Chem Chapter 23
advertisement

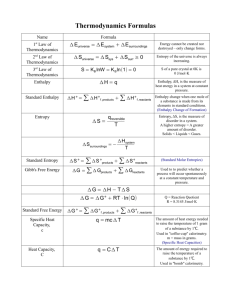
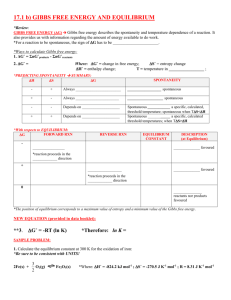
Chemistry Chapter 23 Thermodynamics Teacher Lecture Notes 23-1 Spontaneous Process Spontaneous chemical reactions proceed on their own without outside intervention. Thermodynamics answers the questions The spontaneous direction of a given reaction How far the reaction will proceed until it reaches equilibrium (Keq = 1) Keq >>1 products are favored Section Review 23-1 1. If energy must be put into a reaction to make it go in the opposite direction of the spontaneous direction what does that tell you about energy and the spontaneous rxn? 23-2 Enthalpy Enthalpy of a substance represents its energy. Points to remember Delta H = Hp - Hr Negative enthalpies indicate that energy has been released and therefore products have less energy than the reactants. The lower the energy the more stable the substance Standard enthalpy (Delta H prime) is the heat transferred between reactants and products at 1atm 25C Enthalpy change is proportional to the amount of substance Hess’s Law – net enthalpy can be derived from the sum of two or more reactions Most exothermic reactions are spontaneous, but some endothermic reactions are also spontaneous. Section Review 23-2 1. Is the enthalpy of a rxn a good indicator of its spontaneity? Explain why or why not 2. How are enthalpy changes of rxns determined? 3. What happens to the delta H sign if the rxn is reversed? 23-3 Entropy Entropy (S) is a quantative measure of the disorder, or randomness, in the substance involved in a rxn. The greater the disorder the greater the S value. Where is disorder greater in gases or solids? Entropy changes (delta S) = Sp - Sr Sound familiar? Unlike delta H, you cannot directly measure delta S with heat However if delta S is positive (products are more disordered than the reactants) Delta Srxn = Sp > Sr In any spontaneous process, the overall entropy of the universe always increases. Increase entropy occurs when Solids or liquids become gases Solutions form from liquids or gases More gas molecules are present as products than reactants Temperature of a substance increases Student Notes C2.2e Compare the entropy of solids, liquids, and gases. C3.4e Predict if a chemical reaction is spontaneous given the enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS) changes for the reaction using Gibb’s Free Energy, ΔG = ΔH - TΔS (Note: mathematical computation of ΔG is not required.) C3.4f Explain why some endothermic reactions are spontaneous at room temperature. Delta Universe = delta Srxn – delta Ssurr When Delta Universe is positive the reaction is spontaneous Neg delta H are exothermic, heating up the surroundings, therefore increasing the entropy of the surroundings (+ delta S)! visa versa Sooo - H with a + S are spontaneous + H with a - _S are not spontaneous Section Review 23-3 1. Explain the concept of entropy 2. An endothermic rxn has a positive delta S. Is the rxn spontaneous? (hint look carefully at the table on pg 760) 3. Explain how entropy changes of the surroundings are related to the enthalpy change of the rxn. 4. Why Did Ms. B name her boat entropy? H2O(l) --> H20(g) 23-4 Gibbs Free Energy Gibbs Free Energy incorporates the concepts of entropy and NaCl(s) --> Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) enthalpy G= H -T S 2NH3(g)--> N2(g) + 3H2(g) In other words, the change in Gibbs Free Energy is equal to the enthalpy change minus the product of absolute temperature and the H2O(l, 25C) --> H2O(l, 50C) rxns entropy change When delta G is a large negative number (G<<<0) products are heavily favored (Keq >>1) Conversely if (G>>>0) reactants are heavily favored (Keq <<1) Energy is defined as the ability to do __________. Therefore spontaneous rxns can do __________! So Gibbs Free Energy change (negative delta G) represents the maximum work that a spontaneous rxn can perform! Hence how it got the name “Free Energy” this really represents the amount of energy that is “free” to do work, the remainder is lost to the environment to meet the criterion of increasing entropy of the universe! So cool Gibbs! A positive delta G represents the minimum amount of work that must be put into the rxn to make it run! Section Review 23-4 1. Write the sign for delta G for a spontaneous rxn 2. How is the equilibrium constant for a reaction related to its Free Energy and free energy? Spontaneity 3. What must be the sign of delta G if a process is endothermic and has decreased entropy? Was work done G Rxn Keq by the rxn or work put into the rxn? + Not spon <<1 4. Why must society seek alternative energy sources if spont >>1 “Energy is neither created nor destroyed”? 0 At eq =1 Special Notes ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________