Review-e2
advertisement

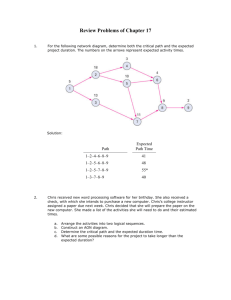
BMGT 583: Exam 2 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Define a project. What is precedence relationship in a project. What is a critical path. Why is knowing the critical path in a project important? What is Activity slack? How is it computed? Explain crashing. Name the three times estimates used in a PERT project. Explain each of them. Define each of the terms peak capacity, and effective capacity. State and explain the principal reasons why economies of scale can occur when output increases. What are the steps involved in making capacity decisions? What is the meaning of diseconomies of scale, and what are two ways for a firm to avoid them? Define each of the following capacity strategies: expansionist, wait-and-see, and followthe-leader. What factors should be considered when selecting the appropriate capacity cushion? How does the choice of capacity cushion relate to other decisions in operations management? To other functional areas? List and briefly explain the dominant factors in locating manufacturing facilities, as discussed in the book. What is the meaning of the term "center of gravity?" Why is the load-distance method a useful, but insufficient, tool for location problems? What are the reasons for the globalization of operations? What are potential advantages and disadvantages of globalization? Identify and discuss of the biggest challenges to managing global operations. Identify and briefly describe the four basic types of layout. What is the theory behind the one worker, multiple machines line (OWMM)? What is the theory behind group technology? What is a REL chart? What is the difference between relative location and absolute location? Which is more closely linked to materials handling? What is the concept of activity settings, relative to office layouts? What types of performance criteria can be important in layout decisions? Problems: 1. Consider the tasks, durations, and predecessor relationships in the following network. Draw the network and answer the questions that follow. Activity Description A B C D E F G H I J a. b. c. 2. a. b. c. Immediate Predecessor(s) --A A B D, C C F F E, G, H I Optimistic (Weeks) 4 2 8 1 6 2 2 6 4 1 Most Likely (Weeks) 7 8 12 2 8 3 2 8 8 2 Pessimistic (Weeks) 10 20 16 3 22 4 2 10 12 3 Schedule the activities of this project and determine (i) the expected project completion time, (ii) the earliest and latest start and finish times, and the slack for all the activities, and (iii) all the critical paths. What is the probability of completion of the project before week 35? With 99% confidence what is your estimate for the project completion time. Consider the following project. Activity Immediate Normal Predecessor(s) Time (Weeks) A 7 B 8 C A 9 D A, B 8 E B 9 F C 10 G D, E 5 H E 10 I F, G 5 Crash Time (Weeks) 4 5 7 Crash cost per week 6000 8000 15000 8 8 2000 17000 8 4 4000 7000 Develop an LP model for crashing the project completion time as much as possible. Modify the LP model for maximum crashing within a budget of $65,000 for crashing activities. Modify the LP model if the project needs to be crashed to 25 weeks at the minimum cost. 3. The single milling machine at Fred's Manufacturing was severely overloaded last year. The plant operates eight hours per day, five days per week, and 50 weeks per year. Management prefers a capacity cushion of 20 percent. Two major types of products are routed through the milling machine. The annual demand for product A is 4000 units and 3000 units for product B. The batch size for A is 20 units and 30 units for B. The standard processing time for A is 0.5 hours/unit and 0.8 for B. The standard setup time for product A is 2 hours and 8 hours for product B. How many new milling machines are required if Fred's does not resort to any short-term capacity options? 4. Fast Lub operates fast oil change. The shop is open for 12 hours per day 6 days of the week all through the year. The shop has two stations, one is drain and inspect and the other is fill and finish. The drain station can handle 10 cars per hour and the fill station can handle 15 cars per hour. The estimated demand for the next quarter is given below as number of cars per day. Day: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Demand 80 100 120 150 175 200 Additional equipment at a cost of $20,000 can increase the capacity of the drain station by 10 cars per day. Each oil change generates $5 before tax towards profits and overhead. Determine the pre-tax cash-flow per quarter. What is the pay-back period in number of quarters for the capital improvement project? 5. A company desires to locate a new facility. Based on preliminary analysis, the choice has been reduced to four locations: A, B, C, and D. These four locations were rated on a scale from 1 worst to 10 best on each of four criteria. Each criterion was also weighted to indicate its importance (i.e., the higher the weight, the more important). The list of ratings and weights follows. Factor Weight Wages 0.40 Labor climate 0.35 Local regulation 0.15 Weather 0.10 6. A 7 6 3 2 Location B C 5 3 5 9 4 3 8 6 D 5 5 2 9 A company has determined the "demand points" and their relative locations as follows: Demand Points A B C D X-Coordinate 10 21 15 21 Y-Coordinate 11 18 12 15 Load 150 150 200 250 a. If a company desires to locate a manufacturing facility at the center of gravity, what would be the x- and y-coordinates of the facility? b. If a facility were to be located at (15, 15), what would be the load-distance score? (Assume rectilinear distance) c. If a facility were to be located at (15, 15), what would be the load-distance score? (Assume Euclidean distance) 7. The operations manager has narrowed down her search for a new plant to three locations. Fixed and variable costs follow: Fixed Costs Variable Costs Location Per Year Per Unit A 70,000 25 B 120,000 22 C 250,000 17 Plot the total cost curves in the chart provided below, and identify the range over which each location would be best. Then use break-even analysis to calculate exactly the breakeven quantity that defines each range. 8. Foster Generators has three plants and four distributions centers. Production capacity over the next three months and the demand forecast for three months at the distributions are given in the following table. The table also gives transportation cost per unit. Distribution center Boston Chicago Cleveland 3 2 Bedford 7 5 York 2 5 Demand 6000 5000 St. Louis 7 2 4 4000 Lexington 6 3 5 2000 Plant Capacity 5000 6000 4000 a. Develop an LP model for the least cost transportation schedule for this problem. Determine the optimal solution. b. Suppoe that Foster is considering building a new plant. Two possible locations, Richmond and Pittsburgh, are under consideration. Assume the fixed cost is about the same for both the locations. The transportation cost and capacity are as given below. Distribution center Boston Chicago Richmond 4 5 Pittsburgh 2 5 St. Louis 3 3 Lexington 6 1 Plant Capacity 2000 2500 Develop an LP model to determine where the new plant must be located. What is the corresponding transportation schedule and cost? 9. A firm of six departments has the following trip matrix and current block plan of all departments: Dept. Name A B C D E F Closeness Rating A B C D --- E F 7 8 9 0 2 --- 6 3 0 10 2 12 0 --- 3 0 --- --- 6 --- A B C D E F a. What is the load-distance score for the current layout? b. Prepare a new plan based on the trip matrix given above and determine the loaddistance score for the layout? (Assume rectilinear distance and that the distance between departments A and B is one unit of distance.) U U A - U E U X - U I E U A - 7. Shipping 6. Inspection O I - 4. Painting A - 3. Machining - 5. Assembly 1. Material Storage 2. Forming 3. Machining 4. Painting 5. Assembly 6. Inspection 7. Shipping 2. Forming A firm has 7 departments. The REL chart is given in the following table. 1. Material Storage 10. A U U U U E - Shipping department has an absolute location as shown in the following chart. Develop a block plan and compute the ALDEP score using the scores described in class. 7 11. Balance the assembly line using the information below, and the longest work-element time rule. The desired output is 240 units per day. Available production time per day is 480 minutes. Determine the idle time, efficiency, and balance delay for the balanced assembly line? Work Element A B C D E F G Time (Sec.) 35 40 55 55 65 40 35 Immediate Predecessor(s) ----A B B C,D D,E Answers: 1. 40 weeks, 0.81 2. Path A-C-F-I A-D-G-I B-D-G-I B-E-G-I B-E-H Project time Crash cost Total crash cost Completion time 31 25 26 27 27 31 A by 3 28 22 26 27 27 28 18 18 I by 1 27 21 25 26 27 27 7 25 C by 1 E by 1 26 21 25 25 26 26 17 42 C by 1 H by 1 25 21 25 25 25 25 19 61 . (a) Min Z = P s.t. YA = 7 – XA YB = 8 – XB YC = YA + 9 – XC YD > YA + 8 YD > YB + 8 YE = YB + 9 – XE YF = YC + 10 – XF YG > YD + 5 YG > YE + 5 YH = YE + 10 – XH YI > YF + 5 – XI YI > YG + 5 – XI XA < 3 XB < 3 XC < 2 XE < 1 XF < 2 XH < 2 XI < 1 P > YH P > YI Xi, Yi, P > 0, for i = A, .., I Solver solution: P = 23 (b) Min Z = P s.t. YA = 7 – XA YB = 8 – XB YC = YA + 9 – XC YD > YA + 8 YD > YB + 8 YE = YB + 9 – XE YF = YC + 10 – XF YG > YD + 5 YG > YE + 5 YH = YE + 10 – XH YI > YF + 5 – XI YI > YG + 5 – XI 6XA + 8XB + 15XC + 2XE + 17XF + 4XH + 7XI < 65 Xi, Yi, P > 0, for i = A, .., I XA < 3 XB < 3 XC < 2 XE < 1 XF < 2 XH < 2 XI < 1 P > YH P > YI Solver solution P = 24.8 (c) Min Z = 6XA + 8XB + 15XC + 2XE + 17XF + 4XH + 7XI YA = 7 – XA YB = 8 – XB YC = YA + 9 – XC YD > YA + 8 YD > YB + 8 YE = YB + 9 – XE s.t. 3. 4. XA < 3 YF = YC + 10 – XF XB < 3 YG > YD + 5 XC < 2 YG > YE + 5 XE < 1 YH = YE + 10 – XH 2 I = FA,< .., YI > YF +X5i,–YXi,I P > 0, for i X YISolver > YG +solution, 5 – XI Cost = 61XH < 2 4 10.26 5. Factor Weighted Score Weight Location B C A 5.55 5.15 5.40 D 4.95 Location A would be the best using this method. 6. a. x* = 17.20, y* = 14.00; 7. Break-even, first crossover point Break-even, second crossover point 8. (a) Excel solution: z = 32,000 (b) Excel solution: z = 35,000 9. 109, 87 A C E D B F b. 4800; c. 4067 16,667 (A vs. B) 26,000 (B vs. C) XI < 1 P > YH P > YI P < 25 10. ALDEP score = 37 7 11. 4 3 1 6 2 5 Cycle time = 120, Idle time = 155, Efficiency = 67.71, Balance delay = 32.29 At maximum capacity, cycle time = 105, Idle time = 95, Efficiency = 77.38%, Balance delay = 22.62%