Larry A. Ryle High School
advertisement

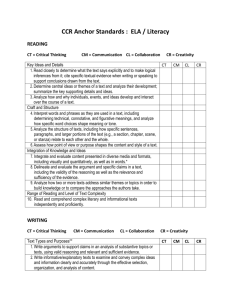
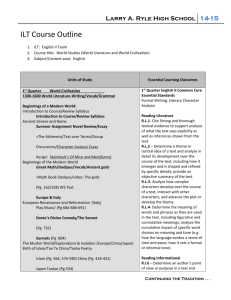
Larry A. Ryle High School 14-15 ILT Course Outline 1. ILT: English II Team 2. Course title: English II 3. Subject/Content area: English Units of Study 1st Quarter Unit 1: Character Analysis, Major Overview of Literary Devices, with Emphasis on Theme and Thesis construction Major Works The Alchemist by Paulo Coelho The Metamorphosis of Narcissus painting by Salvador Dali Narcissus and Echo Critical Essay by Michelle Mariorenzi The Myth of Narcissus Writing: Character Analysis and Literary Analysis Unit 2: Ancient Greek History in relation to World Literature (Greek Tragedy), Recognizing Paradox, Irony, Imagery, Symbolism, & Motifs. Deconstructing and Writing Greek poetry. Major Works Oedipus Rex by Sophocles Antigone by Sophocles Informational Background Reading over Greek Mythology “Ode on a Grecian Urn” poem Writing: Lyric Meditative Ode Essential Learning Outcomes Quarter 1 Formal Writing: Character Analysis Essential Standards Reading Literature R.L.1- Cite Strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. R.L.2 – Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze in detail its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text. R.L.3- Analyze how complex characters develop over the course of a text, interact with other characters, and advance the plot or develop the theme. R.L.4- Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text, including figurative and connotative meanings; analyze the cumulative impact of specific word choices on meaning and tone (e.g. how the language evokes a sense of time and place; how it sets a formal or informal tone). Reading Informational R.I.6 – Determine an author’s point of view or purpose in a text and analyze how an author uses rhetoric to advance that point of view or purpose. Writing W.1 –Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence. W.9 - Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Speaking & Listening SL.1- Initiate and participate effectively in a range of collaborative discussions with diverse partners on grades 9-10 topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively. SL.4- Present information, findings, and supporting evidence clearly, concisely, and logically such that listeners can follow the line of reasoning and the organization, development, substance, and style are appropriate to purpose, audience, and task. Language L.1- Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. L.2- Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. Continuing the Tradition . . . Larry A. Ryle High School 14-15 2nd Quarter Unit 3: Excerpts from King Arthur – characterization, symbolism with the code of chivalry. Allegory in the Middle Ages, Emphasis on symbolism and metaphor. Major Works Excerpts from King Arthur Excerpts from Cantos within Dante’s Inferno Background Informational Reading on Dante Writing: TBD Unit 4: Major Themes in Shakespeare, Comparing a Greek Tragedy to a Shakespearian Tragedy. Emphasis on mood, verse, rhyme scheme, and rhythm. Major Works Macbeth by William Shakespeare The Macbeth Murder Mystery by James Thurber Unit 5: Macbeth & Research. Complete the research process as a scaffold from the senior research paper. Reliable Sources Source Cards Note Cards MLA Format MLA Outline MLA Citations Writing: Mini Research Paper (3-5 pages) Quarter 2 Formal Writing: Research Essential Standards Reading Literature R.L.2 – Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze in detail its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text. R.L.5- Analyze how an author’s choices concerning how to structure a text, order events within it, and manipulate time create such effects as mystery, tension, or surprise. Reading Informational R.I.1- Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. R.I.2- Determine a central idea of a text and analyze its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text. R.I.5-Analyze in detail how an author’s ideas or claims are developed and refined by particular sentences, paragraphs, or larger portions of a text Writing W.2- Write informative /explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas, concepts, and information clearly and accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content. W.5- Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. W.6- Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. W.8- Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assesses the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas; avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. Language L.1- Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. L.2- Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. L.3- Apply knowledge of language to understand how language functions in different contexts, to make effective choices for meaning or style, and to comprehend more fully when reading or listening. Continuing the Tradition . . . Larry A. Ryle High School 14-15 3rd Quarter Unit 6: Ethical Principles in The Great Depression, Justice and Unjust Laws Major Works To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee “Strange Fruit” (song) Billie Holiday To Kill a Mockingbird Movie Writing: Trial Notes and Depositions, Students will present a live court room trial Quarter 3 Formal Writing: Literary Analysis Essential Standards Reading Literature R.L.1- Cite Strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. R.L.2 – Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze in detail its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text. R.L.3- Analyze how complex characters develop over the course of a text, interact with other characters, and advance the plot or develop the theme. R.L.4- Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text, including figurative and connotative meanings; analyze the cumulative impact of specific word choices on meaning and tone (e.g. how the language evokes a sense of time and place; how it sets a formal or informal tone). R.L.5- Analyze how an author’s choices concerning how to structure a text, order events within it, and manipulate time create such effects as mystery, tension, or surprise. Writing W.1 –Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence. W.5- Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. W.9.-Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Language L.1- Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. L.5-Make strategic use of digital media in presentations to enhance understanding of findings, reasoning, and evidence and to add interest. Continuing the Tradition . . . Larry A. Ryle High School 14-15 4th Quarter Unit 7: Rhetorical Devices, Persuasive Techniques and Satire. Students will analyze speeches, commercials & ads, and reflect on methods used to persuade. Quarter 4 Formal Writing: Persuasive Speech Essential Standards Major Works Excerpts from Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare A Modest Proposal by Jonathan Swift Assorted clips from “The Simpsons” Assorted song lyrics by Weird Al “Ebay” The Declaration of Independence The Great Debaters Movie Reading Informational R.I.3- Analyze how the author unfolds an analysis or series of ideas or events, including the order in which the points are made, how they are introduced and developed, and the connections that are drawn between them. R.I.4-Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including figurative, connotative, and technical meanings; analyze the cumulative impact of specific word choices on meaning and tone. R.I.8- Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, assessing whether the reasoning is valid and the evidence is relevant and sufficient; identify false statements and fallacious reasoning. Unit 8: Nonfiction Emphasis on Holocaust, exposure to a memoir, cultural/social/ethical conflicts Writing W.1 –Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence. Major Works Night by Elie Wiesel Speaking & Listening SL.2- Integrate multiple sources of information presented in diverse media or formats evaluating the credibility and accuracy of each source. SL.4- Present information, findings, and supporting evidence clearly, concisely, and logically such that listeners can follow the line of reasoning and the organization, development, substance, and style are appropriate to purpose, audience, and task. S.L.5- Make strategic use of digital media in presentations to enhance understanding of findings, reasoning, and evidence and to add interest. S.L.6- Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and tasks, demonstrating command of formal English when indicated or appropriate. Language L.1- Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. L.3- Apply knowledge of language to understand how language functions in different contexts, to make effective choices for meaning or style, and to comprehend more fully when reading or listening. Continuing the Tradition . . .