(11) Endocrine System
advertisement

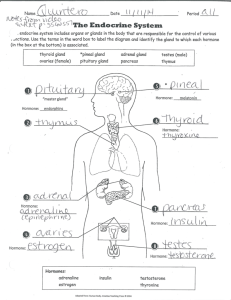
LAB 11 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Objective: To understand the important role of the endocrine system in regulating the activity of body cells. To explain the function of the various hormones and the results of their hyposecretion or hypersecretion. The endocrine system works with the nervous system in controlling much of what goes on in the body. Review these basic facts regarding the endocrine system: 1. It is composed of glands. 2. Glands produce hormones. 3. Hormones are chemical messengers that are released directly into the blood (no ducts). 4. Hormones work at specific locations (targets). 5. Hormones work by attaching to receptors at the target. 6. Receptors may be on the target cell membrane or inside the target cell (intracellular). 7. The pituitary is often called the master gland of the body since it oversees much of the action of other glands. 8. The pituitary gland is controlled by the hypothalamus. 9. The pituitary gland is functionally and structurally related to the hypothalamus. 10. Structural relationships include direct axonal connections between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary and a specialized “portal” system (a capillary network). 11. Functional relationships include release of releasing and inhibiting hormones by the hypothalamus which affect the anterior pituitary and the production of oxytocin and ADH by the hypothalamus which are stored and released as needed by the posterior pituitary. A. Gross Anatomy of the Endocrine System Using models and books, name and locate all of the endocrine glands. Fill in the table below. GLAND HORMONES PRODUCED Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary 41 B. Histology of Selected Endocrine Glands Obtain slides of these glands and observe the histological features listed. Be able to identify each tissue. 1. Thyroid gland 2. 3. a. Find follicles. What is produced by the follicles? How? b. Find parafollicular cells. What is produced here? c. What chemical element is critical in the production of the major thyroid hormones? d. What is the target of the hormone produced by the parafollicular cells? Parathyroid gland a. What is the physical relationship between this gland and the thyroid? b. Normally, how many parathyroid glands are there? c. How can one distinguish the parathyroid gland from the thyroid? d. What hormone is produced by the parathyroid gland? What is its target? Adrenal gland a. Differentiate between the cortex and the medulla. b. How many zones are present in the cortex? Identify them. c. What hormones are produced in each of the cortical zones? (Fill in the following table). CORTICAL ZONE HORMONE CLASS 42 SPECIFIC HORMONE/S 4. d. What is the importance of the medulla? e. What histological feature allows the medulla to do its work quickly and efficiently? f. Why is the medulla often referred to as a “postganglionic sympathetic neuron.” Islets of Langerhans (Pancreas) a. How many cell types make up the Islets of Langerhans? b. What hormones are produced by each of the cell types? CELL TYPE c. 5. HORMONE What is the major function of the Islets of Langerhans? Pituitary gland a. How can one distinguish between the anterior and posterior pituitary? Why? b. What hormones are produced by the posterior pituitary? c. What are the chemical “signals” that cause the anterior pituitary to release its hormones? d. Where do these “signals” come from? e. How do these “signals” get to the anterior pituitary? C. Endocrine Table- Complete the following table of endocrine glands. 43 ENDOCRINE GLANDS: REGULATION AND EFFECTS GLAND HORMONE STIMULATED INHIBITED Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) [supraoptic nucleus of hypothalamus] POSTERIOR PITUITARY Oxytocin [paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus] Growth Hormone (GH) Prolactin (PRL) ANTERIOR PITUITARY Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Luteinizing Hormone (LH) THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND Thyroxin (produced by follicular cells) Calcitonin (produced by parafollicular cells) Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) (secreted by chief cells) 44 TARGET EFFECTS OF HORMONE ENDOCRINE GLANDS: REGULATION AND EFFECTS GLAND HORMONE STIMULATED INHIBITED Glucocorticoids (Cortisol) ADRENAL GLAND (Cortex) Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone) Gonadocorticoids (sex hormones) ADRENAL GLAND (Medulla) Epinephrine & Norepinephrine Insulin (ß cells in islets of Langerhans) PANCREAS TESTES Glucagon (alpha cells in islets of Langerhans) Testosterone Estrogen OVARIES Progesterone PINEAL GLAND Melatonin THYMUS GLAND Thymic Hormones (Thymopoietins & Thymosins) 45 TARGET EFFECTS OF HORMONE