Chapter 7 Cells - Southgate Schools
advertisement
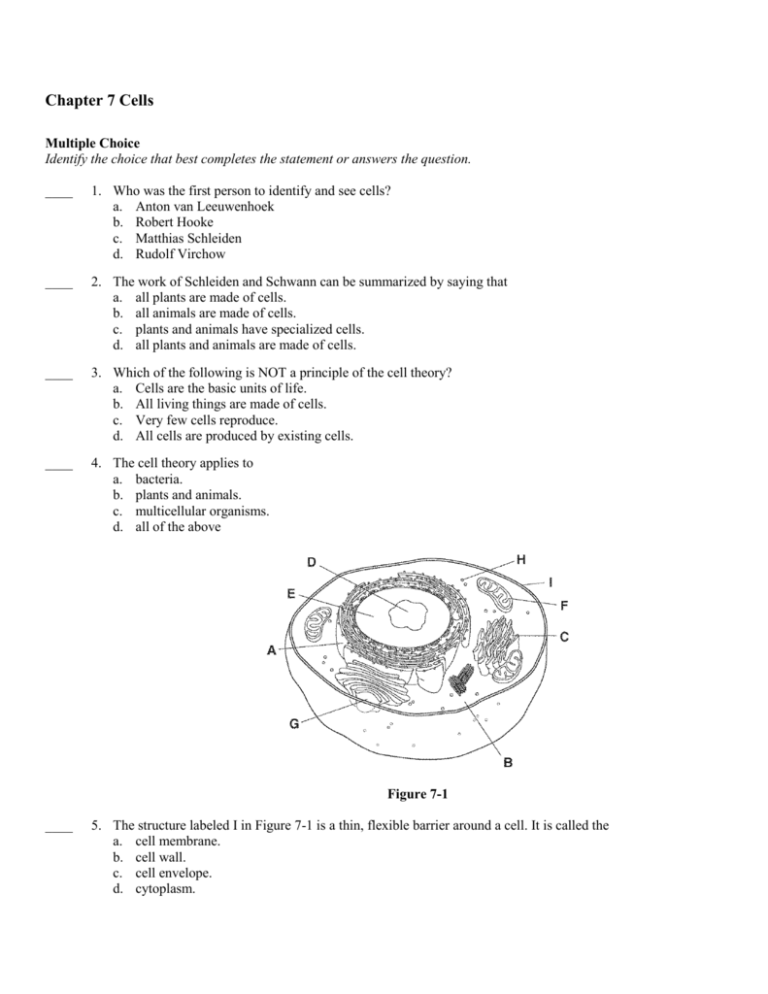
Chapter 7 Cells Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Who was the first person to identify and see cells? a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Robert Hooke c. Matthias Schleiden d. Rudolf Virchow ____ 2. The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by saying that a. all plants are made of cells. b. all animals are made of cells. c. plants and animals have specialized cells. d. all plants and animals are made of cells. ____ 3. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells reproduce. d. All cells are produced by existing cells. ____ 4. The cell theory applies to a. bacteria. b. plants and animals. c. multicellular organisms. d. all of the above Figure 7-1 ____ 5. The structure labeled I in Figure 7-1 is a thin, flexible barrier around a cell. It is called the a. cell membrane. b. cell wall. c. cell envelope. d. cytoplasm. ____ 6. Which cell structure contains the cell’s genetic material and controls the cell’s activities? a. organelle b. nucleus c. cell envelope d. cytoplasm ____ 7. Which structure contains the other? a. nucleus; cytoplasm b. nucleus; genetic material c. cell membrane; cell wall d. prokaryote; organelles ____ 8. Prokaryotes lack a. cytoplasm. b. a cell membrane. c. a nucleus. d. genetic material. ____ 9. Eukaryotes usually contain a. a nucleus. b. specialized organelles. c. genetic material. d. all of the above ____ 10. The main function of the cell wall is to a. support and protect the cell. b. store DNA. c. direct the activities of the cell. d. help the cell move. ____ 11. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is a. found in all organisms. b. composed of a lipid bilayer. c. a flexible barrier. d. made of tough fibers. ____ 12. You won’t find a cell wall in which of these kinds of organisms? a. plants b. animals c. fungi d. none of the above ____ 13. Which of the following is a function of the nucleus? a. stores DNA b. controls most of the cell’s processes c. contains the information needed to make proteins d. all of the above ____ 14. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape b. contains DNA c. surrounds the cell d. helps make proteins ____ 15. Which structures carry out cell movement? a. cytoplasm and ribosomes b. nucleolus and nucleus c. microtubules and microfilaments d. chromosomes ____ 16. Which of the following is an organelle found in the cytoplasm? a. nucleolus b. ribosome c. chromatin d. cell wall ____ 17. Which organelle breaks down food into particles the cell can use? a. Golgi apparatus b. lysosome c. endoplasmic reticulum d. mitochondrion ____ 18. Which organelle makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus b. mitochondrion c. vacuole d. ribosome ____ 19. Which organelle converts food into compounds that the cell uses for growth, development, and movement? a. chloroplast b. Golgi apparatus c. endoplasmic reticulum d. mitochondrion ____ 20. Which organelles help provide cells with energy? a. mitochondria and chloroplasts b. rough endoplasmic reticulum c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum d. Golgi apparatus and ribosomes ____ 21. Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells? a. mitochondrion b. ribosome c. chloroplast d. smooth endoplasmic reticulum ____ 22. Which of the following structures serves as the cell’s boundary from its environment? a. mitochondrion b. cell membrane c. chloroplast d. channel proteins ____ 23. Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? a. breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods b. stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates c. keeps the cell wall in place d. regulates which materials enter and leave the cell ____ 24. The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. bilipids d. proteins ____ 25. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a. an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. b. an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. c. an area of equilibrium to an area of high concentration. d. all of the above ____ 26. Diffusion occurs because a. molecules constantly move and collide with each other. b. the concentration of a solution is never the same throughout a solution. c. the concentration of a solution is always the same throughout a solution. d. molecules never move or collide with each other. ____ 27. When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same, the molecules will a. move across the membrane to the outside of the cell. b. stop moving across the membrane. c. move across the membrane in both directions. d. move across the membrane to the inside of the cell. ____ 28. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? a. diffusion b. osmosis c. facilitated diffusion d. active transport ____ 29. The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called a. osmotic pressure. b. osmosis. c. facilitated diffusion. d. active transport. ____ 30. An animal cell that is surrounded by fresh water will burst because the osmotic pressure causes a. water to move into the cell. b. water to move out of the cell. c. solutes to move into the cell. d. solutes to move out of the cell. ____ 31. Which term refers to cells having different jobs in an organism? a. multicellular b. cell specialization c. levels of organization d. unicellular ____ 32. The cells of multicellular organisms are a. b. c. d. smaller than those of unicellular organisms. simpler than those of unicellular organisms. specialized to perform particular functions. not dependent on one another. ____ 33. All of the following are examples of cell specialization EXCEPT a. a pancreatic cell that produces protein-digesting enzymes. b. nerve cells that transmit messages throughout the body. c. a prokaryotic cell that carries out photosynthesis. d. a red blood cell that carries oxygen. ____ 34. Which of the following is an example of an organ? a. heart b. epithelial tissue c. digestive system d. nerve cell ____ 35. All of the following are types of tissues EXCEPT a. muscle. b. connective. c. digestive. d. nerve. ____ 36. A group of cells that perform similar functions is called a(an) a. organ. b. organ system. c. tissue. d. division of labor. ____ 37. Which of the following is an organ of the digestive system? a. stomach b. nerve tissue c. muscle cell d. epithelial tissue ____ 38. An organ system is a group of organs that a. are made up of similar cells. b. are made up of similar tissues. c. work together to perform a specific function. d. work together to perform all the functions in a multicellular organism. ____ 39. Which list represents the levels of organization in a multicellular organism from the simplest level to the most complex level? a. cell, tissue, organ system b. organ system, organ, tissue, cell c. tissue, organ, organ system d. cell, tissue, organ, organ system 40. Unlike smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum has ____________________ attached to it. a. ribosomes b. Golgi bodies c. mitochondria d. lysosomes Figure 7-2 41. The structure indicated in Figure 7-2 by the letter F is usually larger in ____________________ cells. a. animal b. plant 42. Large molecules such as glucose that cannot cross the lipid bilayer can still move across the membrane with a concentration gradient by _________________________. a. osmosis b. diffusion c. facilitated diffusion d. active transport 43. A hypertonic salt solution has a higher concentration of solutes than a blood cell. Explain what happens when a blood cell is placed in a hypertonic salt solution. a. water enters cell b. water leaves cell USING SCIENCE SKILLS A student put together the experimental setup up shown below. The selectively permeable membrane is permeable to both types of solute molecules shown. Figure 7-4 44. Predicting Describe the movement of the C molecules on side A of the apparatus shown in Figure 7-4. What will happen to these molecules over time? a. the C molecules will stay on the A side b. some of the C molecules will move to the B side 45. Predicting Look at Figure 7-4. Describe the movement of the D molecules over time? a. some of the D molecules will move to side A b. the concentration of D molecules will not change on either side of the membrane 46. Predicting What will the apparatus shown in Figure 7-4 look like when equilibrium is reached? a. it will not change b. there will be equal concentrations of both C and D molecules on both sides of the membrane c. C molecules will be on one side, and D molecules will be on the opposite side USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 7-5 47. Interpreting Graphics Which drawing in Figure 7-5 contains a structure that carries out photosynthesis? What is this structure labeled in the diagram? a. I, F b. II, N c. I, G d. II, O 48. Comparing and Contrasting Look at Figure 7-5. Which structure in drawing I corresponds to structure M in drawing II? What is the name of this structure? a. A - rough endoplasmic reticulum b. D - nucleolus c. H - ribosome d. G - Golgi apparatus 49. Interpreting Graphics Do the drawings in Figure 7-5 represent prokaryotes or eukaryotes? a. prokaryotes b. eukaryotes USING SCIENCE SKILLS The experimental setup below shows an osmometer. An osmometer is a device used to measure the amount of osmotic pressure exerted by a liquid passing through a semipermeable membrane. The graph shows one lab group’s results compared with the results of the rest of the class combined. Line A represents the results of the single lab group. Line B represents the data of the rest of the class. Figure 7-6 50. Analyzing Data Which results in the graph in Figure 7-6 are more likely to be accurate, those represented by line A or by line B? a. line A b. line B Essay - Choose one of the following essay questions to answer. Be sure to write your answer on the paper provided. 51. Compare prokaryotes with eukaryotes. Give an example of each type of cell. 52. Discuss the levels of organization in multicellular organisms and explain why these levels are not used to describe unicellular organisms. 53. Identify each of the cell structures indicated in Figure 7-1. Chapter 7 Cells Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: COMPLETION B D C D A B B C D A D B D A C B B D D A C B D D B A C D B A B C C A C C A C D PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: B A E E B A E B A B A E B B A B A A A E B B A E B A E E B A B A E B E B A A E OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: 7.1.1 7.1.1 7.1.1 7.1.1 7.1.2 7.1.2 7.1.2 7.1.3 7.1.3 7.2.1 7.2.1 7.2.1 7.2.2 7.2.3 7.2.3 7.2.4 7.2.4 7.2.4 7.2.4 7.2.4 7.2.4 7.3.1 7.3.1 7.3.1 7.3.2 7.3.2 7.3.2 7.3.3 7.3.3 7.3.3 7.4.1 7.4.1 7.4.1 7.4.2 7.4.2 7.4.2 7.4.2 7.4.2 7.4.2 40. ANS: a ribosomes PTS: 1 41. ANS: b plant DIF: A OBJ: 7.2.4 PTS: 1 DIF: E 42. ANS: c facilitated diffusion OBJ: 7.2.4 PTS: 1 DIF: E OBJ: 7.3.3 SHORT ANSWER 43. ANS: When a blood cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water flows from the blood cell, through the cell membrane, into the solution. As a result of losing water, the cell shrinks. PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 7.3.3 OTHER 44. ANS: Some of the C molecules will move to the B side of the container. PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 7.3.2 45. ANS: Some of the D molecules will move from side A to side B. The net movement of D molecules will be from side B to side A. PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 7.3.2 46. ANS: B At equilibrium, the concentrations of both C and D molecules will be equal on either side of the selectively permeable membrane. PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 7.3.2 47. ANS: B Drawing II—a plant cell—contains the structure described (a chloroplast). The structure is labeled N. PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 7.2.4 48. ANS: A Structure A; They both represent rough endoplasmic reticulum. PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 7.2.4 49. ANS: B Both drawings represent eukaryotes as evidenced by the presence of a nucleus. PTS: 1 50. ANS: DIF: B OBJ: 7.1.3 B The rest of the class’s results (line B) are more likely to be accurate because they represent a larger sample size. PTS: 1 DIF: E OBJ: 7.3.3 ESSAY 51. ANS: Prokaryotes are generally simpler and smaller than eukaryotes. They have a cell membrane and cytoplasm, but lack a nucleus. Eukaryotes have a nucleus and other specialized organelles. Bacteria and other cells that lack a nucleus are prokaryotes. Plants, animals, fungi, and other microorganisms are eukaryotes. PTS: 1 DIF: E OBJ: 7.1.3 52. ANS: The levels of organization in a multicellular organism include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Similar cells are grouped into tissues; tissues that work together form organs; a group of organs that work together make up an organ system. Unicellular organisms cannot have cell specialization. Instead, all the activities of the organism must be carried out by the single cell. PTS: 1 53. ANS: agadfaf PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 7.4.2