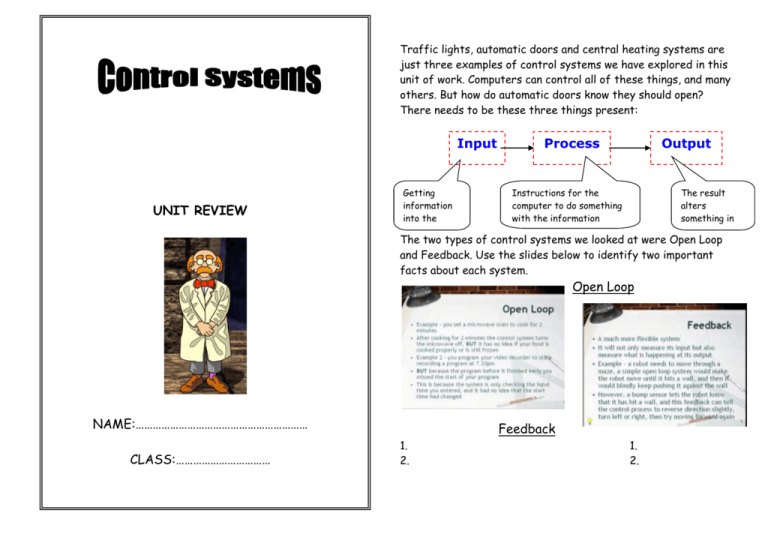
Traffic lights, automatic doors and central heating systems are just three examples of control systems we have explored in this unit of work. Computers can control all of these things, and many others. But how do automatic doors know they should open? There needs to be these three things present: Input UNIT REVIEW Getting information into the computer Process Output Instructions for the computer to do something with the information The result alters something in the outside Open Loop world The two types of control systems we looked at were and Feedback. Use the slides below to identify two important facts about each system. Open Loop NAME:…………………………………………………… CLASS:…………………………… Feedback 1. 2. 1. 2. Examples of Control Systems We have identified many different examples of computer control systems that we see and use in every day life, eg., a car remote control security system. See if you can list three more examples of computer control systems: 1. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Advantages & Disadvantages Now, using the three examples of computer control systems you listed above, think of three advantages and three disadvantages of using computer control systems for each one: My first example is: Advantages 1 2 3 My second example is: Advantages 1 2 3 My third example is: Advantages 1 2 3 Disadvantages Disadvantages Disadvantages Control Systems Test Tick the box with the right answer: 1. Which one of these is a type of control system? Broadband Open Loop Closed Loop Open circuit 2. A microwave oven is a type of open loop system. True False 3. A greenhouse uses which type of sensor? Infra-red Pressure Bump/touch Humidity 4. A computer-controlled robot uses which type of sensor? Bump/touch Humidity Pressure Heat 5. In Logo, which command will move the turtle forwards 5 units? F5 Forward 5 FD5 FD 5 6. In Logo, which command will turn the turtle 90 degrees? RT3 Right 90 R9 RT 90 7. In Logo what shape would these commands produce – REPEAT 4 (FD 50 RT 90) Square Circle Triangle Rectangle 8. Which one of the following is NOT an advantage of control systems? Can be used in dangerous places Can operate without a break Expensive to buy and install Can repeat tasks over and over again 9. What does a feedback loop use to control the output of a device? Computer Information Data Infra-red 10. Feedback systems are more flexible than open loop systems. True False 11. Feedback systems only measure the input data. True False 12. A central heating system is an example of a control system. True False Flow Charts System flowcharts are a way of displaying how data flows in a computer-controlled system, and how decisions are made to control events. There are lots of different symbols used. Basic ones include: On the next page is a flow chart for making a cup of tea. However the commands are missing from the flow chart symbols. Use the answers provided on the left hand side of the page to fill in the symbols. The first one has been filled in for you already. Write the following instructions into the flowchart in pencil, in the order they are carried out to make a cup of tea. Start Glossary of Terms Here is a list of key words from the unit. Use the Definition column to write a meaning for each. The BBC website will help you. Follow this address to get to the right page: Kettle boiled? http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/measurecontrol/index.shtml Milk? Add milk? Wait Add sugar? Stir Yes No Stop Fill kettle with water Switch on No Yes Pour water into cup Sugar? Put tea in cup No Yes No. Key word 1 Analogue 2 Control program 3 Digital 4 Feedback cycle 5 Floor roamer or Turtle 6 Input 7 Interface box 8 Logo 9 Loops 10 Output 11 Processor 12 Sensors Plug kettle in Start Definition







