Recruit and Select Personnel Notes
advertisement

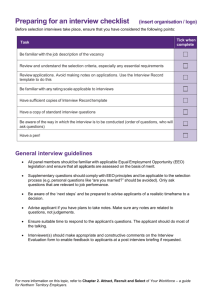
Recruit and Select Personnel The information provided here was accessed from the Flexible Learning Toolbox Retail Management. Toolbox 314 Introduction The task of a retail manager is to maximise sales by making the most productive use of all available resources. These resources include the: operational budget merchandise sales area staff store policies and procedures Each resource has a valuable contribution to make to the store's profitability. When you consider that for many retailers the major expense is staff, you see how important it is to use this particular resource wisely. This is why strategic HRM is crucial to the store's long term profitability. A key activity in this strategy is recruiting skilled people. The recruiting process usually produces a number of applicants whose qualifications must be assessed against the requirements of the job. Making a selection from these applicants is a major function of HRM. Human Resource Planning A central element of strategic HRM is planning the organisation's staff requirements by the number of people required and the skills they must have. Essentially it means estimating the current and future staff needs by ensuring that you have: the right staff, in the right place, at the right time and cost. There are three key points to consider here: 1. 2. 3. HR planning is designed to place the right number of people in the right place at the right time at minimum cost. HR planning is concerned with ensuring that staff levels are in line with customer service requirements. HR planning provides guidelines. The Manager/Supervisor uses the guidelines to make the best decisions. HRM Policies and Procedures Each organisation has its own process for planning their Human Resources needs. What started out as simply 'hiring and firing' has developed into an important strategic planning unit with most businesses. Some large organisations have whole departments dedicated to HR Planning and they use sophisticated technology to plan the future direction of the company. HRM is a complex process due to the continuing flexibility of the economy and its impact on consumer spending and business activity. HRM practitioners must be able to predict the organisation's demand for workers in a similar way as retail buyers predict consumer demand, the only difference is HR managers decide how many staff and what characteristics they should have rather than product related decisions. Factors that the HR manager needs to consider when developing a strategic plan include : the state of the labour market current legislation government policies education and training trends up coming retirements current technology the company's profit targets Staff Planning It's important to consult with relevant staff members when planning to identify their particular staffing needs. Before developing a schedule, ask the following questions: 1. What will be the volume of sales and transactions? 2. When will those sales and transactions be achieved? 3. How many sales people will be needed to service that volume of business at that time? The main aim of planning is to ensure that the store has the right number of suitably skilled people to ensure that the organisation achieves its objectives. If HR planning is to be of any use it should not be done in isolation. It must: be linked to the company's goals be part of an integrated strategy involve all supervisors that will be affected by the decision be supported by higher levels of management be based on two way communication between the HR manager and all line managers. Seeking the Views of Relevant Personnel To develop an accurate job specification talk to the people that actually do or supervise the job. These people know first hand exactly what the requirements of the position are. As the managers are most likely to be affected by the decisions, their input is invaluable and it should be encouraged. Information you should obtain includes: what qualifications are typical of people in this role? what experience is required of people who are successful in this role? Identifying HR Needs When identifying the HR needs of an organisation it is essential that the activities of the company are identified and analysed. This gives a clear indication of the skills and knowledge that current employees have and where any skills gaps exist in the company. A central activity in this process is the job analysis. The information gleaned from this process is used to develop a number of useful HR planning tools. Job Analysis A job analysis is a systematic attempt to break a job down into its component parts. For example, if using the term "customer service", there are a number of component parts: product knowledge selling skills knowledge of stock locations knowledge of company returns procedures knowledge of delivery and other services In a job analysis, the manager must determine the nature of the job. The focus is to determine what tasks, duties and responsibilities are associated with the job. A job analysis requires the answers to the following questions: what is to be done? how is it to be done? why is it done? It also examines the relationship of the job to other positions in the store, the conditions that the job is performed under and the personal qualities of the person doing the job. Below is a typical job analysis process. The information collected during the job analysis also helps the HR manager to: Develop staffing plans Establish if there is a need to recruit additional staff Clarify the relationship of each position in the organisation. Methods of Job Analysis There are two basic methods of conducting a job analysis. The approach taken will influence the type of information that will be collected. The two approaches are: Job or task focus Employee or behaviour focus Job Focus If a job focus is used in job analysis, the information collected will centre on what tasks are done, the responsibilities of the position and any responsibilities that the person has. Employee Focus If an employee focus is used, the information collected will centre on the human behaviour that is used to get the job done. This method identifies any skills or qualifications that the person doing the job would require to be successful. Which Method is Best? Generally, both methods are used in combination to arrive at a detailed picture of the position's requirements. To do this effectively you must be aware of the stores trading trends. For example, when the store is open, quiet or busy. The other side of this question is how many people should be available to assist customers in quiet times? While fixtures have to be filled and housekeeping duties completed, there is a limit to how many people can be involved in these activities at the same time. Confirming the Specification Ensure that you talk to the relevant staff to ensure that your job description and specification accurately reflects the job. The aim is to get their feedback and comments on your job description and specification. People worth talking to include: The employee who is actually performing the job The supervisor or manager Human resource manager From the job analysis, a number of documents are created by the HR manager. These include a: Job description Job specification Job Descriptions Before you can recruit appropriately skilled workers you must identify what skills and knowledge they need to do the job effectively. This is usually done by developing a job description first. A job description defines the key objectives, responsibilities and tasks associated with the job. This document is used to help supervisors and the person doing the job to understand what is expected. It is a useful document to refer to when recruiting new employees, conducting performance appraisals and disciplinary interviews. While, there is no standard format, a typical job description would resemble this example: Job Specification A job specification is developed from the information in the job description. This document focuses on the personal characteristics and qualifications that the person doing the job should have. It usually outlines the specific skills, education and experience needed to perform the job. The job specification identifies the criteria for evaluating applicants during an interview. A job specification may be in the job description document or it may be a separate document. While, there is no standard format, a typical job specification would resemble this example: When developing your job description and specification it is important to be aware of the impact of equal opportunities and anti-discrimination legislation as well as any relevant industrial relations requirements. Staff Selection & EEO According to the Federal Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission Act (HREOCA), discrimination happens when a person is treated less favourably than others on the grounds of their: gender marital status pregnancy parental status sexual preference age race nationality religion physical impairment political belief or activity trade union activity The Federal Sex, Race and Disability Discrimination Acts, administered by the Federal Human Rights Commission, apply when your State or Territory's equal opportunity and anti-discrimination laws do not provide for these categories. Developing Selection Criteria An effective job analysis can provide the background information for the selection criteria used to recruit new staff. When developing a selection criteria: Ensure the job specification is consistent with the job requirements The selection criteria should be consistent with the job specifications and only include skills that are required to be carried out on a regular basis Distinguish between essential criteria and desirable criteria Establish if formal qualifications are essential to the job Ensure the amount of experience required is justifiable for effective performance Ensure there are no unnecessary English language qualifications on the job that may not be required to do the job Be specific with communication skills necessary Determine how criteria will be assessed: interview, referees report, work record, testing etc Job Description and EEO When writing the job description and specification it must be consistent with the job analysis and comply with EEO requirements. It is particularly important not to: Include certain skills or physical requirements in the job description where the job analysis does not support the need. For example, stating that the person must be able to lift 80 kgs when they will only be working at the sales counter, list extensive experience required for the position unless it is necessary to do the tasks associated with the job. Base the job specification and/or description on your personal opinion when the job analysis does not support that opinion. EEO and Job Application Forms It is essential that the company's job application forms do not breach EEO requirements. To achieve this, many companies use a standard application form. This is a useful practice because it ensures that the same information about each applicant is collected and used as the benchmark for short listing applicants. The application form should: Contain language that is relevant to performing the job not include invasive or irrelevant questions be designed to avoid discrimination be treated with strict confidentiality. When developing an application form, there are some questions that are illegal to ask. These include: Marital Status. The applicant cannot be asked about their family situation. However, they can be asked if they are willing and able to be transferred, to travel, work overtime if this is a requirement of the position Ethnic Origin. The applicant cannot be asked about their birthplace, nationality or first language. Relatives. The applicant cannot be asked the names, addresses or relationship to relatives. They can be asked to supply emergency contact details after they have been employed. Photographs. The applicant cannot be asked to provide a photograph unless the job involves modelling, acting or similar activities. Organisations. The applicant cannot be asked about any clubs or organisations that they belong to. Criminal Record. The applicant cannot be asked to supply details of any criminal record on the application form unless it is relevant to the job. They may be asked at the interview however. The only information that can be requested on an application form is information that will help you determine if the person can do the job. The application should however include information relating to: name of applicant, address and phone number for contact education and qualifications employment experience referees Recruitment Policy Effective recruitment is an essential part of HRM planning. Once a need for additional staff is identified, the recruitment process is activated to address this need. For recruitment to be successful, all jobs within the organisation must be clearly defined. In addition, the skills of current staff must also be known. When conducting a recruitment drive it's important to remember that the company's image is at stake. Therefore, the process should be handled in an open and honest manner, though the applicants are unsuccessful, they may still be customers of your store. There are two main pools of potential candidates that the HR manager can draw new staff from: Internal sources External sources Internal Sources Many companies believe that promoting from within the company is the most effective recruitment policy. This policy sees existing staff promoted into the higher level, vacant position and a new employee is recruited from outside the company to fill the lower level position. This strategy has both advantages and disadvantages. Advantages Candidates are well known to the company Candidates know the company and its policies Employees are generally more motivated if there is a possibility of future promotion The company receives the benefits of training staff Disadvantages Staff may be promoted beyond their abilities 'Inbreeding' can reduce creativity within the company Infighting may happen as employees push to be promoted Staff morale may decline if employees are not promoted External Sources There are many external sources that can be used to recruit new employees: advertising in newspapers and/or industry journals using an employment agency contacting educational institutions staff referrals unsolicited resumes The effectiveness of each source largely depends on the state of the economy and the local pool of skilled workers. Like the internal recruitment sources, external sources also have advantages and disadvantages. Advantages There is a larger pool of candidates to draw from New people often bring new ideas into the company New employees do not belong to political 'clicks' in work groups It is often less expensive and faster to recruit from outside sources Disadvantages Orienting the new employee takes longer than an existing employee Existing employees may resent being passed over for promotion The new employee's attitudes and skills may not suit the company's culture Finding a suitable employee may not be an easy task. The Selection Process Selecting someone for a job is a difficult task that requires careful consideration. The process must be fair and the type of process used will depend on the nature of the job. It is unlikely that a single interview will be enough to select a Store Manager but it may be sufficient for recruiting sales assistants. The selection process should be documented so it is clear how the process was conducted. While, the actual selection process will vary from company to company, the basic process is very similar. In each case the aim is to identify the most suitable candidate(s) to be interviewed. Weighted Application Forms To address EEO requirements, a weighted application form is recommended. This type of form encourages the interviewer to score the candidates application on its merit against important criteria related to the job rather than using their own subjective judgement. Developing a weighted application form involves identifying the relationship between the specific tasks and their importance to the position. A score is then assigned to each criteria based on its level of importance. The candidate's responses are then scored against the weighting. The candidates with the highest score are then judged to be the most suitable people for the position and are short listed for interview. This method of selection is predictive of the most likely candidates that will be able to do the job effectively. Processing Applications Effectively processing applications is a critical aspect of the recruitment process. If a business does not have the right people, it can affect the store's ability to operate effectively. Depending on the position, it is important to fill any vacancies as quickly as possible without rushing through the process. It is essential to find a balance between quickly filling a position and hastily hiring an unsuitable candidate. Short Listing Short listing enables you to rank all of the applications in order of merit. This ranking is then used to identify a number of suitable candidates to interview. The weighted application form can be a valuable tool for identifying the most suitable candidates. When short listing applicants: base your decisions on essential criteria first then on desirable criteria Don't make assumptions about: o qualifications or experience o if applicants could handle a particular situation o how current employees or customers may react to them Obtain more information from the candidate if necessary Aim to find the best person for the job Use a consistent method to evaluate each applicant Document the decisions made and reasons for them Effective recruitment aims to minimise the possible mistakes and unnecessary costs that can happen if the process is not handled well. The effectiveness of the interview and selection processes are heavily influenced by the accuracy of your short listing decisions. Conducting an Interview The face to face job interview is the most widely used selection tool for two key reasons: 1. 2. it is relatively inexpensive compared with alternative specialised selection methods, for example executive search consultants, many people feel a strong need to meet and talk with potential employees to get to know them before appointing them. Interview Methods There are many variations of the interview process that can be used depending on the position and the company's approach to recruitment. They can be either structured or unstructured using a selection panel or a single interviewer. Unstructured Interviews This type of interview is generally an informal discussion between the interviewer(s) and the candidates. Because there is no format to the interview it has a tendency to wander from topic to topic without collecting enough relevant information to make an informed selection decision. One major draw back with this method is the difficulty justifying a selection decision if it is challenged because the information collected from each applicant can vary. Structured Interviews In the structured interview process, the interviewer(s) ask each candidate the same specific questions. Their responses are then weighted and scored against a set of criteria. There is little (if any) deviation from the structured format. This method is the most likely to provide a fair comparison of the candidates if it is conducted well. Panel Interviews A panel interview is conducted by a number of people (usually two or three people from management roles) as a group. The benefit of this method is that it allows the interviewers to evaluate the candidate's responses to the same questions, at the same time. It also reduces the potential for personal bias to influence the final selection decision if only one person conducted the interviews. While, it is a more expensive process, it can produce more thorough results to base the final selection on. Interview Steps To conduct an effective interview: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Know the job requirements so the most suitable and capable person is selected Know the personal attributes, experience, skills and qualifications that the most appropriate person should have Have specific objectives for the interview. Know what additional information (from that supplied in the application) you need to make an informed decision Conduct the interview in a suitable venue. It should be comfortable and free from distractions Review each application before the persons interview to identify employment gaps, inconsistencies, frequent job changes etc. Don't allow your personal prejudices to influence your decision or behaviour during the interview Make an effort to put the candidate at ease in the early stages of the interview Keep control of the interview by directing the candidate to the subjects you need to cover Encourage the candidate to do most of the talking. This helps you to gather the information you need to learn as much as you can about the candidate Explain the job, its responsibilities, salary and conditions Give the candidate the opportunity to ask questions Close the interview in a friendly manner and tell them when they can expect an answer Using the notes you took during the interview, write up your report as soon as the interview is over. This reduces the chance of forgetting important information or confusing information from one candidate to another Above all, be prepared for the interview. You are the public face of the company in this situation and successful or not, the candidates could still be customers of your store. Interviewing & EEO Whichever method you select, it is important to ensure that the actual process and particularly the questions you use comply with EEO requirements. Consider the following guidelines: If possible allow applicants to demonstrate what they can offer the organisation. Don't conduct the interview simply to confirm your expectations or to see how the applicants perform under pressure§ Check beforehand if there is a need for any specific arrangements eg; physical access, interpreters etc Have your questions prepared in advance Make sure there is consistency and fairness in your questioning Focus on the needs of the job. Don't stereotype the applicants If an applicant is asked if they can meet the job's requirements (for example travel, or overtime) all applicants must be asked It is appropriate to ask people with disabilities, if they need any adjustments to perform the job Allow the candidate enough time to make their point. Listen actively and clarify their response if necessary Don't make assumptions about a person's ability to do the job based on their physical characteristics Do not ask invasive and irrelevant questions Keep a record of each interview that includes the questions asked and the answers given by each candidate Interview Rating Sheets An interview rating sheet is used to score the responses that each candidate gives against a predetermined criteria and weighting. When developing an interviewing rating sheet consider the job in terms of essential and desirable skills or attributes. Essential criteria must be met and there can be no compromise. Desirable criteria are skills or attributes that would be nice to have. Using this sheet makes the decision process more transparent and fair because candidates without the essential criteria can be immediately excluded and those with the most desirable can be included. A sample interview rating sheet is shown below. Applicant Testing Some companies also request applicants to take specific tests. These vary and should be administered by people qualified to do so. If testing is used it is important to ensure that: tests match the requirements of the job tests are relevant to the job requirements Referee Reports There is much debate over the value of references and referee reports. Your store is likely to have its own policy and attitudes towards them. The approach you take and weight you give to them will depend on this policy. As a general rule, be consistent in your use of referees to rate applicants. Ideally use a standard referee reporting form that matches the selection criteria. This will assist in maintaining a common weighting to all referee reports. Making the Decision When making a decision on which candidate is the most suitable for the position it is important to ensure that it observes EEO legislation and follows the store's policy. Your decision should be based on the selection criteria by: Ranking all applicants according to how they scored on the essential and desirable criteria Assessing all the information that the candidate has provided Recording your decisions and the reasons for them Avoiding value judgements Ensuring that your applicant assessment is kept confidential Providing constructive feedback to unsuccessful applicants on request Informing Candidates All candidates for a position should be promptly informed about the status of their application. This is very important if the recruitment process is expected to take a number of weeks. This notification is usually done in writing and should use language appropriate to the situation. A typical notification process would be: 1. 2. 3. 4. a card is sent to all applicants notifying them that their application has been received and is currently being processed applicants are telephoned and informed of their interview date, time and place if successful the successful applicant is given a letter of appointment unsuccessful applicants are sent a letter informing them that they have been unsuccessful Notifying Unsuccessful Candidates Your store is likely to have a defined procedure for contacting unsuccessful applicants. You should follow this process to the letter. In no procedure exists it is important to remember that the unsuccessful applicant will be disappointed, and your organisation may well be judged by the approach taken. Its advisable to take a professional approach to this delicate task. Contacting the Successful Candidate When you contact the successful candidate it is important to remember to establish a professional relationship from the beginning. Your offer of employment should include the: Hours of duty Salary and conditions Start date and time Contact person Additional documents (if any) that they should bring with them Whether you are contacting the successful candidate to offer them the position or notifying unsuccessful candidates it is essential to ensure that you establish and maintain your store's image as a professional retailer. Offering Wages and Conditions During the recruitment process it is crucial that the wages and conditions of employment you offer a candidate comply with the relevant award or enterprise agreement and the store's policy. Depending on your position in the organisation, it is unlikely that you will have much to do with establishing the award/agreement conditions that apply to your team. This is generally the responsibility of the HR manager. However, it is important to be aware of the award/agreement that applies to the position you are recruiting for. At the interview, the candidates will want to know the terms and conditions that apply to the position. It is worth remembering that if the candidate is currently employed, they are likely to be making a comparison of their current position and the one you are offering when they make their decision to accept or reject your offer of employment. A sound knowledge of the position's terms and conditions will enable you to answer the candidate's questions in a professional manner. Recruitment Records Any records relating to the recruitment process should be kept in a secure and confidential place. These records may include the job analysis findings job descriptions job specifications interview Rating Sheets all applicant files for a specified period response and success rate for different recruiting methods used In addition to recruitment, the human resource manager must keep a number of specific records related to the management of the human resource function. While confidentiality and security must be maintained HRM records must be readily available to authorised personnel Access to Personnel Records A good HRM tracking system is based on the level of information it collects and records. This raises the question of who should be able to access this information and for what purpose it will be used. HRM records provide valuable information in situations such as... paying appropriate salaries based on existing skills staff performance appraisals and career planning being used as supporting evidence in a legal dispute. Confidentiality It is important to treat all personnel records with a high degree of confidentiality. Your store should have a firm policy on collecting, storing and accessing personnel data and how it should be protected. This policy and its associated procedure should be based on legislation like the: Privacy Act (1988) Privacy Amendment Act (1991) Freedom of Information Act (1982) Relevant state laws. HRM Records and Industrial Disputes Any industrial disputes that occur in the workplace should always be recorded, for two reasons: 1. If an industrial problem has led to a dismissal the records provide evidence that the correct procedure was used, as per industrial relations legislation. 2. They provide valuable information when you conduct a performance appraisal.