Economics Name: Ms. Stern Price Controls: Quiz Your Knowledge 1
advertisement

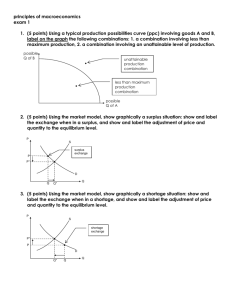
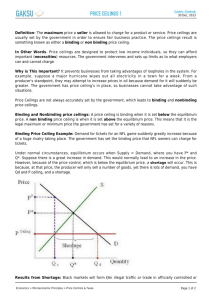
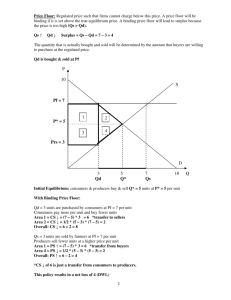
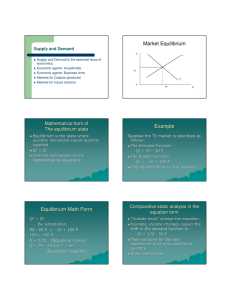
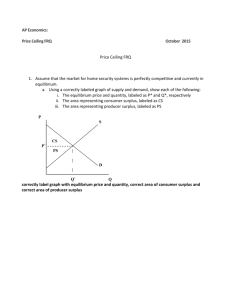
Economics Ms. Stern Name: Price Controls: Quiz Your Knowledge 1.) If a price ceiling above the equilibrium price is imposed on gasoline, which of the following will result? a. There will be a surplus of gasoline. b. The quantity demanded will exceed the quantity supplied. c. The quantity supplied will exceed the quantity demanded. d. The quantity of gasoline demanded will equal the quantity of gasoline supplied. Answer: D 2.) A shortage in the market would result when a. A price ceiling is below the equilibrium price. b. A price ceiling is above the equilibrium price. c. A price ceiling is equal to the equilibrium price. d. Government repeals a price ceiling. Answer: A 3.) Which of the following is an example of a price floor? a. Rent controls on apartments b. Price controls on gasoline in the 1970s c. A law that does not allow lenders to charge a rate of interest above some legally set maximum d. A law stating that milk cannot sell for less than $3 per gallon Answer: D 4.) What would be the result of the price ceiling of $12? a. A shortage of 10 units b. A surplus of 10 units c. Falling market prices moving toward a rising equilibrium price d. The market would be in equilibrium Answer: D 5.) Which of the following is not an example of a price floor? a. A minimum wage law b. Dairy price supports c. Price controls on gasoline in the 1970s d. A legal price intended to maintain prices above the equilibrium price Answer: C 6.) If government sets a price floor of $16 in the market shown in the diagram, the result would be a. A surplus of 40 units b. A surplus of 20 units c. A shortage of 40 units d. A shortage of 20 units Answer: A 7.) If government sets a price ceiling of $8 per unit in the market illustrated in the diagram, the result would be: a. A shortage of 20 units b. A shortage of 10 units c. A surplus of 20 units d. A surplus of 10 units Answer: A 8.) A price ceiling is a. A legal maximum price at which a good can be sold. b. A legal minimum price at which a good can be sold. c. Typically equal to the equilibrium price of a good. d. A price set by government that varies with market conditions. Answer: A 9.) A wage is the price for labor. A minimum wage set above equilibrium wage would be an example of a. A price ceiling. b. A price floor. c. A gap in prices or wages. d. A wage settlement. Answer: B 10.) The effect of rent controls in areas such as Berkeley, California and New York City has been a. To increase the supply of housing. b. To reduce the quantity of housing supplied. c. To increase the vacancy rate. d. To encourage construction of apartment buildings. Answer: B 11.) a. b. c. d. If a price ceiling is placed on the market at $4, The market will quickly clear. Nothing will happen. A shortage of 10 units will result. A shortage of 15 units will result. a. b. c. d. The shortages of gasoline that occurred in the 1970s were partly a result of Government price ceilings on gasoline. Government price floors on gasoline. Government refusing to regulate the market for gasoline. Government repealing price ceilings on gasoline. Answer: C 12.) Answer: A 13.) Suppose that a regulation is in place that does not allow the price of a good to exceed $5. If this price is above the equilibrium price in the market, this would be an example of a a. Binding price ceiling. b. Not binding price ceiling. c. Binding price floor. d. Not binding price floor. Answer: B 14.) Suppose that a regulation is in place that does not allow the price of a good to fall below $10. If this price is above the equilibrium price in the market, this would be an example of a a. Binding price ceiling. b. Not binding price ceiling. c. Binding price floor. d. Not binding price floor. Answer: C 15.) Suppose that a regulation is in place that does not allow the price of a good to exceed $5. If this price is below the equilibrium price in the market, this would be an example of a a. Binding price ceiling. b. Not binding price ceiling. c. Binding price floor. d. Not binding price floor. Answer: A 16.) a. b. c. d. If a price floor is in place and it is binding, the market will Remain in equilibrium, unaffected by the price floor. Experience a shortage. Experience a surplus. Adjust its equilibrium point toward the price floor. a. b. c. d. If a price ceiling is in place and it is binding, the market will: Remain in equilibrium, unaffected by the price floor. Experience a shortage. Experience a surplus. Adjust its equilibrium point toward the price floor. Answer: C 17.) Answer: B 18.) Price controls are usually enacted a. As a means of raising revenue for public purposes. b. When policymakers believe that the market price of a good or service is unfair to buyers or sellers. c. When policymakers detect inefficiencies in a market. d. All of the above are correct. Answer: B 19.) a. b. c. d. Answer: C Price controls Always produce an equitable outcome. Always produce an efficient outcome. Can generate inequities of their own. Produce revenue for the government. 20.) Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the imposition of a price floor in the market for corn? a. Policymakers have studied the effects of the price floor carefully, and they recognize that the price floor is advantageous for society as a whole. b. Buyers and sellers of corn have agreed that the price floor is good for both of them and have therefore pressured policy makers into enacting the price floor. c. Buyers of corn, recognizing that the price floor is good for them, have pressured policy makers into enacting the price floor. d. Sellers of corn, recognizing that the price floor is good for them, have pressured policy makers into enacting the price floor. Answer: D