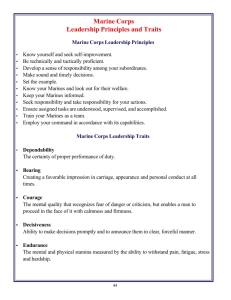
Leadership ELOs - Officer Selection Station Ashland
advertisement

1. 2. 3. LEADERSHIP 2: UCMJ Purpose of Military Law Promote justice; maintain good order and discipline; promote efficiency and effectiveness; strengthen national security Persons Subject to the UCMJ Active duty; cadets, aviation cadets, Midshipmen, Candidates; military retirees; reservists while active; EPOW; prisoners; civilians in public health service and oceanic and atmospheric administration, and civilians serving with military in time of war Article 31 (Rights of the accused) Before Non-Judicial Punishments Right to know offense suspected prior to questioning Protects against being coerced into making a statement Protects from being compelled to make statements or produce evidence in court martial that’s immaterial to the case and degrading After right are read, statements can be used in court Statement obtained from coercion, unlawful influence cannot be used 4. Identify How to Report an Offense If civilians reports offense its treated like military A report should be forwarded ASAP to suspect chain of command 5. Identify the Punitive Articles of the UCMJ Articles 77-134 define crimes punishable under UCMJ 6. Article 86-Absence Without Leave Fails to go to appointed place of duty at time prescribed Leaves from appointment place of duty Absents himself or remains absent from unit, organization, place duty at time UCMJ CONT. 14. Article 128-Assault Simple assault-attempts or offers with unlawful force/violence to do bodily harm; whether or not it happens doesn’t matter Assault Consummated by Battery-does bodily harm Aggravated Assault-assault with dangerous weapon likely to lead to death or body harm 15. Article 134-Gerneral Article Covers other offenses not in punitive articles Covers behaviors prejudicial to good order and discipline of armed forces ex: animal abuse, bigamy, adultery, fraternization, bribery 16. Authorized Punishment for Violation of UCMJ Reprimand-severe oral/written in record; ends or delays careers Forfeiture of pay and allowance Fine Reduction in grade-only for enlisted Restriction to specific limits-deprived liberty Hard labor without confinement Confinement-at bribe or military prison Punitive Separation-as Dismissal, Dishonorable Discharge, or Bad Conduct Discharge Death Confinement on bread and water-assigned to ships brig Arrest in Quarters-officers only Extra Duty-can be menial tasks, but not degrading Correctional custody unit (CCU)-not confinement, used for good Marines who got off-track, helps remotivate (maximum of 7 days) 17. Types of Discharges 5 broken down into 2 categories: punitive and Non-Punitive (aka Administrative Separation) PUNITIVE Discharges-punishments, 2 types: Dishonorable Discharge-only awarded at general court martial (CM). Bad Conduct Discharge-special or general C.M only ELO 17 CONT: UCMJ Non-Punitive Discharges: o Other than Honorable-service was less than honorable due to the commission of 1 or more minor offenses not taken to court o General, Under Honorable Conditions-performance was characterized by significant negative aspects by not meeting standards EX: overweight o Honorable-Average proficiency and conduct marking are greater 3.0/4.0 Officers Retire, Resign, or are Dismissed-they’re not discharged 18. Non-Judicial Punishment Purpose is to provide CO’s a prompt and essential means for maintaining good order and discipline. Serves to correct misconduct without attaching stigma of court conviction Provided for by Article 15 19. When the Administration of NJP is Appropriate Minor offenses (aka when max confinement in UCMJ is less than one year) Person attached to or embarked on vessel-punishment may not be imposed under Article 15 if they demand trial by court martial instead Any service member punished under Art. 15 can appeal if felt unjust 20. Summary Court-Martial Jurisdiction over everyone subject to UCMJ except: officers, cadets, aviation cadets, and Midshipman For any non-capital offense made punishable by manual for C.M. Composition of court: one commanding officer Max. punishment for E$ and lover: confinement 20 days, forfeit 2/3 pay for 1 month, reduction to lowest grade, no punitive discharge can be awarded Max pun. For E 5 and above: restriction 45 days, 2/3 pay 1 month, reduce of one pay grade, no punitive discharge, no hard labor without confinement UCMJ CONT. 7. Article 88-Contempt Towards Officials Words/acts personally contemptuous against President, Vice President, etc. Adverse criticism can’t be charged 8. Article 89-Disrespect Toward a Superior Officer Acts/words against commissioned officer who is: superior in rank or command; in same armed force or if in another force, in the same chain of command; it’s not necessary the officer be in the execution or office; accused must know it was a superior. Not necessary he knows rank, but must be aware or rank. 9. Article 90-Assaulting or Willfully Disobeying a Superior Commissioned Officer Striking; drawing or lifting weapon against them; offering any violence against them; disobeying a lawful command while that superior is in the execution of his office 10. Article 91-Insubordinate Conduct Toward a Warrant Officer, NCO, or Petty officer Assault; willful disobedience of a lawful order; contemptuous or disrespectful treatment in language or department 11. Article 92-Failure to obey an Order or Regulation Disobedience of a lawful order or regulation; failure to obey lawful order by member of Armed Forces 12. Article 112a-Wrognful Use, Possession, etc. of Controlled Substance Heroin; cocaine; weed; etc, a drug listed in Controlled Substance Act or listed by President 13. Article 121-Larceny and Wrongful Appropriation Wrongfully takes, obtains, or withholds any money, personal property, or valuable Larceny-stealing properly permanently Wrongful Appropriation-temporarily depriving property LEADERSHIP 2: MORAL LEADERSHIP 21. Special Court martial Anyone subject for any non-capital offense and under such from president, for capital offenses Composition of Court: not less than 3 members; or a military jedge and no less than 3; or judge, if one has been detailed to the court and the accused so requests. Enlisted accused may request 1/3 court by enlisted Max Punishment-confinment 12 months, 2/3 pay 1 year, reduced to lowest grade, bad0conduct discharge 22. General Court Martial Try anyone for any offense made punishable in manual for CM Composition-judge and no less than 5; or jedge if the accused requests; if enlisted requests 2/3 court be enlisted Max Punishment-death, all pay and allowance reduce to lowest grade, dishonorable discharge 1. Definition of “Military Professional” A Person who has undergone special preparation and training Has the knowledge on which professional actions are based and ability to apply this knowledge in a practical way. Individual accepts the service motive of their work. Wages are not the primary purpose of their work. 2. Select the basis of “Special Trust and Confidence” Based on a natural presumption that Marine Corps officers will practice integrity, good manners, sound judgment, and discretion; and that they will do so with honor and courage. 3. Who has “Special Trust and Confidence” The President of the United States has “special trust and confidence” in the patriotism, valor, fidelity, and abilities of an officer. 4. Four elements of “Special Trust and Confidence” Patriotism – love and loyalty to one’s country Valor – courage in battle; no person can truly know the depth of one’s personal courage until it is tested Abilities – talents and skills each of us possess Fidelity – faithful devotion to duty END OF UCMJ CHAPTER NOTES: 5. Desired Traits of a Professional Competent – Marines must study and work to become an expert in their field while continually striving to improve their knowledge and expertise in all military related skills appropriate to their rank and assignment. Responsible – Marine must first make sure that they know what is expected, and the must work to fulfill those expectations. Dedicated – A marine must be willing to make personal sacrifices. One must put self and personal needs secondary to the needs of the Corps. Duty, honor, and country are the guideposts for a military professional. MORAL LEADERSHIP CONT. 6. Definition of “Morals” Morals - Pertaining to, or concerned with right conduct or the distinction between right and wrong. Morals are much like ethics, except morals are a balance of societal and personal standards. 7. 8. Sources of the military code of ethics Establishes moral opinion and defines expected or acceptable behavior in specialized fields that often encounter new and unique problems. Written: The USMC does not have a specific code of ethics written into one document. It is primarily a continuation of unwritten practices accepted and advocated by our society and supported by our legal system. In written form, documents may include: o The oath of office o Commissioning Document o The Uniform Code of Military Justice (UCMJ) o The Code of Conduct o The Code of Ethics for Government Employees Unwritten: There are many standards of conduct not found in any manual or document. These are the same of the time-honored traditions we learn as Marines. Definition of “Noblesse Oblige” “Noblesse Oblige” – literal translation means “nobility obligates” Originated in 18th & 19th century as men of position saw that by virtue of their position, it was incumbent upon them to render appropriate public service. As officers, noblesse oblige is a principle that applies to personal behavior Officers who violate the code of their profession must expect to be punished. The rank or position is not a shield from justice. The price officers pay for “special trust and confidence” is exacting and unremitting personal accountability. END OF MORAL LEADERSHIP NOTES: 1. LEADERSHIP 2-MISSION AND ORGANIZATION SECNAV Civilian head of Department of Navy, responsible for organization, operation and efficiency 2. CNO Senior military officer of Navy, sits as member of Joint Chiefs Staff 3. Commandant of the Marine Corps Responsibility to SECNAV for admin, discipline, internal organization, unit training, efficiency, and overall readiness of corps Reports to SNO for the readiness of FMF with Navy operations 4. Organization of USMC 4 establishments within USMC organization: a. HQ-at Pentagon in Arlington, contains departments as manpower, installations and logistics; plans, policies and operations are done here b. Operating Forces-divides into 3 organizations 1)Marine Corps Forces (MARFOR) organized as marine-Air Ground Task Forces and are employed as part of naval expeditionary forces or separate as part of larger joint or combined forces. 2) Marine Corps Security Forces (MCSF)—includes 3,400 Marines who protect key installations. 3) Marine Security Guards-provide to Department of State for embassy security. 138 diplomatic posts in 124 counties. c. Supporting Establishment-consists of personnel, bases, activities supporting USMC forces. d. Marine Corps Forces Reserve (MARFORRES) END OF MISSION AND ORGANIZATION CHAPTER NOTES: LEADERSHIP 2: CODE OF CONDUCT/LAW OF WARFARE 1) Article I of the Code of Conduct: I am an American fighting in the forces which guard my country and our way of life. I am prepared to give my life in their defense. 2) Article II of the Code of Conduct: I will never surrender of my own free will. If in command, I will never surrender the members of my command while they still have the means to resist. 3) Article III of the Code of Conduct: If I am captured I will continue to resist by all means available. I will make every effort to escape and aid others to escape. I will accept neither parole nor special favors from the enemy. 4) Article IV of the Code of Conduct: If I become a prisoner of war, I will keep faith with my fellow prisoners. I will give no information or take part in any action which might be harmful to my comrades. If I am senior, I will take command. If not, I will obey the lawful orders of those appointed over me and will back them up in every way. 5) Article V of the Code of Conduct: When questioned, should I become a prisoner of war, I am required to give name, rank, service number and date of birth. I will evade answering further questions to the utmost of my ability. I will make no oral or written statements disloyal to my country and its allies or harmful to their cause. 6) Article VI of the Code of Conduct: I will never forget that I am an American fighting for freedom, responsible for my actions, and dedicated to the principles which made my country free. I will trust in my God and in the United States of America. CODE OF CONDUCT/LAW OF WARFARE CONT. 7) Information POW’s are Required to Surrender to their Captors: Ever Prisoner of war, when questioned on the subject, is bound to give only his surname, first names and rank, date of birth, and army, regimental, personal or serial number, or equivalent information. 8) Consequences of Failing to Surrender Required Information: If he/she willfully infringes this rule, he/she may render himself liable to a restriction of the privileges accorded to his/her rank or status. 9) Rules Applicable in the Law of War: The articles of the Geneva Convention. The UCMJ (Uniform Code of Military Justice). The Code of Conduct (Executive Order 10631). The laws of the Detaining Power are all applicable to a POW. 10) 9 Principles in the Laws of War: 1. Fight only enemy combatants. 2. Do not harm enemies who surrender, disarm them and turn them over to your superior. 3. Do not kill or torture prisoners. 4. Collect and care for the wounded, whether friend or foe. 5. Do not attack medical personnel, facilities, or equipment. 6. Destroy no more than the mission requires. 7. Treat all civilians humanely. 8. Do not steal; respect private property and possessions. 9. Do your best to prevent violations of the law of war; report all violations to your superior, a military lawyer, a chaplain, or provost marshal. END OF CODE OF CONDUCT/LAW OF WARFARE NOTES: