ECON 201 Problem Set 3
ECON 201 Problem Set 3 – Answers
Fall 2004 from the textbook
# 9
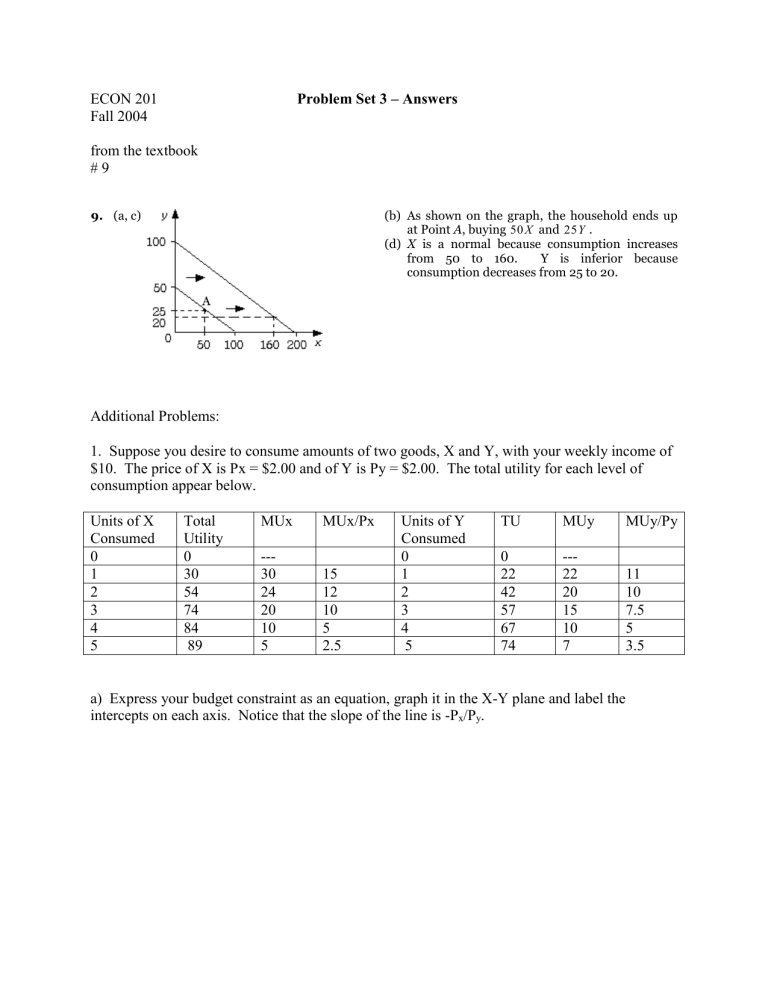
9. (a, c) (b)
(d)
As shown on the graph, the household ends up at Point A, buying
50 X
and
25 Y
.
X is a normal because consumption increases from 50 to 160. Y is inferior because consumption decreases from 25 to 20.
A
Additional Problems:
1. Suppose you desire to consume amounts of two goods, X and Y, with your weekly income of
$10. The price of X is Px = $2.00 and of Y is Py = $2.00. The total utility for each level of consumption appear below.
Units of X
Consumed
0
1
2
3
Total
Utility
0
30
54
74
MUx MUx/Px Units of Y
---
30
24
20
15
12
10
Consumed
0
1
2
3
TU
0
22
42
57
MUy
---
22
20
15
MUy/Py
11
10
7.5
4
5
84
89
10
5
5
2.5
4
5
67
74
10
7 a) Express your budget constraint as an equation, graph it in the X-Y plane and label the intercepts on each axis. Notice that the slope of the line is -P x
/P y
.
5
3.5
Y
5 slope = -2/2 = -1
5
X b) Calculate total utility for all of the affordable bundles of X and Y. Which bundle yields the highest utility? The bundle X=3 and Y=2 maximizes total utility.
TU Bundle (X,Y)
0,5
1,4
0 + 74 = 74
30 + 67 = 97
2,3
3,2
4,1
54 + 57 = 111
74 + 42 = 116
84 + 22 = 106
5,0 89 + 0 = 89 c) See table above: MUx/Px = MUy/Py only when X=3 and Y=2. For this bundle MUx/Px =
MUy/Py = 10/
2.
Suppose that you consume two goods, A and B, to a point where MU a
= MU b
= 3. That is, the last unit of X you consumed and the last unit of Y consumed each yielded you 3 additional units of utility. However, P a
= $2 and P b
=$4. Explain the adjustment you should make to maximize your utility. (you simply need to explain which good you should buy more of and which you should buy less of)
Because P a
/P b
= $2/$4 = ½ but MU a
/MU b
= 3utils/3utils = 1 this bundle does not maximize utility. Look at it this way MU a
/P a
= 3/2 = 1.5 utils per dollar. But MU b
/P b
= ¾ = 0.75 utils per dollar. If you spend $1 less on B, your utility falls by 0.75 utils, but you have an extra dollar to spend on A which increases your utility by 1.5 utils. As you buy less B, MU b
increases. As you buy more A, MU a
falls. You rearrange your bundle until MU a
/P a
= MU b
/P b
.











